Sjogren's syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disorder primarily affecting the moisture-producing glands, leading to symptoms like dry eyes and dry mouth. This condition can also cause joint pain, fatigue, and complications involving other organs such as the kidneys and lungs. Discover more about the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for Sjogren's syndrome in the following article.
Table of Comparison
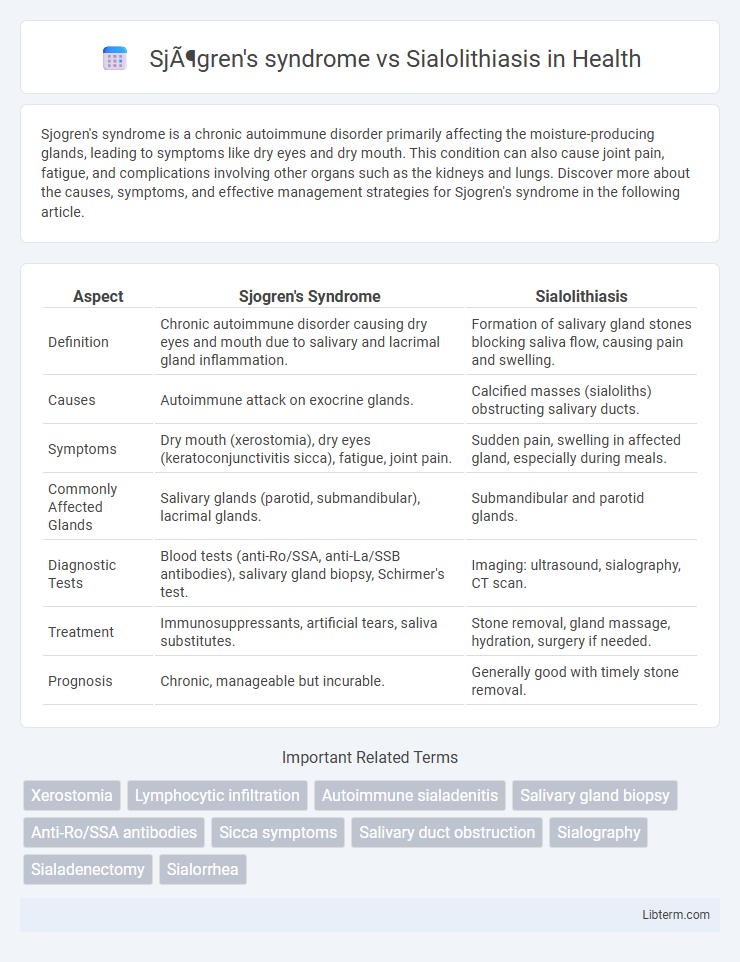
| Aspect | Sjogren's Syndrome | Sialolithiasis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic autoimmune disorder causing dry eyes and mouth due to salivary and lacrimal gland inflammation. | Formation of salivary gland stones blocking saliva flow, causing pain and swelling. |
| Causes | Autoimmune attack on exocrine glands. | Calcified masses (sialoliths) obstructing salivary ducts. |
| Symptoms | Dry mouth (xerostomia), dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca), fatigue, joint pain. | Sudden pain, swelling in affected gland, especially during meals. |
| Commonly Affected Glands | Salivary glands (parotid, submandibular), lacrimal glands. | Submandibular and parotid glands. |
| Diagnostic Tests | Blood tests (anti-Ro/SSA, anti-La/SSB antibodies), salivary gland biopsy, Schirmer's test. | Imaging: ultrasound, sialography, CT scan. |
| Treatment | Immunosuppressants, artificial tears, saliva substitutes. | Stone removal, gland massage, hydration, surgery if needed. |
| Prognosis | Chronic, manageable but incurable. | Generally good with timely stone removal. |
Introduction to Sjögren's Syndrome and Sialolithiasis
Sjogren's syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system attacking the body's moisture-producing glands, leading to dry mouth and dry eyes along with potential systemic complications. Sialolithiasis, on the other hand, involves the formation of calcified stones within the salivary glands or ducts, causing pain and swelling due to obstructed saliva flow. While both conditions impact salivary gland function, Sjogren's syndrome primarily results from autoimmune dysfunction, whereas sialolithiasis stems from physical blockage by salivary stones.
Overview of Salivary Gland Disorders
Sjogren's syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by lymphocytic infiltration and destruction of salivary glands, leading to dry mouth and impaired saliva production. Sialolithiasis involves the formation of calcified stones blocking salivary ducts, causing pain and swelling during meals and potential secondary infections. Both conditions affect salivary gland function but differ in etiology, with Sjogren's being systemic and inflammatory, while sialolithiasis is a mechanical obstruction.
