Eurythmia promotes harmonious movement and balance, enhancing both physical and emotional well-being through rhythmic exercises. This practice supports coordination, flexibility, and mental clarity, making it ideal for improving overall health. Discover how integrating eurythmia into Your routine can transform Your body and mind by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
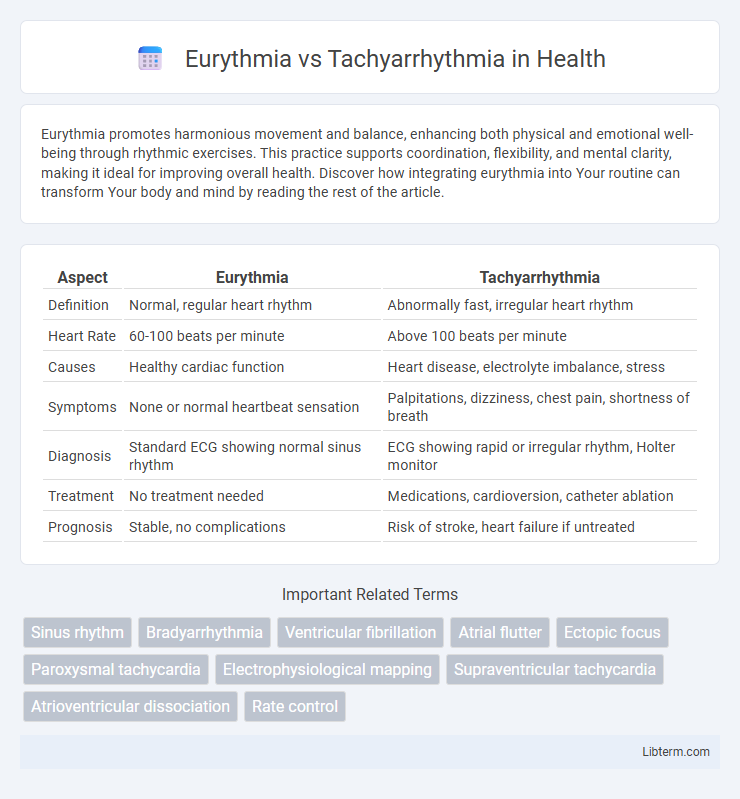
| Aspect | Eurythmia | Tachyarrhythmia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Normal, regular heart rhythm | Abnormally fast, irregular heart rhythm |
| Heart Rate | 60-100 beats per minute | Above 100 beats per minute |
| Causes | Healthy cardiac function | Heart disease, electrolyte imbalance, stress |
| Symptoms | None or normal heartbeat sensation | Palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath |
| Diagnosis | Standard ECG showing normal sinus rhythm | ECG showing rapid or irregular rhythm, Holter monitor |
| Treatment | No treatment needed | Medications, cardioversion, catheter ablation |
| Prognosis | Stable, no complications | Risk of stroke, heart failure if untreated |
Understanding Eurythmia: Definition and Significance
Eurythmia refers to a normal, regular rhythm of the heart, characterized by consistent intervals between beats that ensure efficient cardiac function and adequate blood circulation. Tachyarrhythmia denotes an abnormally fast and irregular heart rhythm, often exceeding 100 beats per minute, which can lead to symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, and increased risk of stroke or heart failure. Understanding eurythmia is crucial for distinguishing healthy cardiac patterns from pathological tachyarrhythmias, guiding accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment in cardiovascular care.
What is Tachyarrhythmia? Types and Features
Tachyarrhythmia is a rapid heart rhythm disorder characterized by an abnormally fast heartbeat exceeding 100 beats per minute, resulting from irregular electrical activity in the heart. Common types include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardia, each with distinct origins in the atria or ventricles and varying clinical implications. Features of tachyarrhythmia involve symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath, and can lead to complications such as stroke, heart failure, or sudden cardiac arrest if untreated.
