Preventing issues before they arise saves time, money, and stress by addressing potential risks early on. Effective prevention strategies involve regular monitoring, adopting best practices, and staying informed about new developments. Explore the rest of this article to learn how you can implement these preventive measures successfully.
Table of Comparison
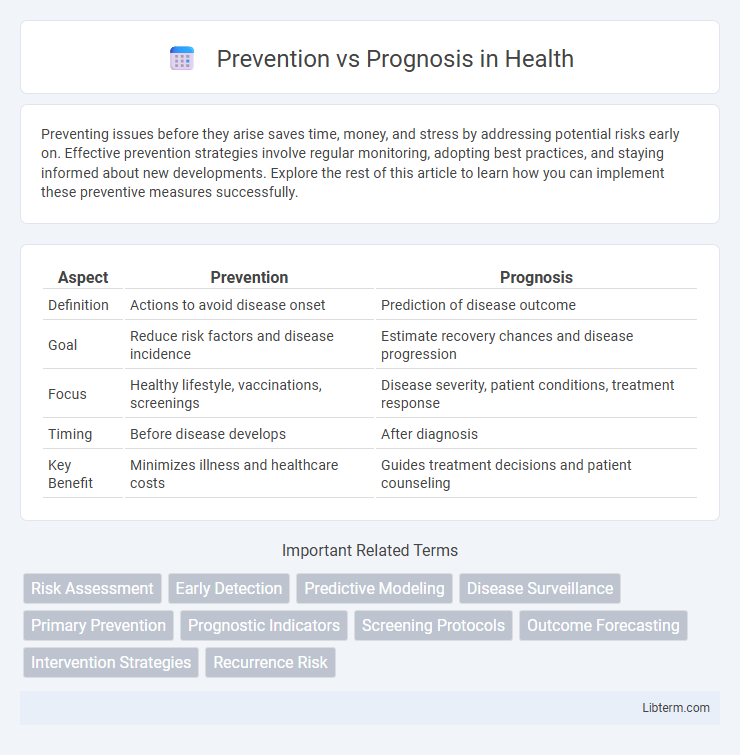
| Aspect | Prevention | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions to avoid disease onset | Prediction of disease outcome |
| Goal | Reduce risk factors and disease incidence | Estimate recovery chances and disease progression |
| Focus | Healthy lifestyle, vaccinations, screenings | Disease severity, patient conditions, treatment response |
| Timing | Before disease develops | After diagnosis |
| Key Benefit | Minimizes illness and healthcare costs | Guides treatment decisions and patient counseling |
Understanding Prevention and Prognosis
Prevention involves strategies and interventions aimed at reducing the risk or occurrence of diseases, emphasizing lifestyle changes, vaccinations, and screenings to maintain health. Prognosis refers to the predicted course and outcome of a disease based on clinical data, patient history, and diagnostic tests, providing insights into survival rates and recovery chances. Understanding prevention and prognosis helps healthcare professionals tailor treatment plans and prioritize measures to improve patient outcomes.
Key Differences Between Prevention and Prognosis
Prevention involves measures and strategies designed to stop diseases or conditions from occurring, focusing on risk reduction and health promotion. Prognosis refers to the predicted course and outcome of a disease after diagnosis, including chances of recovery or progression. Key differences lie in prevention targeting future health avoidance, while prognosis assesses existing disease outlook and patient management.
The Role of Prevention in Disease Management
Prevention plays a crucial role in disease management by reducing the incidence and severity of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Implementing lifestyle changes, vaccinations, and early screening programs can significantly lower healthcare costs and improve patient outcomes. Effective prevention strategies enhance quality of life and reduce the burden on healthcare systems worldwide.
Prognosis: What It Means for Patients
Prognosis refers to the predicted course and outcome of a disease, providing patients with essential insights into their health future and potential treatment effectiveness. Understanding prognosis helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions on management strategies and lifestyle adjustments tailored to the disease's expected progression. Accurate prognosis models integrate clinical data, biomarkers, and patient history to improve personalized care and optimize clinical outcomes.
Factors Affecting Prevention Strategies
Effective prevention strategies depend on multiple factors including genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, and lifestyle choices such as diet and physical activity. Socioeconomic status and access to healthcare resources significantly influence the implementation and success of preventive measures. Tailoring prevention efforts to demographic variables and risk profile enhances early intervention and reduces disease incidence.
Determinants of Prognosis Outcomes
Determinants of prognosis outcomes include patient-specific factors such as age, genetic predisposition, comorbidities, and lifestyle habits, which significantly influence disease progression and treatment response. Biomarkers and early diagnostic indicators also play a critical role in predicting clinical outcomes by providing measurable signs of disease severity and potential complications. Effective prognosis modeling integrates these determinants with clinical data to tailor personalized management plans, improving overall patient survival and quality of life.
Integrating Prevention and Prognosis in Healthcare
Integrating prevention and prognosis in healthcare enhances patient outcomes by combining early intervention strategies with accurate predictions of disease progression. Utilizing predictive analytics and personalized risk assessments enables healthcare providers to tailor preventative measures while anticipating future health challenges. This synergy supports proactive care management, reduces healthcare costs, and improves quality of life for patients through timely, targeted treatments.
Benefits of Early Prevention vs. Prognosis
Early prevention significantly reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases by addressing risk factors before symptoms arise, leading to improved quality of life and lower healthcare costs. Preventive measures enable timely interventions that slow or stop disease progression, enhancing long-term health outcomes compared to managing diseases after diagnosis. Prognosis relies on disease stage and severity, often limiting treatment effectiveness, whereas prevention maximizes the potential for maintaining optimal health.
Challenges in Balancing Prevention and Prognosis
Balancing prevention and prognosis in healthcare involves significant challenges such as allocating resources effectively between early intervention strategies and managing patients with established conditions. Predicting disease outcomes requires accurate biomarkers and personalized data, yet prevention efforts demand broad public health measures that may lack immediate, measurable results. Integrating predictive analytics with preventive care requires overcoming disparities in healthcare access and ensuring continuous monitoring without overwhelming healthcare systems.
Future Trends in Prevention and Prognosis
Emerging technologies in prevention increasingly leverage artificial intelligence and wearable devices to enable real-time health monitoring and personalized intervention strategies. Advances in genomics and biomarker analysis enhance prognosis accuracy by predicting disease progression and treatment response more precisely. Integration of big data analytics fosters a holistic approach, improving early detection and individualized patient management for future healthcare outcomes.
Prevention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com