Quadriplegia is a condition characterized by partial or total loss of use of all four limbs and torso, resulting from spinal cord injury or neurological disorders. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help improve quality of life and provide effective management strategies for those affected. Explore the full article to learn how you can navigate the challenges and support recovery in quadriplegia.
Table of Comparison
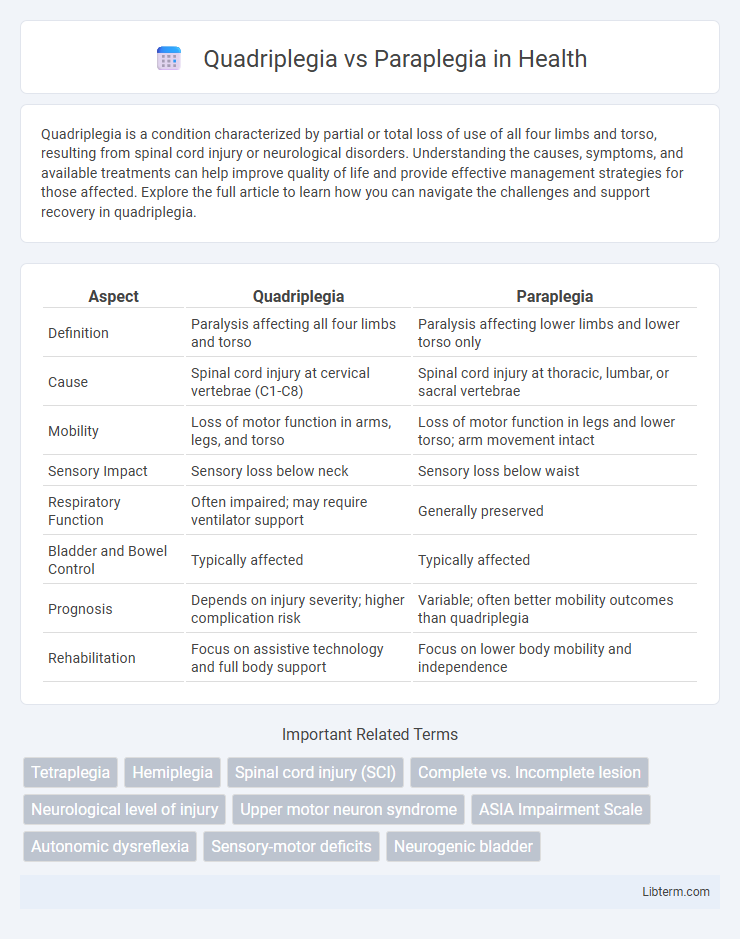
| Aspect | Quadriplegia | Paraplegia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Paralysis affecting all four limbs and torso | Paralysis affecting lower limbs and lower torso only |
| Cause | Spinal cord injury at cervical vertebrae (C1-C8) | Spinal cord injury at thoracic, lumbar, or sacral vertebrae |
| Mobility | Loss of motor function in arms, legs, and torso | Loss of motor function in legs and lower torso; arm movement intact |
| Sensory Impact | Sensory loss below neck | Sensory loss below waist |
| Respiratory Function | Often impaired; may require ventilator support | Generally preserved |
| Bladder and Bowel Control | Typically affected | Typically affected |
| Prognosis | Depends on injury severity; higher complication risk | Variable; often better mobility outcomes than quadriplegia |
| Rehabilitation | Focus on assistive technology and full body support | Focus on lower body mobility and independence |
Introduction to Quadriplegia and Paraplegia
Quadriplegia, also known as tetraplegia, results from injury to the cervical spinal cord, causing paralysis of all four limbs and torso. Paraplegia involves damage to the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral spinal cord segments, leading to paralysis of the lower body and legs while sparing arm function. Understanding the distinct spinal cord injury levels is essential for accurate diagnosis, rehabilitation, and treatment planning in patients with paralysis.
Defining Quadriplegia: Causes and Symptoms
Quadriplegia, also known as tetraplegia, refers to paralysis affecting all four limbs and the torso, typically caused by injury to the cervical spinal cord segments C1-C8. Common causes include traumatic events such as car accidents, falls, or sports injuries that damage the upper spinal cord, resulting in loss of motor and sensory function below the injury site. Symptoms often include complete or partial paralysis of the arms and legs, impaired respiratory function, and loss of bladder and bowel control.
