Pharmacovigilance is essential for monitoring the safety and efficacy of medications throughout their lifecycle, ensuring adverse effects are promptly identified and managed. It plays a crucial role in protecting public health by analyzing data from clinical trials, healthcare providers, and patients to mitigate risks associated with drug use. Explore the rest of the article to understand how effective pharmacovigilance practices can safeguard your health and improve medication safety.
Table of Comparison
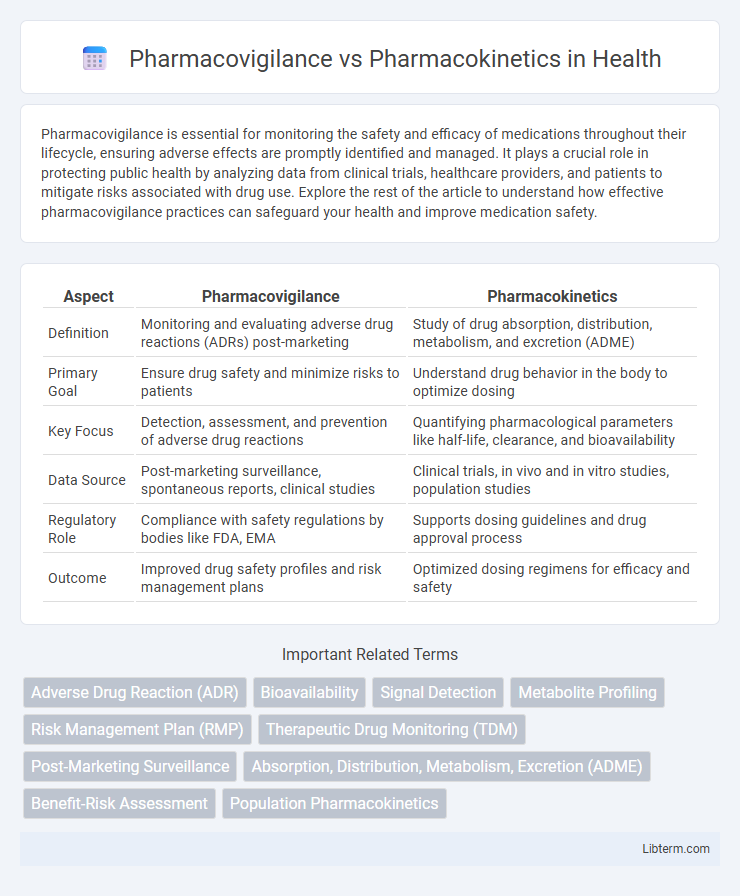
| Aspect | Pharmacovigilance | Pharmacokinetics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monitoring and evaluating adverse drug reactions (ADRs) post-marketing | Study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) |
| Primary Goal | Ensure drug safety and minimize risks to patients | Understand drug behavior in the body to optimize dosing |
| Key Focus | Detection, assessment, and prevention of adverse drug reactions | Quantifying pharmacological parameters like half-life, clearance, and bioavailability |
| Data Source | Post-marketing surveillance, spontaneous reports, clinical studies | Clinical trials, in vivo and in vitro studies, population studies |
| Regulatory Role | Compliance with safety regulations by bodies like FDA, EMA | Supports dosing guidelines and drug approval process |
| Outcome | Improved drug safety profiles and risk management plans | Optimized dosing regimens for efficacy and safety |
Introduction to Pharmacovigilance and Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacovigilance involves the detection, assessment, and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problems, ensuring drug safety throughout its market lifespan. Pharmacokinetics studies the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, providing critical data on drug concentration and timing in the body. Both fields are essential in drug development and therapeutic monitoring, with pharmacovigilance focusing on post-marketing safety and pharmacokinetics emphasizing the drug's behavior within biological systems.
