Genetic diversity is essential for the resilience and adaptability of species, providing a broad range of traits that enhance survival in changing environments. Maintaining this variability supports ecosystem stability and can improve agricultural productivity and disease resistance. Explore the full article to understand how preserving genetic diversity benefits Your world and future generations.
Table of Comparison
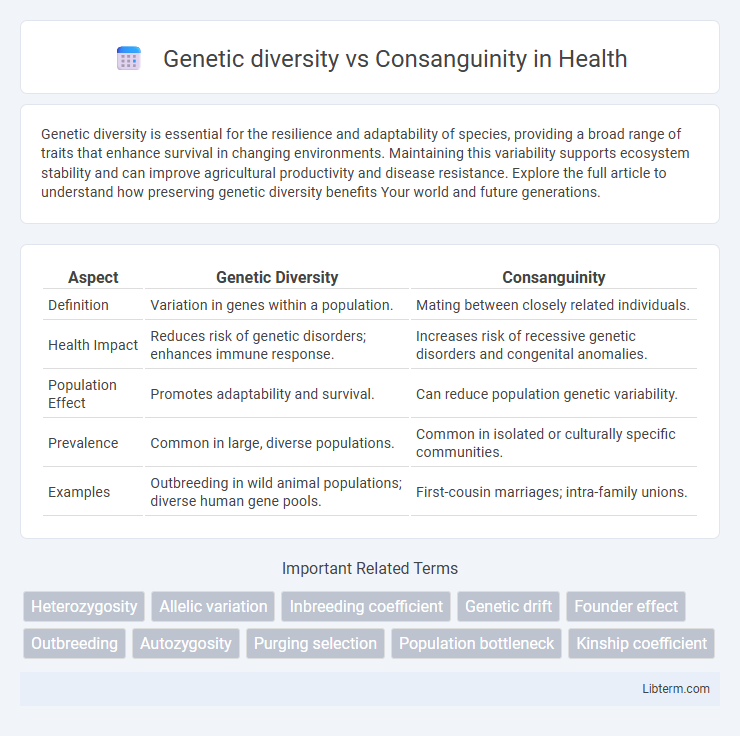
| Aspect | Genetic Diversity | Consanguinity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Variation in genes within a population. | Mating between closely related individuals. |
| Health Impact | Reduces risk of genetic disorders; enhances immune response. | Increases risk of recessive genetic disorders and congenital anomalies. |
| Population Effect | Promotes adaptability and survival. | Can reduce population genetic variability. |
| Prevalence | Common in large, diverse populations. | Common in isolated or culturally specific communities. |
| Examples | Outbreeding in wild animal populations; diverse human gene pools. | First-cousin marriages; intra-family unions. |
Introduction: Understanding Genetic Diversity and Consanguinity
Genetic diversity refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species, which enhances populations' ability to adapt to environmental changes and resist diseases. Consanguinity, the practice of marrying or reproducing within closely related individuals, reduces genetic diversity by increasing the probability of homozygosity, thereby elevating the risk of inherited genetic disorders. Understanding the balance between maintaining genetic diversity and the implications of consanguinity is crucial for improving population health and managing genetic risks.
Defining Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species, providing a crucial foundation for adaptation and survival. It encompasses variation in genes and alleles among individuals within populations, enhancing resilience to environmental changes and diseases. Consanguinity, the practice of mating between closely related individuals, tends to reduce genetic diversity by increasing homozygosity and the risk of inherited disorders.
What is Consanguinity?
Consanguinity refers to the genetic relationship between individuals who share common ancestors, typically defined as unions between second cousins or closer relatives. This practice increases the probability of homozygosity, elevating the risk of recessive genetic disorders within offspring due to reduced genetic diversity. In contrast, greater genetic diversity decreases the likelihood of inheriting detrimental genes, promoting overall population health.
The Role of Genetic Diversity in Population Health
Genetic diversity enhances population health by increasing resilience to diseases and reducing the prevalence of inherited disorders, as it involves a wide range of gene variants that improve adaptability. Consanguinity, or mating within close relatives, decreases genetic diversity and raises the risk of autosomal recessive diseases due to shared genetic mutations. Populations with higher genetic diversity exhibit lower rates of congenital conditions and stronger immune responses, emphasizing the critical role of diverse gene pools in maintaining public health.
Genetic Consequences of Consanguineous Marriages
Consanguineous marriages, or unions between close relatives, significantly reduce genetic diversity by increasing homozygosity, which elevates the risk of autosomal recessive disorders. This genetic consequence results in higher incidences of congenital anomalies, inherited metabolic disorders, and reduced overall population fitness. Population studies reveal that consanguinity doubles the probability of genetic diseases, emphasizing the critical need for genetic counseling in communities with prevalent intrafamily marriages.
Risks Associated with Reduced Genetic Diversity
Reduced genetic diversity increases the risk of hereditary diseases by amplifying recessive genetic disorders common within consanguineous populations. Consanguinity, or mating between close relatives, elevates the probability of homozygosity for deleterious alleles, leading to increased incidence of congenital anomalies and reduced immune system variability. This genetic uniformity diminishes population resilience against environmental changes and infectious diseases.
Benefits and Challenges of Consanguinity
Consanguinity increases genetic relatedness within families, promoting strong kinship ties and cultural cohesion, but it also elevates the risk of autosomal recessive disorders due to reduced genetic diversity. This practice can enhance social stability and resource sharing in close-knit communities while posing significant challenges, such as higher incidence of congenital anomalies and genetic disorders. Public health strategies must balance the cultural benefits of consanguinity with the need for genetic counseling and awareness to mitigate associated health risks.
Genetic Disorders Linked to Consanguinity
Consanguinity increases the risk of genetic disorders by promoting homozygosity of recessive alleles, leading to a higher prevalence of autosomal recessive conditions such as cystic fibrosis, thalassemia, and Tay-Sachs disease. Populations with low genetic diversity experience greater genetic disorder incidence because shared ancestry amplifies deleterious gene variants. Genetic counseling and screening are critical in consanguineous unions to mitigate the risk of inherited diseases and improve population health outcomes.
Strategies to Promote Genetic Diversity
Promoting genetic diversity involves strategies such as encouraging outbreeding and creating awareness about the risks of consanguinity, which increases the likelihood of inherited genetic disorders. Implementing community education programs and genetic counseling can help reduce consanguineous marriages and enhance gene pool variation. Population-level policies that support diverse mating patterns contribute to healthier genetic outcomes and reduce the prevalence of recessive genetic diseases.
Balancing Cultural Traditions and Genetic Health
Genetic diversity plays a crucial role in maintaining population health by reducing the risk of inherited disorders often associated with consanguinity, which involves mating between closely related individuals. Balancing cultural traditions that favor consanguineous marriages with genetic health requires implementing community education programs and offering accessible genetic counseling to inform couples about potential health risks. Promoting awareness and integrating these strategies supports the preservation of cultural values while minimizing genetic disease incidence.
Genetic diversity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com