Mifepristone is a medication commonly used for medical abortion and managing certain hormonal disorders. It works by blocking progesterone, a hormone necessary for pregnancy continuation, leading to the termination of early pregnancy. Explore the article to understand how mifepristone may affect your health and the options available for its use.
Table of Comparison
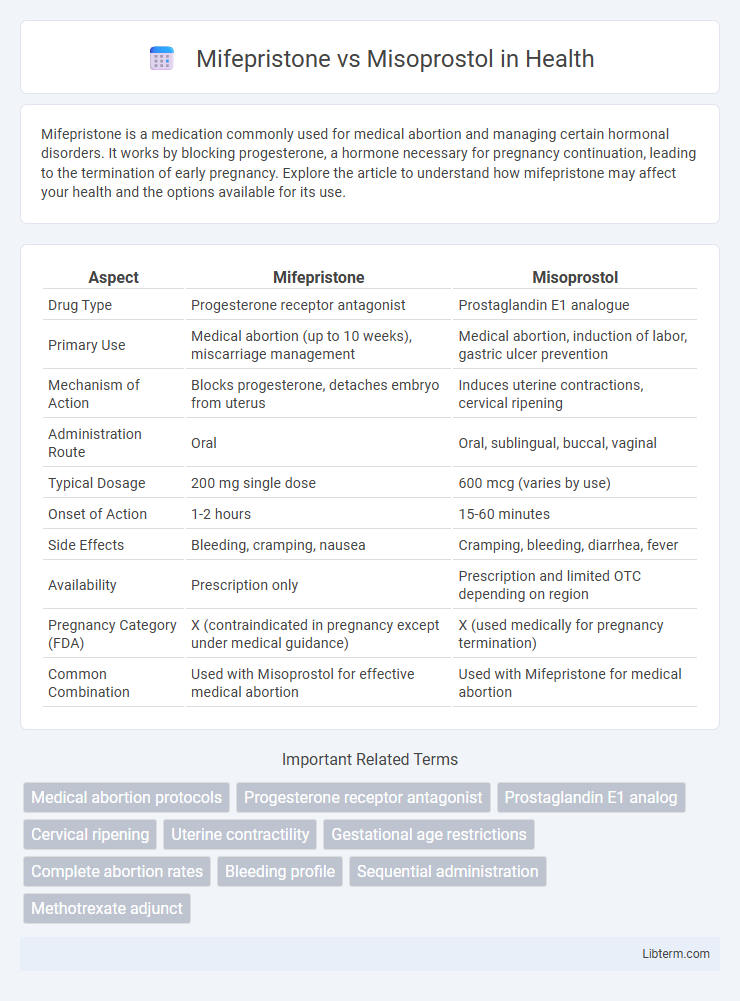
| Aspect | Mifepristone | Misoprostol |
|---|---|---|
| Drug Type | Progesterone receptor antagonist | Prostaglandin E1 analogue |
| Primary Use | Medical abortion (up to 10 weeks), miscarriage management | Medical abortion, induction of labor, gastric ulcer prevention |
| Mechanism of Action | Blocks progesterone, detaches embryo from uterus | Induces uterine contractions, cervical ripening |
| Administration Route | Oral | Oral, sublingual, buccal, vaginal |
| Typical Dosage | 200 mg single dose | 600 mcg (varies by use) |
| Onset of Action | 1-2 hours | 15-60 minutes |
| Side Effects | Bleeding, cramping, nausea | Cramping, bleeding, diarrhea, fever |
| Availability | Prescription only | Prescription and limited OTC depending on region |
| Pregnancy Category (FDA) | X (contraindicated in pregnancy except under medical guidance) | X (used medically for pregnancy termination) |
| Common Combination | Used with Misoprostol for effective medical abortion | Used with Mifepristone for medical abortion |
Introduction to Mifepristone and Misoprostol
Mifepristone is a progesterone receptor antagonist primarily used to medically induce abortion by blocking the hormone necessary for pregnancy continuation. Misoprostol, a prostaglandin E1 analog, induces uterine contractions to expel pregnancy tissue and is commonly administered following mifepristone for increased efficacy. Both drugs are integral to non-surgical abortion protocols, with combined use demonstrating higher success rates compared to misoprostol alone.