Causes: Autoimmunity vs Obstruction
Sjogren's syndrome is caused by an autoimmune response in which the body's immune system attacks its own moisture-producing glands, particularly the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to dry mouth and eyes. In contrast, sialolithiasis results from physical obstruction caused by the formation of calcified stones within the salivary ducts, blocking saliva flow and causing pain and swelling. These differing etiologies--autoimmunity in Sjogren's syndrome versus mechanical obstruction in sialolithiasis--dictate distinct clinical presentations and treatment approaches.
Common Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Sjogren's syndrome commonly presents with dry mouth (xerostomia) and dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca) due to autoimmune destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to symptoms like difficulty swallowing and persistent oral dryness. Sialolithiasis typically manifests as acute unilateral salivary gland swelling and pain, especially during meals, caused by obstructive salivary duct stones. Both conditions can cause salivary gland swelling, but Sjogren's syndrome often involves chronic systemic symptoms, whereas sialolithiasis features episodic, painful gland enlargement linked to duct obstruction.
Diagnostic Approaches: Differentiating the Conditions
Sjogren's syndrome diagnosis relies on serological tests for autoantibodies such as anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB, along with salivary gland biopsy revealing lymphocytic infiltration. Sialolithiasis is primarily diagnosed through imaging modalities like ultrasound or sialography that detect salivary duct stones causing obstruction and swelling. Differentiating the two conditions involves correlating clinical presentation with lab results and imaging findings, where autoimmune markers and glandular histopathology suggest Sjogren's, while radiographic evidence confirms sialolithiasis.
Imaging Techniques and Laboratory Testing
Imaging techniques for Sjogren's syndrome often include salivary gland ultrasonography, which reveals glandular heterogeneity and hypoechoic areas, while sialography and MRI may show characteristic ductal changes and gland inflammation; in contrast, sialolithiasis is primarily diagnosed through non-contrast CT scans or ultrasonography identifying calcified salivary stones causing ductal obstruction. Laboratory testing for Sjogren's syndrome focuses on detecting autoantibodies such as anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La, alongside elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers and increased inflammatory markers, whereas sialolithiasis lacks specific serological markers and relies on clinical presentation supported by imaging. The combination of detailed imaging modalities and specific serological profiles is crucial for differentiating autoimmune glandular inflammation of Sjogren's syndrome from mechanical duct obstruction in sialolithiasis.
Treatment Modalities for Sjögren’s Syndrome
Treatment modalities for Sjogren's syndrome primarily focus on symptom management and improving quality of life, including the use of artificial tears and saliva substitutes to alleviate dry eyes and mouth. Immunomodulatory drugs such as hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and autoimmune activity. In severe cases, biologic agents like rituximab may be considered to target specific immune pathways involved in glandular dysfunction.
Management Strategies for Sialolithiasis
Management strategies for sialolithiasis primarily involve conservative measures such as hydration, gland massage, and sialogogues to promote stone expulsion. In cases where stones are persistent or cause recurrent infections, minimally invasive techniques like sialendoscopy or extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) are effective options. Surgical removal of the affected salivary gland remains a last resort for refractory cases or when complications arise.
Prognosis and Long-Term Complications
Sjogren's syndrome typically presents a chronic autoimmune prognosis with potential long-term complications including lymphoma, severe dry mouth, and dental caries due to persistent salivary gland dysfunction. Sialolithiasis, caused by salivary gland duct obstruction from stones, generally has a favorable prognosis with proper treatment but may lead to recurrent infections, gland swelling, and possible chronic sialadenitis if left untreated. Monitoring and management of Sjogren's focus on mitigating systemic autoimmune effects, whereas sialolithiasis care aims at resolving obstructions to prevent recurrent gland damage.
Key Differences and Clinical Decision-Making
Sjogren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation and lymphocytic infiltration of exocrine glands, leading to dry mouth and eyes, whereas sialolithiasis involves salivary gland duct obstruction caused by calcified stones, resulting in painful swelling and infection. Clinical decision-making relies on serologic markers like anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB antibodies for Sjogren's diagnosis, while imaging techniques such as ultrasound or sialography identify sialoliths in sialolithiasis. Treatment for Sjogren's targets systemic immunomodulation and symptomatic relief, contrasting with the mechanical removal or lithotripsy approach needed for sialolithiasis.
Sjögren's syndrome Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com