Recovery is a vital phase where the body and mind heal after injury, illness, or stress to restore full function and well-being. Effective recovery involves rest, proper nutrition, and sometimes targeted therapies to accelerate the healing process. Explore the rest of this article to learn how your recovery can be optimized for faster and more complete results.
Table of Comparison
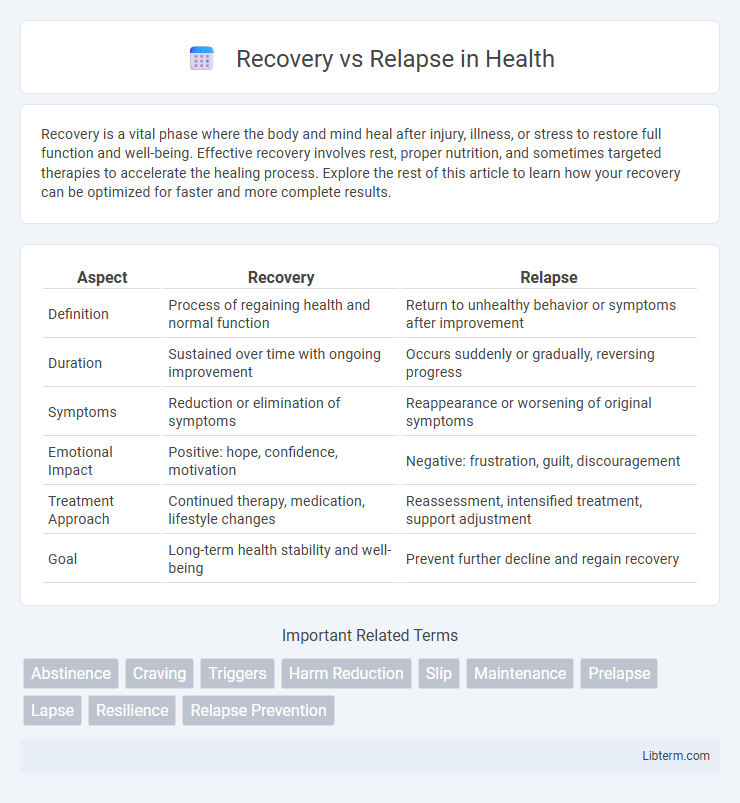
| Aspect | Recovery | Relapse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of regaining health and normal function | Return to unhealthy behavior or symptoms after improvement |
| Duration | Sustained over time with ongoing improvement | Occurs suddenly or gradually, reversing progress |
| Symptoms | Reduction or elimination of symptoms | Reappearance or worsening of original symptoms |
| Emotional Impact | Positive: hope, confidence, motivation | Negative: frustration, guilt, discouragement |
| Treatment Approach | Continued therapy, medication, lifestyle changes | Reassessment, intensified treatment, support adjustment |
| Goal | Long-term health stability and well-being | Prevent further decline and regain recovery |
Understanding Recovery and Relapse
Recovery is a dynamic process involving sustained efforts to achieve and maintain physical, mental, and emotional wellness after addiction or illness. Relapse occurs when an individual returns to previous harmful behaviors, often triggered by stress, environmental cues, or inadequate support systems. Understanding recovery and relapse requires recognizing signs, developing coping strategies, and building resilience through therapy, support groups, and lifestyle changes.
Key Differences Between Recovery and Relapse
Recovery involves sustained behavioral and psychological improvements marked by consistent abstinence from addictive substances or habits, whereas relapse is characterized by a return to previous patterns of substance use or destructive behavior after a period of recovery. Key differences include changes in brain chemistry, coping skills, and support system engagement; recovery strengthens neural pathways associated with self-control and resilience, while relapse disrupts these improvements, often triggered by stress or environmental cues. Monitoring progress through therapy, support groups, and relapse prevention strategies is crucial to maintaining recovery and minimizing setbacks.
Stages of the Recovery Process
Stages of the recovery process include acknowledgment, detoxification, and stabilization, where individuals gain control over substance use and physical health. During the middle stage, rebuilding life skills and establishing a support system are critical to prevent relapse. The maintenance phase requires continuous self-monitoring and coping strategies to sustain long-term sobriety and manage triggers effectively.
Common Triggers Leading to Relapse
Common triggers leading to relapse often include high-stress situations, social pressures, and exposure to environments associated with past substance use. Emotional distress, such as anxiety or depression, can significantly increase vulnerability to relapse. Recognizing these triggers early and developing effective coping strategies is essential for sustained recovery.
Early Warning Signs of Relapse
Identifying early warning signs of relapse is crucial for maintaining long-term recovery from addiction or mental health challenges. Common indicators include increased cravings, withdrawal from support networks, changes in mood or behavior, and neglect of coping strategies. Timely recognition and intervention upon noticing these signs significantly improve the chances of sustaining recovery and preventing a full relapse.
Strategies to Maintain Long-Term Recovery
Effective strategies to maintain long-term recovery include establishing a strong support network involving family, friends, and support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous or SMART Recovery. Developing personalized relapse prevention plans that identify triggers and implement coping mechanisms like mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral techniques, and regular therapy sessions can significantly reduce the risk of relapse. Consistent health monitoring and lifestyle changes, including balanced nutrition, exercise, and stress management, promote sustained sobriety and improve overall well-being.
The Role of Support Systems in Recovery
Support systems play a crucial role in maintaining long-term recovery by providing emotional encouragement, accountability, and practical assistance that reduce the risk of relapse. Engaging with trusted family members, support groups, and professional counselors fosters resilience and helps individuals develop coping strategies for triggers and stressors. Consistent social support strengthens motivation and reinforces positive behavioral changes essential for sustained recovery.
Overcoming Setbacks After Relapse
Overcoming setbacks after relapse requires a strong commitment to reestablish recovery goals and implement adaptive coping strategies. Identifying triggers and seeking professional support through counseling or support groups enhances resilience and reduces the risk of repeated relapse. Emphasizing self-compassion and gradual progress fosters long-term sobriety and mental well-being.
Creating a Personalized Relapse Prevention Plan
Creating a personalized relapse prevention plan involves identifying individual triggers, warning signs, and coping strategies tailored to each person's recovery journey. Incorporating evidence-based techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness enhances the plan's effectiveness in maintaining long-term sobriety. Regularly updating the plan with support from healthcare professionals and peer support groups ensures adaptability and sustained resilience against relapse.
Building Resilience for Sustainable Recovery
Building resilience is crucial for sustainable recovery by strengthening coping mechanisms to manage triggers and stress effectively. Developing emotional regulation, cultivating supportive relationships, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits enhance the ability to withstand setbacks and reduce the risk of relapse. Consistent practice of resilience strategies fosters long-term recovery and promotes psychological well-being.
Recovery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com