Lipedema is a chronic disorder characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat, primarily in the legs and arms, leading to pain and swelling that can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding treatment options can help you manage the condition more effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify lipedema and discover strategies for relief and care.
Table of Comparison
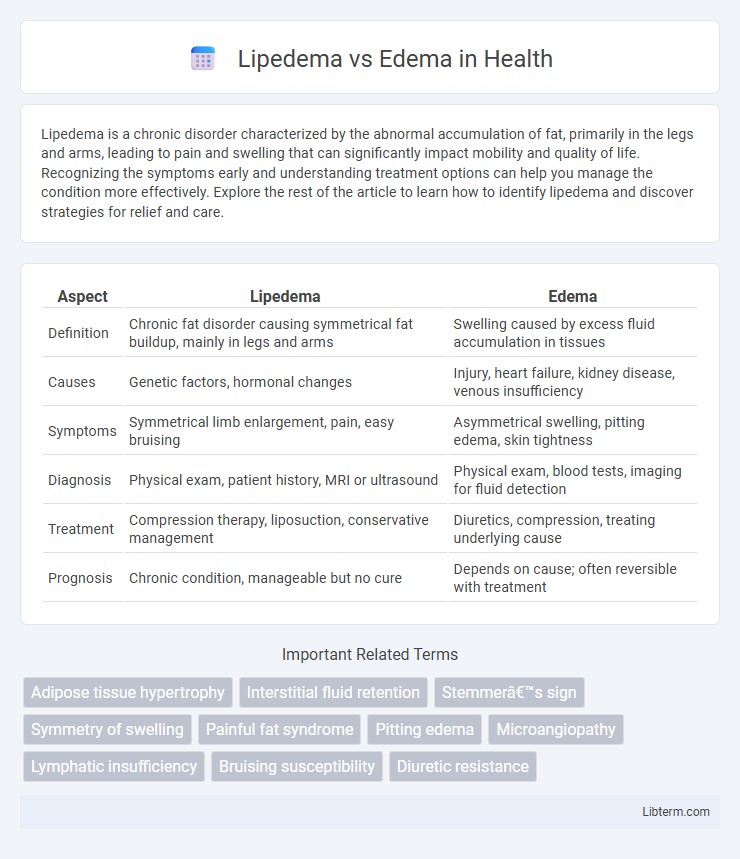
| Aspect | Lipedema | Edema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic fat disorder causing symmetrical fat buildup, mainly in legs and arms | Swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation in tissues |
| Causes | Genetic factors, hormonal changes | Injury, heart failure, kidney disease, venous insufficiency |
| Symptoms | Symmetrical limb enlargement, pain, easy bruising | Asymmetrical swelling, pitting edema, skin tightness |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam, patient history, MRI or ultrasound | Physical exam, blood tests, imaging for fluid detection |
| Treatment | Compression therapy, liposuction, conservative management | Diuretics, compression, treating underlying cause |
| Prognosis | Chronic condition, manageable but no cure | Depends on cause; often reversible with treatment |
Understanding Lipedema: Definition and Overview
Lipedema is a chronic disorder characterized by a symmetrical accumulation of painful fat deposits primarily in the lower limbs, often confused with edema but distinct in its pathophysiology and lack of response to conventional diuretics. Unlike edema, which involves fluid retention due to underlying conditions like heart or kidney failure, lipedema results from abnormal fat cell proliferation and connective tissue abnormalities. Understanding lipedema requires recognizing its genetic predisposition, progressive nature, and common symptoms such as tenderness, bruising, and disproportionate lower body enlargement, which are critical for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
What is Edema? Causes and Basic Concepts
Edema is the swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues, often occurring in the feet, ankles, and legs. Common causes include prolonged standing, heart failure, kidney disease, and inflammation or injury. Understanding edema involves recognizing fluid accumulation due to impaired circulation or lymphatic drainage, distinguishing it from conditions like lipedema where fat deposits rather than fluid cause swelling.
