Hyperesthesia refers to an increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, causing normal sensations to feel excessively intense or painful. This condition can affect various senses such as touch, sound, or light, significantly impacting daily comfort and activities. Explore the rest of the article to understand the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for hyperesthesia to better manage Your condition.
Table of Comparison
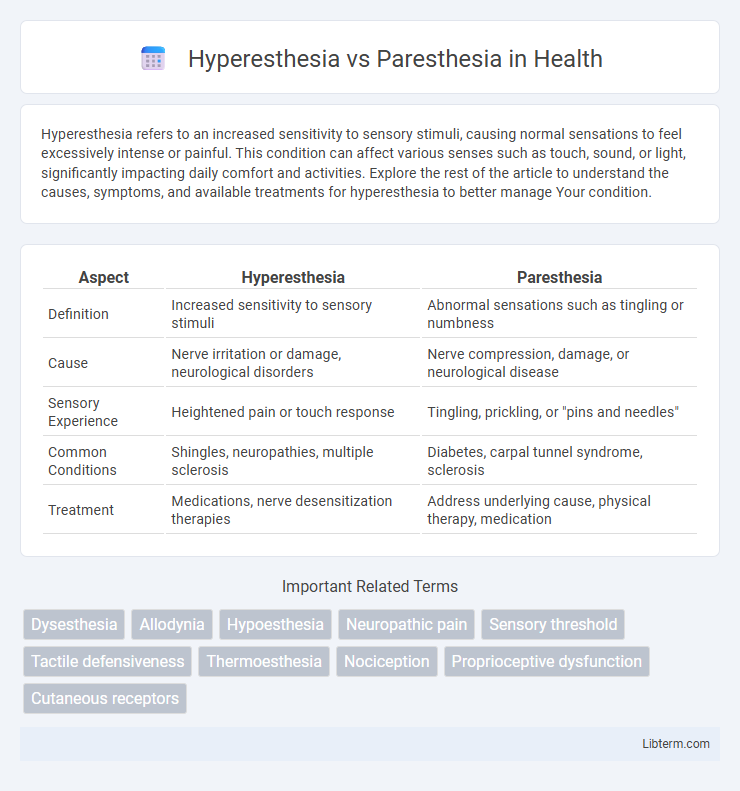
| Aspect | Hyperesthesia | Paresthesia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli | Abnormal sensations such as tingling or numbness |
| Cause | Nerve irritation or damage, neurological disorders | Nerve compression, damage, or neurological disease |
| Sensory Experience | Heightened pain or touch response | Tingling, prickling, or "pins and needles" |
| Common Conditions | Shingles, neuropathies, multiple sclerosis | Diabetes, carpal tunnel syndrome, sclerosis |
| Treatment | Medications, nerve desensitization therapies | Address underlying cause, physical therapy, medication |
Understanding Hyperesthesia and Paresthesia
Hyperesthesia is characterized by an increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, often resulting in heightened pain or tactile sensations due to nerve irritation or damage. Paresthesia involves abnormal sensations such as tingling, numbness, or "pins and needles," frequently caused by nerve compression or neuropathy. Understanding the differences between hyperesthesia and paresthesia is essential for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment in neurological disorders.
Defining Hyperesthesia: Symptoms and Causes
Hyperesthesia is characterized by an increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, including touch, sound, or light, often resulting in discomfort or pain. Symptoms typically involve heightened tactile perception, burning sensations, or sensitivity to temperature changes, which can arise from nerve damage, neuropathic conditions, or infections such as shingles. Understanding the underlying causes of hyperesthesia, such as peripheral neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, or chronic pain disorders, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What Is Paresthesia? Key Characteristics
Paresthesia is characterized by abnormal sensations such as tingling, numbness, or a "pins and needles" feeling, often caused by nerve damage or pressure. Unlike hyperesthesia, which involves increased sensitivity to stimuli, paresthesia typically results in reduced or altered sensory perception. Common causes include neuropathy, nerve compression, and conditions like diabetes or multiple sclerosis.
Comparing Hyperesthesia vs Paresthesia
Hyperesthesia refers to an increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, often causing discomfort or pain from normal touch, whereas paresthesia involves abnormal sensations such as tingling, numbness, or prickling without an external cause. Hyperesthesia typically results from nerve damage or inflammation that heightens sensory input processing, while paresthesia frequently arises from nerve compression, injury, or neurological conditions disrupting normal nerve signals. Understanding the distinct sensory experiences and underlying mechanisms of hyperesthesia versus paresthesia is essential for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies.
Common Causes of Hyperesthesia and Paresthesia
Hyperesthesia commonly results from conditions such as nerve damage, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, and infections like shingles, which increase sensitivity to stimuli. Paresthesia often arises due to nerve compression, vitamin deficiencies (particularly B12), repetitive strain injuries, or systemic diseases like diabetes and peripheral neuropathy. Both conditions share overlapping causes but differ in symptom presentation, with hyperesthesia involving heightened sensitivity and paresthesia characterized by abnormal sensations like tingling or numbness.
Diagnosis Methods for Sensory Disorders
Diagnosis of hyperesthesia and paresthesia involves comprehensive neurological examinations, including detailed patient history to identify symptom onset and triggers. Advanced diagnostic tools such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), and quantitative sensory testing (QST) help assess nerve function and differentiate these sensory disorders. Imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans are also utilized to detect underlying structural causes affecting sensory pathways.
Treatment Options for Hyperesthesia
Treatment options for hyperesthesia primarily focus on addressing the underlying causes, such as nerve damage, infections, or neuropathic disorders, often involving medications like anticonvulsants, antidepressants, or topical anesthetics to alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy and desensitization techniques can aid in reducing hypersensitivity by gradually acclimating the affected nerves to stimuli. In severe cases, interventions such as nerve blocks or surgical procedures may be considered to manage persistent hyperesthetic pain effectively.
Managing Paresthesia: Best Practices
Managing paresthesia involves identifying underlying causes such as nerve compression, vitamin deficiencies, or diabetic neuropathy to provide targeted treatment options. Effective strategies include lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, medications like anticonvulsants or analgesics, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention to relieve nerve pressure. Regular monitoring and early intervention are crucial to prevent persistent nerve damage and improve patient outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for hyperesthesia if you experience sudden, severe sensitivity to touch or pain that disrupts daily activities, or if it is accompanied by muscle weakness, numbness, or changes in bladder or bowel control. Paresthesia warrants prompt evaluation when symptoms persist beyond a few days, worsen over time, or are associated with underlying conditions like diabetes, neuropathy, or stroke risk factors. Early diagnosis and treatment by a neurologist can prevent complications and improve quality of life for both hyperesthesia and paresthesia patients.
Preventing and Coping with Sensory Issues
Preventing and coping with sensory issues related to hyperesthesia and paresthesia involve tailored strategies to manage nerve sensitivity and abnormal sensations. Techniques such as avoiding triggers like extreme temperatures or repetitive motions, maintaining proper hydration, and engaging in regular gentle exercises can reduce symptom severity. Incorporating mindfulness practices and consulting healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans also enhance coping effectiveness and promote nerve health.
Hyperesthesia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com