Key Differences Between Eurythmia and Tachyarrhythmia
Eurythmia refers to a normal, regular heart rhythm with a stable rate typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute, indicating healthy cardiac function. Tachyarrhythmia is characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute with irregular or rapid rhythms that can lead to symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or syncope. The key differences lie in heart rate, rhythm regularity, and clinical implications, where eurythmia represents physiological normalcy and tachyarrhythmia signifies potential cardiac pathology requiring medical evaluation.
Causes of Eurythmic and Tachyarrhythmic Heart Rhythms
Eurythmia refers to a normal, regular heart rhythm typically caused by the proper functioning of the sinoatrial node and balanced autonomic nervous system input. Tachyarrhythmia results from abnormal electrical impulses often triggered by factors such as ischemic heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, or structural heart abnormalities. Understanding the distinct pathological mechanisms behind eurythmic and tachyarrhythmic rhythms aids in accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies.
Clinical Presentation: Recognizing Eurythmia vs Tachyarrhythmia
Eurythmia presents with a regular, steady heart rhythm often perceived as normal or slightly slowed, while tachyarrhythmia is characterized by an abnormally rapid heartbeat exceeding 100 beats per minute, leading to symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, or chest discomfort. Clinical recognition of eurythmia involves identifying consistent pulse and rhythm without associated hemodynamic instability, whereas tachyarrhythmia requires prompt assessment due to potential risks of compromised cardiac output or syncope. Accurate differentiation through ECG monitoring and symptom evaluation is critical for effective management and prevention of complications in arrhythmic conditions.
Diagnostic Approaches: Monitoring Heart Rhythm
Eurythmia is characterized by a regular, normal heart rhythm, often confirmed through standard electrocardiogram (ECG) recordings and Holter monitoring. In contrast, tachyarrhythmia involves abnormally fast heart rhythms, requiring advanced diagnostic tools such as continuous ambulatory ECG monitoring, event recorders, and electrophysiological studies to capture transient or episodic arrhythmias. Accurate heart rhythm monitoring with these methods is crucial for differentiating between normal eurythmic patterns and pathological tachyarrhythmias, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Health Risks Associated with Tachyarrhythmias
Tachyarrhythmias are characterized by abnormally fast heart rhythms exceeding 100 beats per minute, posing significant health risks including increased chances of stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac arrest. Unlike eurythmia, which refers to normal, regular heart rhythms, tachyarrhythmias can disrupt effective blood circulation, leading to organ damage and reduced oxygen delivery. Early diagnosis and treatment of tachyarrhythmias are crucial to prevent complications such as thromboembolism and myocardial ischemia.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Eurythmia, characterized by a normal and regular heartbeat, generally requires no specific treatment beyond routine cardiac monitoring and lifestyle management such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise. Tachyarrhythmia, involving abnormally fast heart rhythms, demands more intensive treatment strategies including antiarrhythmic medications like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, electrical cardioversion, and in some cases, catheter ablation to restore normal rhythm. Effective management of tachyarrhythmia also involves addressing underlying causes such as electrolyte imbalances, heart disease, or thyroid dysfunction to prevent recurrence and complications.
Preventive Measures for Arrhythmia and Maintaining Eurythmia
Maintaining eurythmia, or normal heart rhythm, relies on preventive measures such as managing electrolyte balance, controlling blood pressure, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and excessive alcohol. Regular physical activity, stress reduction techniques, and adherence to prescribed medications help reduce the risk of tachyarrhythmia, a condition characterized by abnormally fast heart rhythms. Continuous monitoring and lifestyle modifications, combined with timely medical intervention, are essential to prevent arrhythmia and sustain eurythmia.
Patient Outcomes: Prognosis in Eurythmia vs Tachyarrhythmia
Eurythmia, characterized by a regular and stable heart rhythm, generally leads to favorable patient outcomes with lower risks of complications such as stroke or heart failure. In contrast, tachyarrhythmia involves abnormally fast and irregular heartbeats, significantly increasing the likelihood of adverse events including thromboembolism and sudden cardiac arrest. Effective management and early intervention in tachyarrhythmia are critical to improving the prognosis and reducing mortality rates compared to the comparatively benign course seen in eurythmic patients.
Eurythmia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com