Key Differences Between Lipedema and Edema
Lipedema is a chronic disorder characterized by symmetrical fat accumulation, primarily in the lower body, often resistant to diet and exercise, whereas edema involves fluid retention causing swelling that can affect any body part. Lipedema typically presents with pain, easy bruising, and a disproportionate fat distribution, while edema manifests as pitting swelling and resolves with elevation or diuretics. Distinguishing these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment, as lipedema requires specialized management and edema often responds to underlying condition treatment.
Common Symptoms: Lipedema vs Edema
Lipedema primarily causes symmetrical swelling and fatty deposits in the legs and buttocks, often accompanied by pain, tenderness, and easy bruising, while edema typically results in localized, pitting swelling due to fluid accumulation in tissues, often affecting the lower limbs or other body parts. Lipedema swelling does not usually affect the feet, whereas edema commonly involves the feet and ankles with noticeable indentation when pressed. Both conditions present with swelling, but lipedema is characterized by disproportionate fat distribution and chronic discomfort, whereas edema is linked to fluid retention and may fluctuate based on activity or underlying health issues.
Diagnostic Criteria: How to Differentiate
Lipedema is characterized by symmetrical, bilateral fat accumulation primarily in the lower limbs, sparing the feet, and presents with pain and easy bruising, whereas edema involves fluid retention that can affect any part of the body, often accompanied by pitting on pressure. Diagnostic criteria for lipedema include disproportionate fat distribution, negative Stemmer's sign, and absence of significant pitting edema, helping differentiate it from lymphedema and other causes of edema. Imaging techniques like lymphoscintigraphy and ultrasound aid in distinguishing lipedema by revealing normal lymphatic function compared to impaired drainage in edema conditions.
Underlying Causes and Risk Factors
Lipedema is a chronic disorder characterized by abnormal fat accumulation primarily in the lower body, often linked to hormonal changes and genetic predisposition, whereas edema results from fluid retention caused by factors such as venous insufficiency, heart failure, or lymphatic obstruction. Risk factors for lipedema include female gender, family history, and hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, while edema risk factors encompass prolonged immobility, certain medications, infections, and systemic diseases like kidney or liver dysfunction. Understanding these distinct underlying causes is essential for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies.
Treatment Approaches for Lipedema and Edema
Treatment approaches for lipedema primarily involve conservative methods such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and specialized exercise programs to reduce pain and prevent progression. In contrast, edema treatment often focuses on addressing underlying causes through diuretics, limb elevation, and dietary sodium restriction to manage fluid retention. While lipedema management emphasizes symptom relief and quality of life improvement, edema therapy targets fluid balance restoration and cardiovascular or renal function support.
Managing Pain and Swelling
Lipedema and edema both cause swelling, but managing pain and swelling in lipedema focuses on specialized treatments like manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and tailored exercise to reduce fat deposits and improve lymphatic flow. In contrast, edema management often involves addressing underlying causes like heart or kidney issues, using diuretics, elevation, and compression garments to minimize fluid retention. Effective pain control in lipedema may require combination approaches including gentle movement, pain medication, and maintaining a healthy weight to alleviate pressure on affected tissues.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular low-impact exercise like swimming or walking can help manage symptoms of lipedema and reduce fluid retention associated with edema. Wearing compression garments improves lymphatic flow and decreases swelling, while a balanced diet low in salt supports vascular health and minimizes water retention. Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting and elevating the legs frequently are effective lifestyle practices to prevent worsening of both lipedema and edema.
Frequently Asked Questions: Lipedema vs Edema
Lipedema is a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat cells, primarily in the legs and arms, often causing pain and swelling, while edema involves fluid retention leading to swelling, usually due to underlying medical issues such as heart, kidney, or liver problems. Lipedema typically presents symmetrically with a distinct "column-like" leg shape and is resistant to diet and exercise, whereas edema can fluctuate throughout the day and may respond to elevation or diuretics. Diagnosis relies on clinical examination, with lipedema often confused for edema or obesity, highlighting the importance of distinguishing between fat buildup and fluid retention for effective treatment.
Lipedema Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com