Effective medical management involves a comprehensive approach to diagnosing, treating, and monitoring health conditions using evidence-based therapies and personalized care plans. It aims to optimize your overall health outcomes while minimizing complications through regular follow-ups and medication adjustments. Discover more about how tailored medical management can improve your quality of life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
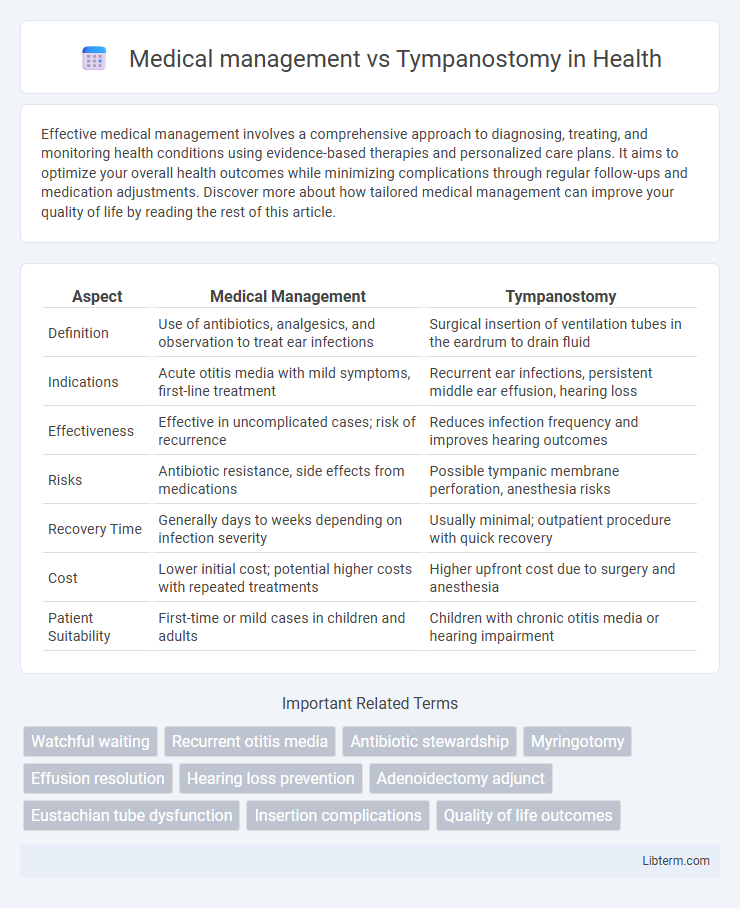
| Aspect | Medical Management | Tympanostomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of antibiotics, analgesics, and observation to treat ear infections | Surgical insertion of ventilation tubes in the eardrum to drain fluid |
| Indications | Acute otitis media with mild symptoms, first-line treatment | Recurrent ear infections, persistent middle ear effusion, hearing loss |
| Effectiveness | Effective in uncomplicated cases; risk of recurrence | Reduces infection frequency and improves hearing outcomes |
| Risks | Antibiotic resistance, side effects from medications | Possible tympanic membrane perforation, anesthesia risks |
| Recovery Time | Generally days to weeks depending on infection severity | Usually minimal; outpatient procedure with quick recovery |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; potential higher costs with repeated treatments | Higher upfront cost due to surgery and anesthesia |
| Patient Suitability | First-time or mild cases in children and adults | Children with chronic otitis media or hearing impairment |
Introduction to Otitis Media Management
Otitis media management involves balancing medical treatment with surgical options like tympanostomy to effectively address middle ear infections. Medical management typically includes antibiotics and analgesics to reduce infection and pain, while tympanostomy provides direct ventilation and drainage through ear tube insertion. Choosing between these approaches depends on factors such as the frequency and severity of infections, presence of effusion, and impact on hearing and development.
Overview of Medical Management
Medical management of middle ear infections primarily involves the use of antibiotics, analgesics, and decongestants to reduce infection, alleviate pain, and decrease inflammation. This approach aims to resolve acute otitis media without surgical intervention, relying on close observation and symptom control to prevent complications. Effectiveness depends on the infection's severity, duration, and patient-specific factors, with guidelines recommending medical treatment as the initial step before considering tympanostomy tubes for recurrent or chronic cases.