Understanding Paraplegia: Causes and Symptoms
Paraplegia is characterized by paralysis affecting the lower half of the body, primarily caused by spinal cord injuries or diseases impacting the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. Common symptoms include loss of motor function and sensation in the legs, bladder and bowel dysfunction, and varying degrees of muscle spasticity. Unlike quadriplegia, which involves paralysis of all four limbs, paraplegia typically spares arm and hand movements, allowing greater independence in daily activities.
Key Differences Between Quadriplegia and Paraplegia
Quadriplegia results from spinal cord injury in the cervical region, causing paralysis in both the upper and lower limbs, while paraplegia affects only the lower limbs due to injuries in the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral spinal segments. Quadriplegia typically involves impaired motor and sensory function in the arms, hands, trunk, legs, and pelvic organs, whereas paraplegia primarily impacts the trunk, legs, and pelvic functions, leaving arm movement intact. Respiratory complications and higher dependency levels are more common in quadriplegia due to the involvement of cervical spinal nerves controlling diaphragm function.
Common Causes of Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries leading to quadriplegia typically result from trauma to the cervical vertebrae, such as severe car accidents, falls, or sports-related impacts, causing paralysis in all four limbs. Paraplegia usually occurs due to damage to the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions, often caused by spinal fractures or penetrating injuries impacting the lower body and legs. Both conditions commonly arise from high-energy trauma, but the injury level dictates the extent of paralysis and motor function loss.
Diagnosis and Assessment Techniques
Diagnosis of quadriplegia and paraplegia relies heavily on detailed neurological assessments, including the International Standards for Neurological Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) exam to determine the level and extent of motor and sensory loss. Imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans are essential to identify spinal cord lesions, fractures, or compression causing paralysis. Electrophysiological studies such as somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) and electromyography (EMG) further aid in assessing nerve conduction and muscle function to differentiate between quadriplegic and paraplegic presentations.
Treatment Options for Quadriplegia and Paraplegia
Treatment options for quadriplegia primarily focus on managing paralysis affecting all four limbs and torso, often involving intensive physical therapy, occupational therapy, and the use of assistive technologies such as powered wheelchairs and respiratory support devices. Paraplegia treatment emphasizes rehabilitation for lower body paralysis, including mobility training with wheelchairs and adaptive equipment, alongside physical therapy to enhance upper body strength and functionality. Both conditions may benefit from advanced interventions like nerve stimulation, exoskeleton-assisted walking, and emerging stem cell therapies aimed at nerve regeneration.
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process
Rehabilitation for quadriplegia involves intensive physical, occupational, and respiratory therapy to improve motor function and adapt to limitations in all four limbs, often requiring specialized equipment and caregiver support. Paraplegia rehabilitation typically focuses on enhancing mobility and independence in the upper body and lower extremities, utilizing strategies like wheelchair training and lower limb strengthening exercises. Recovery outcomes depend on the severity and location of spinal cord injury, with advanced neurorehabilitation techniques such as functional electrical stimulation and robotic-assisted therapy showing promising results in both conditions.
Daily Challenges and Quality of Life
Quadriplegia results in paralysis of all four limbs, severely limiting motor functions and daily activities such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene, often necessitating full-time care and adaptive technologies to maintain quality of life. Paraplegia affects the lower half of the body, allowing individuals to retain upper body strength, enabling greater independence in daily tasks like wheelchair mobility, self-care, and employment, though challenges with bowel, bladder, and skin management persist. Both conditions require tailored rehabilitation and social support systems to optimize physical health, mental well-being, and overall life satisfaction.
Support Resources and Coping Strategies
Support resources for quadriplegia and paraplegia include specialized rehabilitation centers, peer support groups, and assistive technology programs tailored to specific mobility impairments. Coping strategies emphasize adaptive skills training, psychological counseling, and community integration to enhance independence and quality of life. Access to multidisciplinary care teams and personalized therapy plans significantly improves functional outcomes and emotional well-being in individuals with spinal cord injuries.
Quadriplegia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com