Osmophobia is an intense sensitivity or aversion to certain smells, often linked to migraines or neurological conditions, causing significant discomfort and triggering symptoms. This condition can affect your daily life by making environments with strong odors unbearable, leading to social withdrawal or avoidance behaviors. Explore the rest of the article to understand osmophobia's causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
Table of Comparison
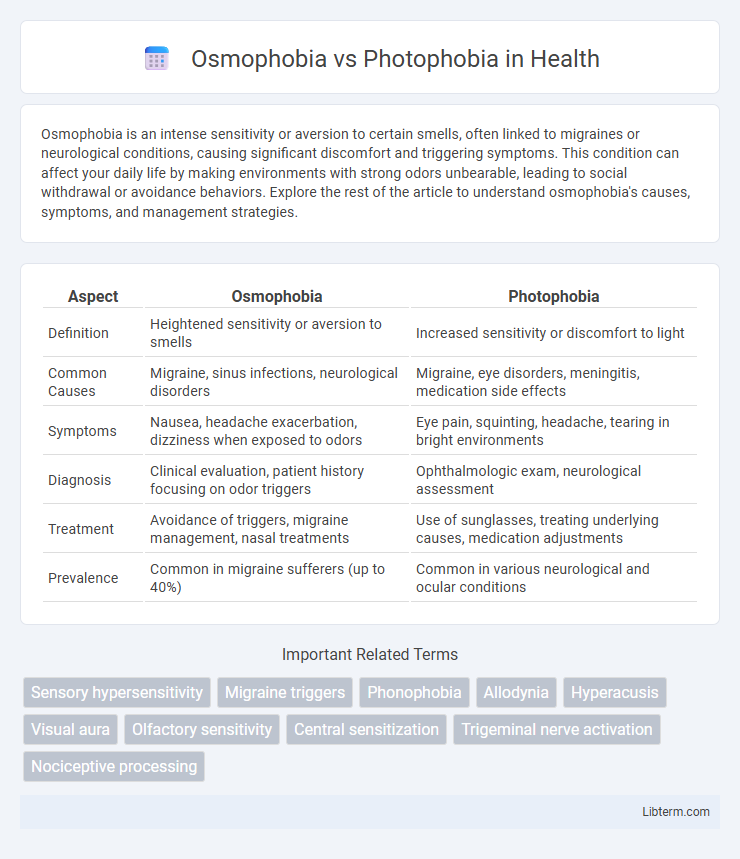
| Aspect | Osmophobia | Photophobia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heightened sensitivity or aversion to smells | Increased sensitivity or discomfort to light |
| Common Causes | Migraine, sinus infections, neurological disorders | Migraine, eye disorders, meningitis, medication side effects |
| Symptoms | Nausea, headache exacerbation, dizziness when exposed to odors | Eye pain, squinting, headache, tearing in bright environments |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, patient history focusing on odor triggers | Ophthalmologic exam, neurological assessment |
| Treatment | Avoidance of triggers, migraine management, nasal treatments | Use of sunglasses, treating underlying causes, medication adjustments |
| Prevalence | Common in migraine sufferers (up to 40%) | Common in various neurological and ocular conditions |
Understanding Osmophobia: Definition and Causes
Osmophobia is characterized by an intense sensitivity or aversion to specific odors, often linked to migraines, neurological disorders, or psychological conditions. Unlike photophobia, which involves discomfort or pain from light exposure, osmophobia triggers nausea, dizziness, or worsening headache due to smell stimuli. Common causes include migraine attacks, sinus infections, and chemical sensitivities, making accurate diagnosis crucial for targeted treatment and symptom management.
What is Photophobia? Key Insights
Photophobia is a sensitivity to light that causes discomfort or pain in the eyes, often linked to conditions like migraines, meningitis, or eye injuries. It differs from osmophobia, which is a heightened sensitivity to smells, commonly associated with migraines. Recognizing photophobia involves noting symptoms such as squinting, eye watering, or headaches triggered by bright or flickering lights.