Indications for Tympanostomy Tubes
Tympanostomy tubes are primarily indicated for children with recurrent acute otitis media, defined as three or more episodes in six months or four episodes in one year, especially when associated with persistent middle ear effusion lasting longer than three months. Persistent middle ear effusion causing hearing loss, speech delay, or behavioral issues also warrants tympanostomy tube insertion to improve aeration and drainage. Medical management, including antibiotics and watchful waiting, is preferred initially, but surgical intervention with tubes is recommended when infections are recurrent or effusions show no resolution.
Effectiveness of Medical Therapy
Medical management of otitis media emphasizes antibiotic and anti-inflammatory therapies to reduce infection and inflammation, aiming for symptom resolution without surgical intervention. Studies show that while medical therapy can be effective in mild to moderate cases, its success rates decline with recurrent or chronic otitis media, where persistent middle ear effusion and hearing loss may persist. Tympanostomy tubes often provide superior long-term outcomes in recurrent cases by facilitating middle ear drainage and reducing infection recurrence.
Risks and Benefits of Tympanostomy Tubes
Tympanostomy tubes offer significant benefits for children with recurrent otitis media, including improved middle ear ventilation and reduced frequency of ear infections. Risks associated with tympanostomy tubes include persistent perforation, otorrhea, and potential scarring of the tympanic membrane. Medical management with antibiotics avoids surgical risks but may lead to repeated infections and antibiotic resistance, making tympanostomy a valuable option when conservative treatment fails.
Comparing Outcomes: Medical vs Surgical
Medical management of otitis media primarily involves antibiotic therapy and watchful waiting, aiming to resolve infection without invasive intervention. Tympanostomy, a surgical procedure inserting ventilation tubes, directly addresses middle ear fluid and recurrent infections, often resulting in faster symptomatic relief and improved hearing outcomes. Studies indicate tympanostomy typically yields superior long-term resolution of middle ear effusion and reduces recurrence rates compared to exclusive medical management.
Patient Selection Criteria
Patient selection criteria for medical management of otitis media primarily include cases with mild to moderate symptoms, absence of recurrent infections, and no significant hearing loss or structural damage. Tympanostomy is recommended for patients with recurrent acute otitis media (>=3 episodes in 6 months or >=4 in 12 months), persistent middle ear effusion for more than 3 months with hearing impairment, or anatomical abnormalities predisposing to infection. Accurate diagnosis through otoscopic examination, audiometry, and assessment of risk factors is essential for selecting appropriate treatment strategies.
Complications and Adverse Events
Medical management of otitis media typically involves antibiotics and analgesics, with complications including antibiotic resistance, gastrointestinal upset, and allergic reactions. Tympanostomy, a surgical intervention involving the insertion of ear tubes, carries risks such as tympanic membrane perforation, otorrhea, and anesthesia-related adverse events. Studies indicate that while surgery may reduce recurrence rates, it has a higher incidence of localized adverse events compared to conservative medical management.
Long-term Prognosis and Recurrence
Medical management of otitis media primarily involves antibiotics and watchful waiting, but exhibits higher rates of recurrence and may lead to chronic effusion impacting long-term prognosis. Tympanostomy tube insertion offers improved ventilation and drainage of the middle ear, significantly reducing recurrence rates and promoting better hearing outcomes over extended periods. Studies show that tympanostomy provides superior long-term control of middle ear infections compared to medical therapy alone, especially in children with recurrent acute otitis media.
Clinical Guidelines and Recommendations
Clinical guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend initial medical management with analgesics and observation for uncomplicated acute otitis media, reserving tympanostomy tube insertion for recurrent infections or persistent middle ear effusion beyond three months. The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery endorses tympanostomy tubes primarily for children with bilateral effusion lasting over three months and associated hearing loss or developmental concerns. Evidence-based recommendations emphasize personalized treatment decisions based on infection frequency, symptom severity, and response to medical therapy to optimize patient outcomes.
Medical management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com