Medication plays a crucial role in managing various health conditions by alleviating symptoms and improving overall well-being. Understanding the proper usage, potential side effects, and interactions of your prescribed drugs ensures effective and safe treatment. Explore the rest of this article to learn how medication can optimize your health outcomes.
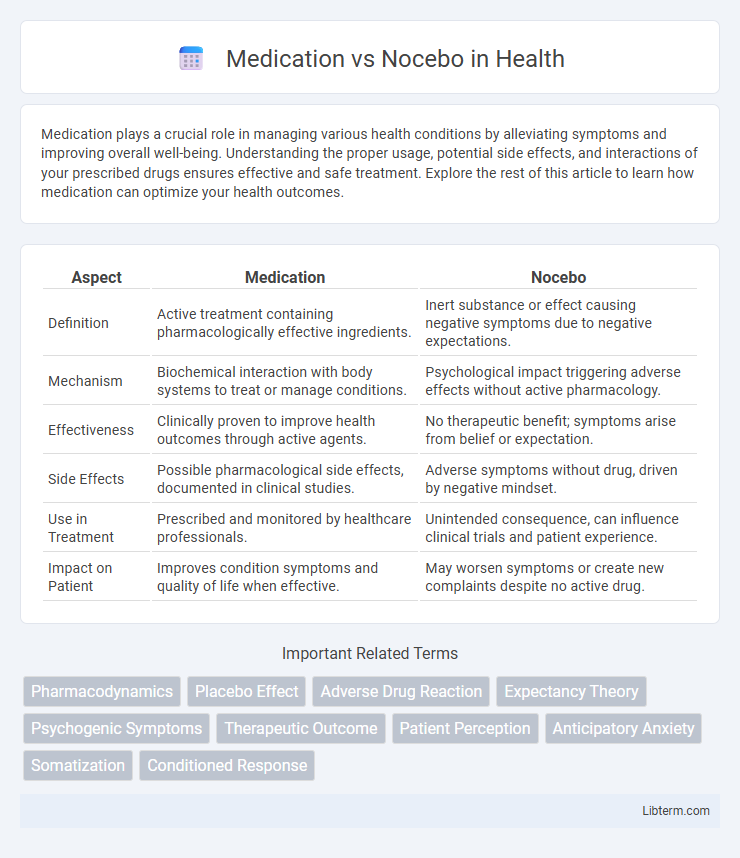
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Medication | Nocebo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active treatment containing pharmacologically effective ingredients. | Inert substance or effect causing negative symptoms due to negative expectations. |
| Mechanism | Biochemical interaction with body systems to treat or manage conditions. | Psychological impact triggering adverse effects without active pharmacology. |
| Effectiveness | Clinically proven to improve health outcomes through active agents. | No therapeutic benefit; symptoms arise from belief or expectation. |
| Side Effects | Possible pharmacological side effects, documented in clinical studies. | Adverse symptoms without drug, driven by negative mindset. |
| Use in Treatment | Prescribed and monitored by healthcare professionals. | Unintended consequence, can influence clinical trials and patient experience. |
| Impact on Patient | Improves condition symptoms and quality of life when effective. | May worsen symptoms or create new complaints despite no active drug. |
Understanding Medication: Mechanisms and Benefits
Medications interact with specific biological targets, such as receptors or enzymes, to alter physiological processes and treat various health conditions effectively. Understanding their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics is crucial for optimizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing adverse effects. By activating or inhibiting precise molecular pathways, medications can provide measurable benefits that surpass the psychological impact often associated with the nocebo effect.
The Nocebo Effect: How Negative Expectations Impact Health
The nocebo effect occurs when negative expectations about a medication or treatment trigger adverse health outcomes without an active pharmacological cause. Studies show patients anticipating side effects often experience those symptoms purely due to psychological influences, highlighting the powerful mind-body connection influencing clinical outcomes. Understanding and addressing nocebo-induced responses in healthcare can improve treatment adherence and patient well-being by minimizing unnecessary negative health effects.
Comparing Medication Efficacy and Perceived Outcomes
Medication efficacy is objectively measured through clinical trials showing significant symptom improvement and physiological changes, while nocebo effects arise from negative expectations, leading to perceived worsening without pharmacological action. Studies reveal patients receiving active drugs report greater symptom relief compared to those experiencing nocebo responses, despite similar conditioning and psychological factors influencing both groups. Understanding the distinction between biochemical efficacy of medications and the psychosomatic impact of nocebo aids in optimizing treatment adherence and patient outcomes.
Psychological Influences on Medical Treatment
Psychological influences profoundly impact the effectiveness of medication, as patients' expectations can trigger placebo effects that enhance therapeutic outcomes or nocebo effects that exacerbate side effects and reduce efficacy. Neurobiological mechanisms involving brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex and amygdala mediate these responses by modulating pain perception, immune function, and drug metabolism. Understanding the interplay between psychological factors and pharmacological treatments is crucial for optimizing patient adherence, minimizing adverse reactions, and improving overall clinical success.
Patient Beliefs: Shaping Response to Medication
Patient beliefs significantly influence the efficacy of medication through the interplay between pharmacological effects and nocebo responses. Negative expectations can trigger adverse symptoms, diminishing therapeutic outcomes and complicating treatment adherence. Understanding and addressing patient beliefs is crucial for optimizing medication response and minimizing nocebo-related side effects.
Distinguishing Side Effects: Drug Reactions vs. Nocebo Responses
Distinguishing side effects from actual drug reactions versus nocebo responses requires careful clinical assessment, as both can produce similar symptoms such as headaches, nausea, or fatigue. Drug reactions are pharmacologically driven and dose-dependent, while nocebo responses stem from negative expectations or psychological conditioning without a pharmacological basis. Understanding patient history, placebo-controlled trials, and monitoring symptom onset relative to medication initiation can help differentiate true adverse effects from nocebo phenomena.
Clinical Evidence: Medication vs. Nocebo in Research
Clinical evidence consistently demonstrates that medications outperform nocebo effects in controlled trials, showing statistically significant improvements in target symptoms and biomarkers. Placebo-controlled studies reveal that true pharmacological agents activate specific biochemical pathways, whereas nocebo responses primarily influence subjective symptom perception through negative expectations. Meta-analyses confirm that while nocebo effects can induce adverse symptoms, their incidence and severity are substantially lower than those observed with active medications.
Communication Strategies: Reducing the Nocebo Effect
Effective communication strategies play a crucial role in reducing the nocebo effect by framing medication information positively without withholding essential risks. Emphasizing the therapeutic benefits and using neutral language to describe potential side effects can minimize patient anxiety and negative expectations. Clear, empathetic dialogue between healthcare providers and patients enhances treatment adherence and overall clinical outcomes.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Managing Expectations
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in managing patient expectations by delivering clear, empathetic communication about medication benefits and potential side effects. They help differentiate genuine drug effects from nocebo responses by fostering trust and educating patients on the psychological impact of negative expectations. Effective provider-patient dialogue reduces anxiety, enhances treatment adherence, and improves overall therapeutic outcomes.
Optimizing Treatment: Balancing Medication Benefits and Nocebo Risks
Optimizing treatment requires carefully balancing the therapeutic benefits of medication with the risks posed by nocebo effects, which can manifest as adverse symptoms triggered by negative expectations rather than the pharmacological action. Implementing patient-centered communication strategies and educating patients about potential side effects can minimize nocebo-induced responses, thereby improving adherence and overall treatment outcomes. Integrating psychological support and monitoring symptom reporting closely enhances the ability to distinguish true drug reactions from nocebo effects, enabling more precise and effective medication management.
Medication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com