Normal sinus rhythm indicates a healthy, regular heartbeat originating from the sinus node, ensuring efficient blood circulation throughout the body. It reflects the heart's proper electrical functioning, which is crucial for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. Discover more about how normal sinus rhythm affects your wellbeing and how to recognize its significance in the following article.
Table of Comparison
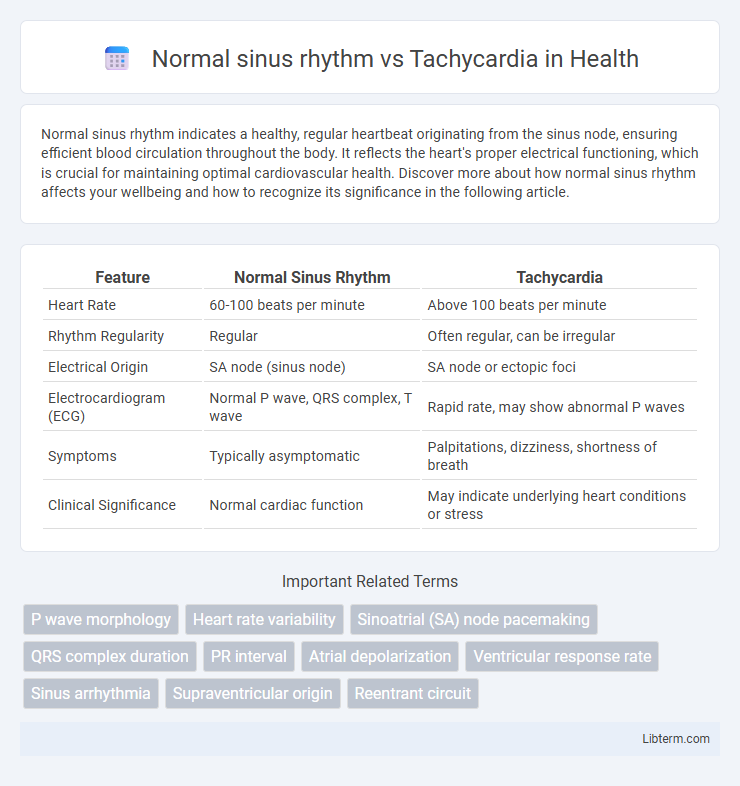
| Feature | Normal Sinus Rhythm | Tachycardia |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 60-100 beats per minute | Above 100 beats per minute |
| Rhythm Regularity | Regular | Often regular, can be irregular |
| Electrical Origin | SA node (sinus node) | SA node or ectopic foci |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Normal P wave, QRS complex, T wave | Rapid rate, may show abnormal P waves |
| Symptoms | Typically asymptomatic | Palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath |
| Clinical Significance | Normal cardiac function | May indicate underlying heart conditions or stress |
Introduction to Normal Sinus Rhythm and Tachycardia
Normal sinus rhythm represents the standard heart rhythm, characterized by a consistent rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute originating from the sinoatrial node. Tachycardia is defined by an elevated heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, often resulting from physiological stress, heart conditions, or other medical factors. Understanding the differences between normal sinus rhythm and tachycardia is critical for diagnosing cardiac health and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Understanding the Heart’s Electrical Conduction System
Normal sinus rhythm originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node, producing a regular heart rate of 60-100 beats per minute with coordinated atrial and ventricular contractions. Tachycardia arises when the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute due to abnormal impulses in the SA node, atria, or ventricles, disrupting the normal electrical conduction pathway. Understanding the heart's conduction system, including the SA node, atrioventricular (AV) node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers, is crucial for differentiating these rhythms and diagnosing arrhythmias.
Defining Normal Sinus Rhythm: Features and Parameters
Normal sinus rhythm is characterized by a heart rate ranging from 60 to 100 beats per minute with a regular rhythm and normal P-wave morphology indicating proper sinoatrial node function. The PR interval typically measures 120 to 200 milliseconds, and QRS complexes are narrow and uniform, reflecting coordinated ventricular depolarization. In contrast, tachycardia involves an elevated heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, often with altered rhythm regularity and potential changes in waveform intervals, signaling abnormal cardiac conduction or heightened sympathetic stimulation.
What is Tachycardia?
Tachycardia is a cardiac condition characterized by a resting heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, contrasting with normal sinus rhythm which ranges from 60 to 100 bpm in adults. This rapid heart rate originates from abnormal electrical signals in the heart's atria or ventricles, potentially leading to inefficient blood circulation and symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath. Identifying tachycardia involves electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis, which reveals accelerated heart rhythms that may require medical intervention based on underlying causes like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
Key Differences: Normal Sinus Rhythm vs. Tachycardia
Normal sinus rhythm (NSR) is characterized by a heart rate of 60-100 beats per minute with regular intervals between P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves indicating proper electrical conduction through the sinoatrial node. Tachycardia presents as a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, often resulting from increased automaticity, reentry circuits, or triggered activity causing rapid and sometimes irregular rhythms. Key differences include heart rate thresholds, rhythm regularity, and the underlying electrophysiological mechanisms, crucial for diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Common Causes of Tachycardia
Normal sinus rhythm refers to the regular, steady heartbeat originating from the sinoatrial node, typically between 60 to 100 beats per minute in adults. Tachycardia occurs when the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute, often triggered by factors such as fever, anxiety, dehydration, anemia, hyperthyroidism, and substance use like caffeine or stimulants. Understanding these common causes is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of tachycardia to prevent complications such as arrhythmias or cardiac arrest.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
Normal sinus rhythm presents with a regular heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute and generally lacks symptoms, maintaining efficient cardiac output and stable hemodynamics. Tachycardia, characterized by a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, often manifests with palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and sometimes syncope due to decreased ventricular filling time and compromised cardiac output. Clinical examination may reveal irregular pulse, hypotension, or signs of heart failure in tachycardic patients, highlighting the importance of prompt diagnosis and management.
Diagnostic Approaches: ECG Interpretation
Normal sinus rhythm presents on an ECG with a regular rhythm, heart rate between 60-100 bpm, and consistent P waves preceding each QRS complex, reflecting normal SA node activity. Tachycardia is characterized by a heart rate above 100 bpm, with ECG showing rapid, sometimes irregular rhythms that may include narrowed or widened QRS complexes depending on type (supraventricular or ventricular). Detailed ECG interpretation involves analyzing rate, rhythm regularity, P wave morphology, PR interval, and QRS duration to differentiate between normal sinus rhythm and various tachycardia forms.
Treatment Strategies for Tachycardia
Treatment strategies for tachycardia depend on the underlying cause and type, with options including medication such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmics to control heart rate and rhythm. In cases of sustained or symptomatic tachycardia, procedures like catheter ablation or electrical cardioversion may be necessary to restore normal sinus rhythm. Lifestyle modifications, including stress reduction, avoiding stimulants, and managing comorbid conditions, play a supportive role in preventing recurrent episodes.
Prognosis and Importance of Early Detection
Normal sinus rhythm indicates a regular heart rate typically between 60-100 beats per minute, associated with a favorable prognosis and lower risk of cardiovascular complications. Tachycardia, defined as a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, may lead to increased cardiac workload, arrhythmias, and potential heart failure if left untreated. Early detection of tachycardia is crucial for initiating timely interventions to prevent adverse outcomes and improve long-term cardiac health.
Normal sinus rhythm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com