Definition and Core Concepts
Pharmacovigilance involves the detection, assessment, and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problems, ensuring drug safety throughout its lifecycle. Pharmacokinetics studies how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body, focusing on the time course of drug concentration in tissues and fluids. While pharmacovigilance emphasizes monitoring and managing drug safety in populations, pharmacokinetics centers on understanding drug behavior at the individual biological level.
Objectives of Pharmacovigilance
Pharmacovigilance primarily aims to monitor, detect, assess, and prevent adverse drug reactions and safety issues post-marketing, ensuring patient safety and improving therapeutic outcomes. Unlike pharmacokinetics, which studies drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion to understand drug behavior in the body, pharmacovigilance focuses on real-world drug safety surveillance. Key objectives include identifying unknown side effects, evaluating risk-benefit profiles, and facilitating regulatory actions to minimize drug-related risks.
Objectives of Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics primarily aims to quantify the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs to optimize dosing regimens for maximum efficacy and minimal toxicity. Its objectives include determining bioavailability, half-life, clearance rates, and the impact of physiological variables on drug behavior in the body. These parameters provide critical data for drug development, therapeutic drug monitoring, and personalized medicine, distinguishing pharmacokinetics from pharmacovigilance, which focuses on drug safety and adverse effect monitoring post-marketing.
Methodologies Used in Pharmacovigilance
Pharmacovigilance employs methodologies such as spontaneous reporting systems, signal detection algorithms, and risk management plans to monitor, assess, and prevent adverse drug reactions in real-world clinical settings. Tools like disproportionality analysis and data mining techniques analyze large pharmacovigilance databases including VigiBase and FAERS for safety signals. These active surveillance strategies contrast with pharmacokinetics, which utilizes compartmental modeling and bioanalytical assays to study drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion at the molecular level.
Analytical Techniques in Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics relies on advanced analytical techniques such as liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to quantitatively assess drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in biological matrices. These precise methods enable the determination of drug concentration-time profiles, essential for pharmacokinetic modeling and dose optimization. In contrast, pharmacovigilance primarily involves post-marketing surveillance using data mining, signal detection algorithms, and spontaneous reporting systems to monitor drug safety rather than detailed quantitative analysis.
Role in Drug Development and Safety
Pharmacovigilance plays a critical role in drug development and safety by monitoring adverse drug reactions and ensuring ongoing patient safety post-marketing through systematic data collection and analysis. Pharmacokinetics focuses on understanding the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs, which informs dosing regimens and optimizes therapeutic efficacy during clinical trials. Together, pharmacovigilance and pharmacokinetics provide comprehensive insights essential for evaluating drug safety profiles and enhancing clinical decision-making throughout the drug development lifecycle.
Regulatory Requirements and Guidelines
Pharmacovigilance involves monitoring the safety of pharmaceutical products post-marketing, focusing on adverse event reporting as mandated by regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA under guidelines such as ICH E2E. Pharmacokinetics studies drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, providing critical data for dosage and safety evaluations required by regulatory frameworks including ICH M3(R2) and FDA's guidance on pharmacokinetic studies. Regulatory requirements demand thorough documentation in both areas to ensure drug safety and efficacy throughout clinical development and market lifecycle.
Challenges and Limitations
Pharmacovigilance faces challenges in detecting rare adverse drug reactions due to underreporting and delays in signal detection, limiting its ability to ensure drug safety comprehensively. Pharmacokinetics encounters limitations in translating in vitro or animal model data to human subjects, leading to variability in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion predictions. Both fields struggle with integrating big data and personalized medicine approaches, complicating the optimization of drug efficacy and safety profiles.
Future Perspectives and Emerging Trends
Future perspectives in pharmacovigilance emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and real-world data analytics to enhance drug safety monitoring and adverse event prediction. Emerging trends in pharmacokinetics focus on precision medicine approaches, utilizing genomic and metabolic profiling to optimize individualized drug dosing and efficacy. Both fields increasingly leverage big data and machine learning to improve patient outcomes and streamline drug development processes.
Pharmacovigilance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com