An allergic reaction occurs when your immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance as a threat, triggering symptoms like itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Common allergens include pollen, pet dander, certain foods, and insect stings. Discover more about causes, symptoms, and effective treatments to better manage your allergies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
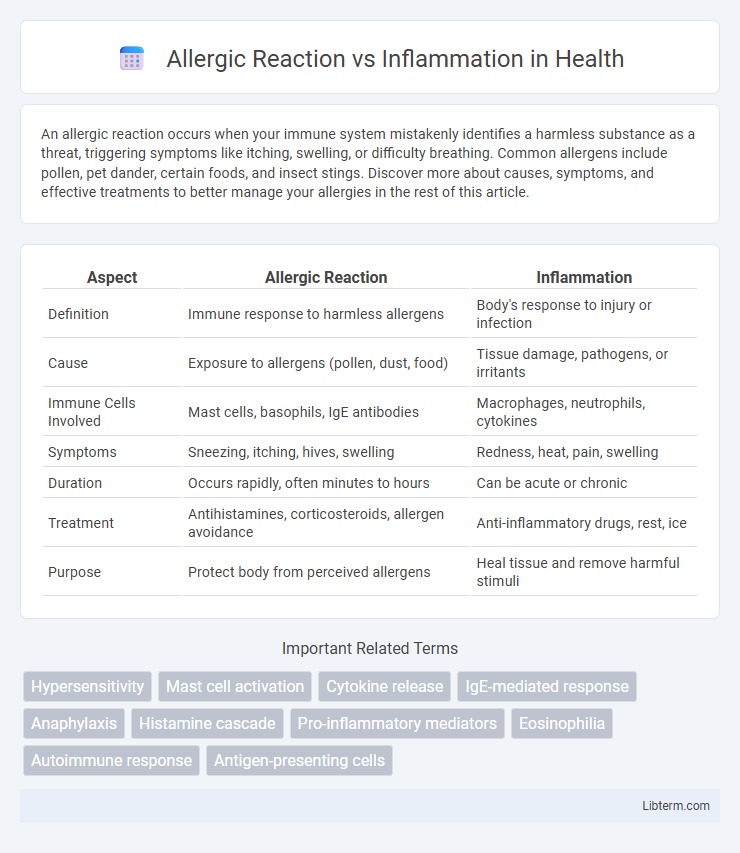
| Aspect | Allergic Reaction | Inflammation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immune response to harmless allergens | Body's response to injury or infection |
| Cause | Exposure to allergens (pollen, dust, food) | Tissue damage, pathogens, or irritants |
| Immune Cells Involved | Mast cells, basophils, IgE antibodies | Macrophages, neutrophils, cytokines |
| Symptoms | Sneezing, itching, hives, swelling | Redness, heat, pain, swelling |
| Duration | Occurs rapidly, often minutes to hours | Can be acute or chronic |
| Treatment | Antihistamines, corticosteroids, allergen avoidance | Anti-inflammatory drugs, rest, ice |
| Purpose | Protect body from perceived allergens | Heal tissue and remove harmful stimuli |
Understanding Allergic Reactions: Definition and Causes
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances like pollen, pet dander, or certain foods, mistaking them for threats. This hypersensitivity triggers the release of histamines and other chemicals, causing symptoms such as itching, swelling, and redness. Unlike general inflammation, which is a broad immune response to injury or infection, allergic reactions are specific immune responses to allergens.
What Is Inflammation? Key Concepts and Triggers
Inflammation is the body's complex biological response to harmful stimuli such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Key concepts include the activation of immune cells, release of pro-inflammatory mediators like cytokines and histamines, and increased blood flow to the affected tissue to initiate healing. Common triggers for inflammation encompass infections, physical injury, chemical exposure, and autoimmune reactions.
Allergic Reaction vs Inflammation: Core Differences
Allergic reactions involve an immune system hypersensitivity to typically harmless substances, triggering the release of histamines that cause symptoms like itching, swelling, and redness. Inflammation is a broader biological response to injury or infection, characterized by redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function aimed at tissue repair and pathogen elimination. Core differences include that allergic reactions are specific immune responses to allergens, while inflammation can occur from various stimuli, including infections, trauma, or immune activation without allergen involvement.
Common Symptoms of Allergic Reactions
Common symptoms of allergic reactions include itching, swelling, hives, and redness of the skin, often accompanied by sneezing, nasal congestion, and watery eyes. In contrast, inflammation typically presents with localized pain, heat, redness, and swelling as a response to tissue injury or infection. While both involve immune system activation, allergic reactions are triggered by allergens, causing systemic symptoms like anaphylaxis in severe cases.
Typical Signs of Inflammation in the Body
Typical signs of inflammation in the body include redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of function at the affected site. These symptoms result from increased blood flow, immune cell activation, and the release of inflammatory mediators such as histamines and cytokines. Inflammation serves as the body's protective response to injury or infection, distinct from allergic reactions that involve hypersensitivity to specific allergens.
The Immune System’s Role in Allergies and Inflammation
The immune system triggers allergic reactions by identifying harmless substances as threats, leading to the release of histamines and other chemicals that cause symptoms like itching, swelling, and redness. Inflammation is a broader immune response aimed at protecting the body from injury or infection, marked by increased blood flow, immune cell activation, and tissue repair processes. While both involve immune system activation, allergies specifically involve hypersensitivity to allergens, whereas inflammation encompasses various physiological responses to pathogens or damage.
Diagnostic Methods: How to Identify Each Condition
Allergic reactions are typically identified through skin prick tests, blood tests measuring specific IgE antibodies, and patient history of exposure to allergens. Inflammation diagnosis involves evaluating clinical signs such as redness, swelling, heat, and pain, supported by laboratory tests like elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Imaging techniques, including MRI and ultrasound, can help assess underlying inflammatory conditions, while allergy testing is more specific to hypersensitivity responses.
Treatment Options for Allergic Reactions
Treatment options for allergic reactions primarily include antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine for severe anaphylaxis. Antihistamines block histamine receptors to reduce symptoms like itching and swelling, while corticosteroids decrease inflammation and immune response. Epinephrine injections provide rapid relief by constricting blood vessels and opening airways, essential in life-threatening allergic reactions.
Managing and Reducing Inflammation Effectively
Managing and reducing inflammation effectively involves identifying triggers such as allergens, infections, or injuries and implementing targeted treatments like antihistamines, corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, regular physical activity, and stress management also play critical roles in controlling chronic inflammation. Monitoring symptoms and consulting healthcare professionals ensures appropriate interventions to prevent complications from allergic reactions or persistent inflammation.
Prevention Tips: Minimizing Allergies and Inflammatory Responses
To minimize allergic reactions and inflammatory responses, avoid known allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and specific foods by maintaining a clean environment and using air purifiers. Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, omega-3 fatty acids, and leafy greens into your diet to reduce chronic inflammation. Regular exercise and stress management techniques also support immune regulation, decreasing the likelihood of both allergies and excessive inflammation.
Allergic Reaction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com