Symptoms Comparison: Osmophobia vs Photophobia
Osmophobia symptoms include an intense sensitivity to odors, often triggering nausea, headaches, or migraines, while photophobia is characterized by an abnormal intolerance to light, resulting in eye pain, squinting, or headaches. Both conditions share headache as a common symptom, but osmophobia specifically involves olfactory triggers, whereas photophobia involves visual stimuli. Differentiating these symptoms helps in diagnosing underlying issues such as migraines, neurological disorders, or eye conditions.
Neurological Triggers in Sensory Sensitivities
Osmophobia and photophobia are sensory sensitivities often linked to neurological triggers such as migraine and central nervous system disorders. Osmophobia involves heightened sensitivity to odors, frequently triggered by abnormal activity in the olfactory pathways and limbic system, while photophobia results from increased excitability in the visual cortex and trigeminal nerve pathways. Both conditions share overlapping neural mechanisms related to sensory processing dysfunction and heightened cortical excitability.
Medical Conditions Linked to Osmophobia
Osmophobia, characterized by an increased sensitivity or aversion to odors, is frequently associated with medical conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and certain neurological disorders. Unlike photophobia, which involves sensitivity to light and is common in conditions like meningitis and uveitis, osmophobia often signals underlying issues related to the trigeminal nerve or central nervous system dysfunction. Identifying osmophobia in patients can aid clinicians in diagnosing and managing chronic headaches and neuroinflammatory diseases.
Disorders Commonly Associated with Photophobia
Photophobia is commonly associated with neurological disorders such as migraine, meningitis, and concussion, which cause heightened sensitivity to light. Unlike osmophobia, which involves an aversion to odors and is often linked to migraines and certain psychiatric conditions, photophobia primarily relates to eye and brain disorders, including uveitis and encephalitis. Understanding the distinct causes and symptoms of photophobia aids in diagnosing underlying conditions and differentiating it from osmophobia.
Diagnostic Approaches: Osmophobia vs Photophobia
Diagnostic approaches for osmophobia involve detailed patient history focusing on odor-triggered symptoms and olfactory sensitivity tests, often used in migraine and neurological disorder evaluations. Photophobia assessment includes standardized light exposure tests and patient-reported light sensitivity scales to identify underlying ocular or neurological conditions. Differentiating between osmophobia and photophobia relies on specific symptom triggers--olfactory stimuli versus light stimuli--guiding targeted diagnostic pathways and treatment strategies.
Treatment and Management Options
Osmophobia treatment primarily involves avoiding strong or triggering odors and may include the use of antihistamines or corticosteroids to reduce nasal inflammation. Photophobia management focuses on reducing exposure to bright lights using sunglasses or tinted lenses, alongside addressing underlying causes such as migraines with medications like triptans or analgesics. Both conditions often require personalized approaches combining lifestyle adjustments and pharmacologic therapies tailored to symptom severity and patient response.
Daily Life Impact: Coping Strategies
Osmophobia and photophobia significantly affect daily life by triggering strong aversions to smells and light, respectively, often leading to discomfort in common environments such as workplaces or social settings. Coping strategies for osmophobia include avoiding exposure to strong odors, using air purifiers, and selecting fragrance-free personal care products, while managing photophobia involves wearing tinted glasses, adjusting screen brightness, and ensuring access to dimly lit or dark spaces. Both conditions benefit from structured lifestyle adjustments and professional guidance to minimize sensory triggers and enhance overall quality of life.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Osmophobia, an intense sensitivity to odors, can be managed by avoiding strong scents such as perfumes, cleaning agents, and smoke, and by maintaining well-ventilated living spaces. Photophobia, characterized by an extreme sensitivity to light, requires wearing sunglasses with UV protection, using dim lighting indoors, and wearing wide-brimmed hats when outdoors. Both conditions benefit from stress reduction techniques, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and consulting healthcare professionals for tailored advice and treatment.
Osmophobia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com