Evolution drives the diversity of life through natural selection and genetic variation, shaping species over millions of years. Understanding evolution unlocks insights into how organisms adapt, survive, and thrive in changing environments. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge about the fascinating processes behind evolution.
Table of Comparison
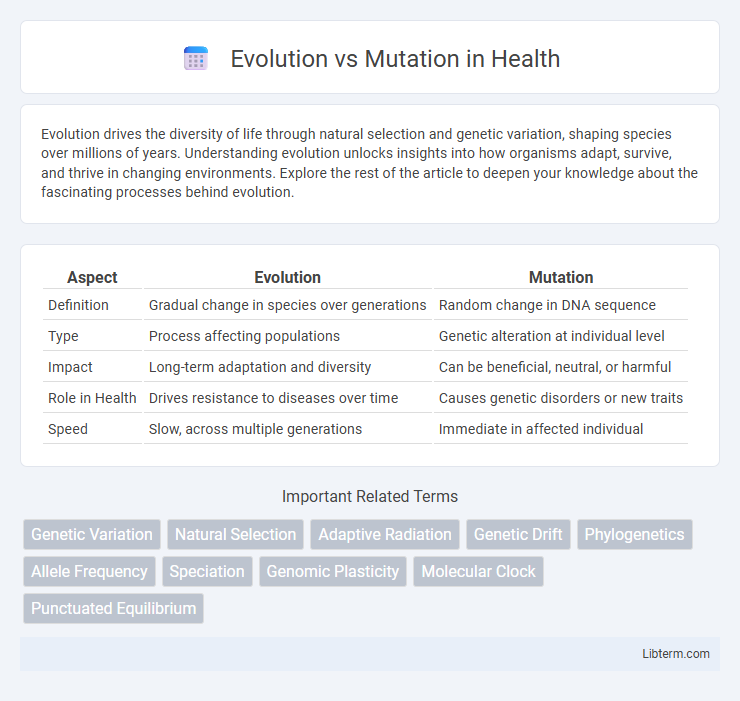
| Aspect | Evolution | Mutation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual change in species over generations | Random change in DNA sequence |
| Type | Process affecting populations | Genetic alteration at individual level |
| Impact | Long-term adaptation and diversity | Can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful |
| Role in Health | Drives resistance to diseases over time | Causes genetic disorders or new traits |
| Speed | Slow, across multiple generations | Immediate in affected individual |
Understanding Evolution: A Broad Perspective
Evolution encompasses changes in the genetic composition of populations over generations driven by mechanisms such as natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation. Mutation serves as the fundamental source of genetic variation, introducing new alleles that can be acted upon by evolutionary forces. Understanding evolution requires recognizing the interplay of multiple factors shaping species diversity and adaptation beyond mutation alone.
What is Mutation? Defining Genetic Change
Mutation refers to a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence of an organism, resulting in genetic variation that can affect traits and be passed to future generations. These changes occur spontaneously or due to environmental factors such as radiation or chemicals, leading to substitutions, insertions, deletions, or duplications in the genetic code. Mutations serve as the raw material for evolution by introducing new genetic variants within populations, influencing natural selection and species adaptation over time.
The Role of Mutations in Evolutionary Processes
Mutations serve as the primary source of genetic variation, providing the raw material for evolutionary change by introducing new alleles into populations. These random changes in DNA sequences can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful, but only advantageous mutations tend to increase in frequency through natural selection. Over successive generations, accumulated mutations contribute to adaptation, speciation, and the overall diversification of life forms.
Natural Selection: Filtering Mutations
Natural selection acts as a filter that determines which mutations persist within a population by favoring those that enhance an organism's survival and reproduction. Beneficial mutations increase an individual's fitness, leading to greater reproductive success and the propagation of advantageous traits. Harmful mutations are typically eliminated over time, while neutral mutations may accumulate, contributing to genetic diversity without immediate impact on fitness.
Types of Mutations and Their Biological Impact
Types of mutations include point mutations, insertions, deletions, and chromosomal rearrangements, each affecting genetic sequences differently and driving evolutionary change. Point mutations, such as substitutions, can alter protein function by changing amino acid sequences, while insertions and deletions may cause frameshift mutations leading to significant phenotypic variations. Chromosomal rearrangements, including inversions and translocations, contribute to genome evolution by creating new gene combinations and promoting speciation through reproductive isolation.
Mutation Rate: Frequency and Effects
Mutation rate, the frequency at which genetic mutations occur, directly influences evolutionary processes by generating genetic diversity within populations. High mutation rates can increase variability, potentially accelerating adaptation, but also risk accumulating deleterious mutations that may reduce fitness. Mutation effects range from neutral to harmful or beneficial, with beneficial mutations driving evolutionary change and shaping species' survival over generations.
Evolution vs Mutation: Key Differences
Evolution is a gradual process driven by the accumulation of genetic changes over generations, whereas mutation refers to a sudden, random alteration in the DNA sequence of an organism. While mutations serve as the raw material for evolution by introducing genetic diversity, evolution encompasses the broader mechanisms such as natural selection and genetic drift that influence allele frequencies within populations. Key differences include the scope and timescale, with mutations being individual events and evolution representing long-term population-level changes.
Adaptive Mutations: Fuel for Evolution
Adaptive mutations serve as a critical driver in the evolutionary process by increasing an organism's fitness within its environment. These beneficial genetic changes arise spontaneously and are selected for over generations, enabling populations to survive and thrive under changing conditions. The accumulation of adaptive mutations fuels evolutionary diversity and complexity across species.
Case Studies: Mutations Driving Evolution
Case studies reveal that specific mutations in genes like FOXP2 have driven evolutionary advancements in language and speech in humans. Research on the peppered moth (Biston betularia) demonstrates how mutations in the cortex gene facilitated industrial melanism, allowing survival through camouflage changes. Similarly, the sickle cell mutation in the HBB gene illustrates evolutionary adaptation by providing malaria resistance in certain populations.
Conclusion: Interdependence of Evolution and Mutation
Evolution and mutation are fundamentally interdependent processes driving biological diversity and adaptation. Mutations provide the genetic variations essential for natural selection, while evolution shapes these variations into complex organisms over generations. The continuous interaction between mutation and evolution underpins the dynamic nature of life's development on Earth.
Evolution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com