Antihistamines are medications that effectively relieve allergy symptoms by blocking histamine receptors in the body, reducing itching, swelling, and congestion. They are commonly used to treat conditions like hay fever, hives, and allergic reactions to insect bites or foods. Discover how antihistamines can improve your quality of life and explore the best options for your needs in the full article.
Table of Comparison
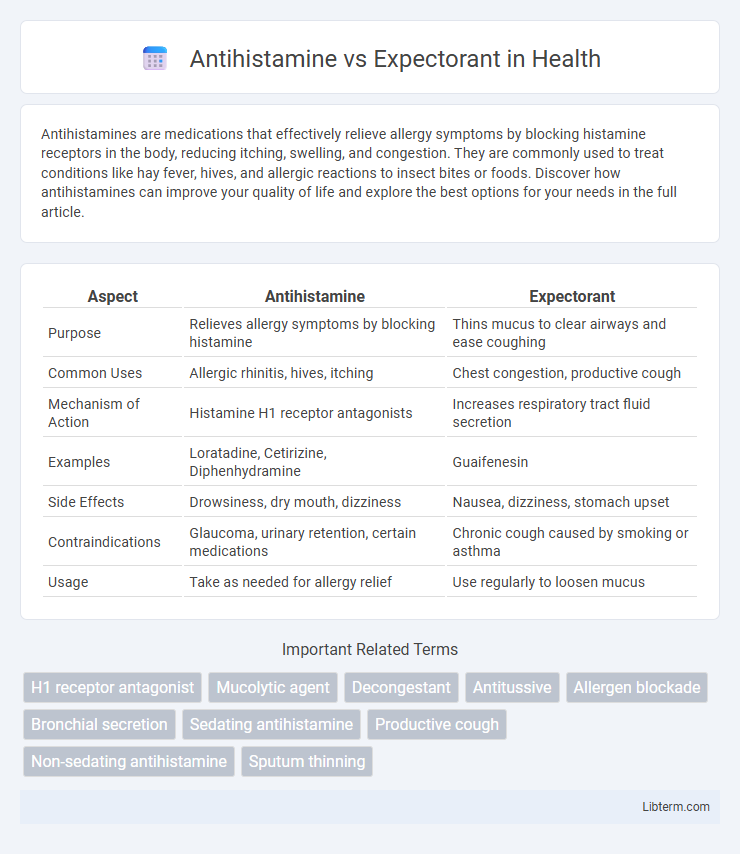
| Aspect | Antihistamine | Expectorant |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Relieves allergy symptoms by blocking histamine | Thins mucus to clear airways and ease coughing |
| Common Uses | Allergic rhinitis, hives, itching | Chest congestion, productive cough |
| Mechanism of Action | Histamine H1 receptor antagonists | Increases respiratory tract fluid secretion |
| Examples | Loratadine, Cetirizine, Diphenhydramine | Guaifenesin |
| Side Effects | Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness | Nausea, dizziness, stomach upset |
| Contraindications | Glaucoma, urinary retention, certain medications | Chronic cough caused by smoking or asthma |
| Usage | Take as needed for allergy relief | Use regularly to loosen mucus |
Introduction to Antihistamines and Expectorants
Antihistamines are medications that block histamine receptors to reduce allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Expectorants, on the other hand, work by thinning mucus in the airways, making it easier to cough up and clear congestion from the respiratory tract. Both drug classes target different mechanisms to alleviate symptoms of respiratory conditions, with antihistamines addressing allergic reactions and expectorants facilitating mucus clearance.
What Are Antihistamines?
Antihistamines are medications that block histamine receptors to reduce allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose. They effectively treat conditions like hay fever, urticaria, and allergic conjunctivitis by preventing histamine from triggering inflammatory responses. Unlike expectorants, which loosen mucus in the respiratory tract, antihistamines target allergic reactions at the cellular level for symptom relief.
What Are Expectorants?
Expectorants are medications designed to thin and loosen mucus in the airways, facilitating easier coughing and expulsion from the lungs, commonly used to relieve symptoms of congestion in conditions like bronchitis and the common cold. Unlike antihistamines, which block histamine receptors to reduce allergic reactions and mucus production, expectorants actively promote mucus clearance to improve respiratory function. Popular expectorants include guaifenesin, which increases respiratory tract fluid secretion, helping clear mucus and alleviate chest congestion.
Key Differences Between Antihistamines and Expectorants
Antihistamines primarily block histamine receptors to reduce allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose, while expectorants thin and loosen mucus in the respiratory tract to facilitate easier coughing and mucus clearance. Antihistamines are commonly used to treat allergic reactions and hay fever, whereas expectorants target chest congestion from colds and bronchitis. Unlike expectorants, which enhance mucus expulsion, antihistamines can cause dryness and sedation as side effects.
How Antihistamines Work
Antihistamines work by blocking histamine receptors, specifically H1 receptors, to reduce allergy symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and runny nose. They inhibit the effects of histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions that causes inflammation and increased mucus production. In contrast, expectorants facilitate the expulsion of mucus from the respiratory tract by thinning the mucus, improving clearance and relieving congestion.
How Expectorants Work
Expectorants work by thinning and loosening mucus in the airways, making it easier to cough up and clear congestion from the respiratory tract. They increase the hydration of airway secretions, which reduces mucus viscosity and promotes effective clearance. Unlike antihistamines, which block histamine receptors to reduce allergy symptoms, expectorants directly target mucus production and clearance to aid breathing.
Common Uses and Indications
Antihistamines are primarily used to relieve allergy symptoms such as sneezing, itching, runny nose, and hives by blocking histamine receptors. Expectorants, like guaifenesin, are indicated for loosening mucus in the respiratory tract to alleviate productive cough and improve airway clearance. Both medications target different symptoms: antihistamines for allergic reactions and expectorants for chest congestion and mucus buildup.
Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Antihistamines commonly cause drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness, with first-generation antihistamines posing higher risks, especially in elderly patients. Expectorants like guaifenesin are generally well-tolerated but may lead to gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting in some cases. Both drug classes require caution in patients with underlying conditions, and consultation with healthcare providers is essential to avoid adverse effects and drug interactions.
Choosing Between Antihistamines and Expectorants
Choosing between antihistamines and expectorants depends on the underlying symptoms and cause of respiratory discomfort. Antihistamines effectively reduce allergy-related symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itching by blocking histamine receptors, while expectorants help loosen and thin mucus in the airways to facilitate coughing and clearing of congestion. For patients with allergic rhinitis or hay fever, antihistamines are preferred, whereas expectorants are recommended for productive coughs associated with common colds or bronchitis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Antihistamines block histamine receptors to reduce allergy symptoms like sneezing and itching, while expectorants thin mucus to ease coughing and clear airways. Common FAQs include their usage: antihistamines are recommended for allergies or hay fever, whereas expectorants are used for productive coughs with thick mucus. Potential side effects often queried are drowsiness for antihistamines and mild gastrointestinal discomfort for expectorants.
Antihistamine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com