General anesthesia induces a controlled and reversible state of unconsciousness, ensuring that patients experience no pain during surgical procedures. It involves the administration of anesthetic drugs that affect the entire body, rendering you completely unaware and immobile. Explore the detailed aspects of general anesthesia, including its types, risks, and recovery process, in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
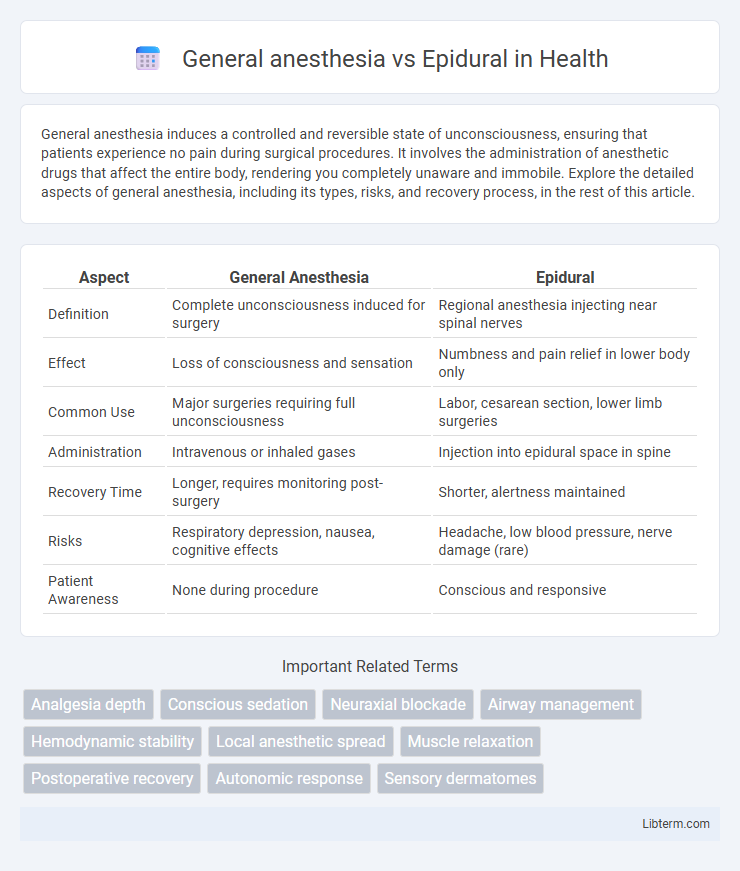
| Aspect | General Anesthesia | Epidural |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete unconsciousness induced for surgery | Regional anesthesia injecting near spinal nerves |
| Effect | Loss of consciousness and sensation | Numbness and pain relief in lower body only |
| Common Use | Major surgeries requiring full unconsciousness | Labor, cesarean section, lower limb surgeries |
| Administration | Intravenous or inhaled gases | Injection into epidural space in spine |
| Recovery Time | Longer, requires monitoring post-surgery | Shorter, alertness maintained |
| Risks | Respiratory depression, nausea, cognitive effects | Headache, low blood pressure, nerve damage (rare) |
| Patient Awareness | None during procedure | Conscious and responsive |
Introduction to Anesthesia Methods
General anesthesia induces complete unconsciousness and loss of sensation, making it ideal for extensive surgical procedures requiring total patient immobility and pain control. Epidural anesthesia involves the injection of anesthetic near the spinal cord, resulting in localized numbness primarily used in labor and lower body surgeries while allowing the patient to remain awake. Understanding the differences in onset time, risk factors, and recovery profiles is essential in selecting the appropriate anesthesia method tailored to specific medical requirements.
What is General Anesthesia?
General anesthesia is a medically induced state of unconsciousness used during major surgeries to ensure the patient feels no pain or awareness. It involves the administration of intravenous drugs and inhaled gases to suppress the central nervous system completely. This contrasts with epidural anesthesia, which numbs a specific region of the body while the patient remains awake.
What is Epidural Anesthesia?
Epidural anesthesia involves the injection of local anesthetics into the epidural space surrounding the spinal cord, providing targeted pain relief typically during childbirth or lower body surgeries. Unlike general anesthesia, which induces unconsciousness, epidural anesthesia allows patients to remain awake while blocking pain sensations in specific regions. This method minimizes systemic side effects and facilitates quicker recovery times compared to general anesthesia.
Key Differences Between General and Epidural Anesthesia
General anesthesia induces complete unconsciousness and loss of sensation throughout the body by affecting the central nervous system, commonly used in major surgeries requiring full patient immobility. Epidural anesthesia involves injecting anesthetic near the spinal nerves to numb specific regions, typically the lower body, allowing the patient to remain awake and maintain vital reflexes. Unlike general anesthesia, epidurals minimize systemic effects, reduce recovery time, and lower the risk of complications such as respiratory depression.
Indications for General vs Epidural Anesthesia
General anesthesia is indicated for major surgeries requiring complete unconsciousness and muscle relaxation, such as open abdominal or thoracic procedures. Epidural anesthesia is preferred for childbirth, lower limb surgeries, and chronic pain management due to its targeted nerve block and ability to maintain patient consciousness. Patient health status, surgical site, and procedure duration critically influence the choice between general and epidural anesthesia.
Benefits of General Anesthesia
General anesthesia provides complete unconsciousness and muscle relaxation, enabling intricate surgical procedures without patient awareness or pain. It ensures controlled airway management and stable vital signs, reducing the risk of intraoperative complications. This type of anesthesia is ideal for lengthy or complex surgeries requiring immobility and deep sedation.
Benefits of Epidural Anesthesia
Epidural anesthesia offers targeted pain relief primarily during labor and certain surgeries, minimizing overall systemic effects compared to general anesthesia. It allows patients to remain awake and alert while effectively blocking pain in the lower body, facilitating quicker postoperative recovery and reducing risks associated with airway management. The technique also tends to lower the incidence of nausea and allows for earlier mobilization, enhancing overall patient comfort and safety.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
General anesthesia carries potential risks such as respiratory complications, allergic reactions, and post-operative nausea, along with a rare chance of cognitive dysfunction. Epidural anesthesia risks include headache, low blood pressure, nerve damage, and infection at the injection site. Both methods require careful monitoring to manage side effects and minimize complications during and after the procedure.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Anesthesia
Factors influencing the choice between general anesthesia and epidural include the type and duration of surgery, patient health conditions such as respiratory or cardiac issues, and potential risks of anesthesia complications. Surgical site plays a crucial role, with epidurals preferred for lower body procedures like childbirth or lower limb surgeries, while general anesthesia is often necessary for extensive or upper body operations. Patient preference, surgeon and anesthesiologist expertise, and the need for postoperative pain control also contribute significantly to the decision-making process.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Anesthesia Option
Selecting the appropriate anesthesia between general anesthesia and epidural depends on factors such as the type of surgery, patient health, and recovery goals. General anesthesia induces complete unconsciousness, ideal for extensive procedures, while epidural anesthesia numbs specific body regions, minimizing systemic effects and promoting faster recovery. Consulting with an anesthesiologist ensures a tailored approach, balancing effectiveness and safety for optimal patient outcomes.
General anesthesia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com