Mechanism of Action: How Each Drug Works
Mifepristone functions as a progesterone receptor antagonist, blocking the hormone progesterone necessary to maintain pregnancy, leading to the breakdown of the uterine lining. Misoprostol acts as a prostaglandin E1 analog, stimulating uterine contractions and promoting cervical ripening to facilitate the expulsion of pregnancy tissue. Together, these drugs provide a synergistic approach for medical abortion by first halting pregnancy support and then inducing uterine contractions.
Medical Uses and Indications
Mifepristone is primarily used for medical termination of intrauterine pregnancy up to 70 days gestation, functioning as a progesterone receptor antagonist to halt fetal development. Misoprostol, a prostaglandin E1 analog, induces uterine contractions and cervical ripening, facilitating expulsion of pregnancy tissue following mifepristone administration or managing missed miscarriage. Both drugs are indicated for early pregnancy termination, with misoprostol also indicated for treatment of postpartum hemorrhage and prevention of gastric ulcers.
Effectiveness Comparison
Mifepristone demonstrates higher effectiveness in medical abortion when compared to misoprostol alone, with success rates exceeding 95% within the first 7 weeks of pregnancy. Misoprostol, while effective, typically shows lower efficacy, around 80-85%, when used as a sole agent. Combining mifepristone with misoprostol increases the overall success of abortion procedures, reducing the need for surgical intervention.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Mifepristone is typically administered as a single oral dose of 200 mg, followed by Misoprostol 24 to 48 hours later, usually 800 mcg either buccally, sublingually, or vaginally. Misoprostol dosage and route vary based on gestational age and clinical protocols, with the most effective administration often being 800 mcg vaginally. Proper adherence to the recommended timing and dosage between these medications is critical for maximizing efficacy and minimizing complications in medical abortion.
Side Effects and Safety Profiles
Mifepristone and Misoprostol are commonly used together for medical abortion, with Mifepristone acting to block progesterone and Misoprostol inducing uterine contractions. Mifepristone's side effects primarily include mild bleeding and cramping, while Misoprostol often causes gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. Both drugs have strong safety profiles when used as directed, with serious complications being rare and typically manageable under medical supervision.
Contraindications and Precautions
Mifepristone is contraindicated in patients with chronic adrenal failure, hemorrhagic disorders, and concurrent anticoagulant therapy, while Misoprostol is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to prostaglandins or active cardiovascular disease. Precautions for Mifepristone include close monitoring of patients with severe asthma or immunodeficiency due to potential immunosuppressive effects. Misoprostol requires cautious use in patients with a history of uterine surgery or cesarean section to reduce the risk of uterine rupture.
Accessibility and Legal Considerations
Mifepristone and misoprostol vary significantly in accessibility due to differing regulatory approvals and availability across countries, with mifepristone often subject to stricter prescription controls and limited distribution channels. Legal considerations impact both drugs, as some regions impose restrictions or bans influenced by abortion laws, affecting where and how these medications can be obtained and used. Access to misoprostol is generally broader because it is also used for other medical conditions, but safe and legal use depends heavily on local abortion legislation and healthcare provider policies.
Patient Experiences and Outcomes
Mifepristone combined with Misoprostol demonstrates higher efficacy rates in medical abortion, with patient experiences highlighting fewer side effects and faster completion times compared to Misoprostol alone. Studies indicate improved patient satisfaction and lower rates of incomplete abortion when using the Mifepristone-Misoprostol regimen, enhancing overall treatment outcomes. Psychological impacts also favor the combined therapy, showing reduced anxiety and better coping during the abortion process.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Mifepristone and Misoprostol
Mifepristone and misoprostol are both effective medications used for medical abortion, with mifepristone typically administered first to block progesterone, followed by misoprostol to induce uterine contractions. Choosing between these drugs depends on factors such as gestational age, availability, patient preference, and healthcare guidance, as mifepristone has higher efficacy when combined with misoprostol. Misoprostol alone is more accessible in some regions but may have a slightly lower success rate, making a combined regimen the preferred option for most medical abortion protocols.
Mifepristone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com