Ager assignatus refers to land allocated by Roman authorities for specific public or private uses, often granted to veterans or settlers as a form of reward or colonization. Understanding the legal and historical significance of ager assignatus helps clarify ancient land distribution practices and their impact on social organization. Explore the full article to uncover how ager assignatus shaped Roman society and land management.
Table of Comparison
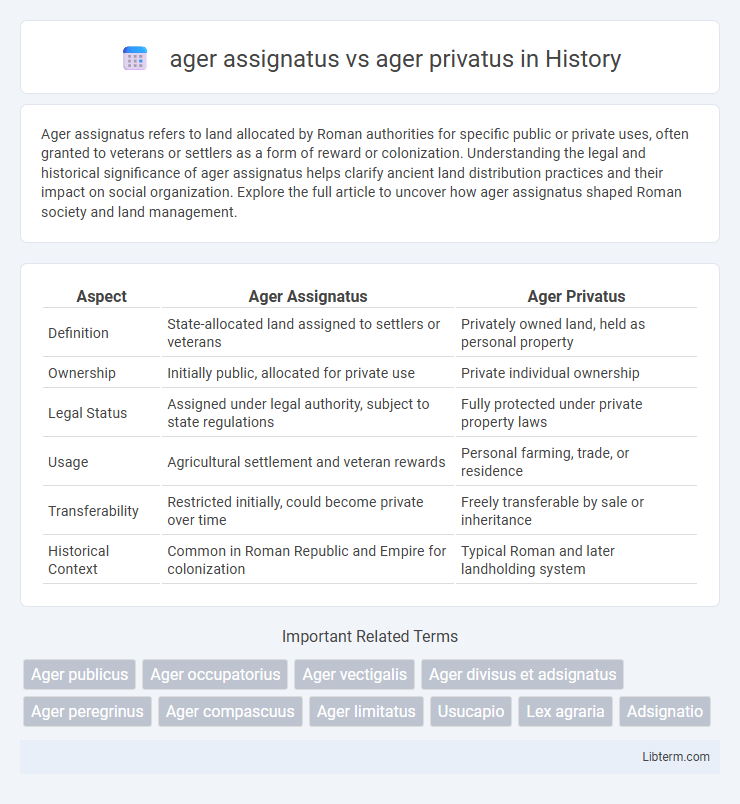
| Aspect | Ager Assignatus | Ager Privatus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State-allocated land assigned to settlers or veterans | Privately owned land, held as personal property |
| Ownership | Initially public, allocated for private use | Private individual ownership |
| Legal Status | Assigned under legal authority, subject to state regulations | Fully protected under private property laws |
| Usage | Agricultural settlement and veteran rewards | Personal farming, trade, or residence |
| Transferability | Restricted initially, could become private over time | Freely transferable by sale or inheritance |
| Historical Context | Common in Roman Republic and Empire for colonization | Typical Roman and later landholding system |
Introduction to Roman Land Tenure
Ager assignatus refers to land allocated by the Roman state for specific public or private purposes, often distributed to settlers or veterans, while ager privatus denotes privately owned land held as property by individuals. Roman land tenure was characterized by a clear distinction between public land (ager publicus) that could be assigned (ager assignatus) and privately owned estates (ager privatus), forming the basis of Roman agricultural economy and social organization. The legal framework regulating these land types established rights of ownership, possession, and transfer, influencing Roman property law and land management practices.
Defining *Ager Assignatus*
Ager assignatus refers to land that has been specifically allocated or assigned for a particular purpose, often by a public authority for distribution or use, distinguishing it from ager privatus, which denotes privately owned land under individual ownership and control. This concept was significant in Roman law, where ager assignatus was designated for public projects, military colonies, or veteran settlements. Understanding the distinction between ager assignatus and ager privatus highlights differing legal statuses and rights associated with land ownership and usage.
Understanding *Ager Privatus*
*Ager Privatus* refers to privately owned land in ancient Roman law, distinguished by individual ownership rights and the ability to sell, lease, or bequeath the property. Unlike *Ager Assignatus*, which was public land allocated temporarily for specific uses such as military colonies or settlements, *Ager Privatus* granted the owner exclusive and permanent control over the land. Understanding *Ager Privatus* is crucial for comprehending Roman land tenure systems, as it reflects the legal recognition of private property in contrast to the communal or state-held *ager* categories.
Historical Background of Land Distribution
Ager assignatus and ager privatus represent two distinct categories of land in ancient Rome, reflecting different ownership and usage rights. Ager assignatus referred to public land allocated by the state to individuals, often as a political reward or for military service, while ager privatus denoted privately owned land held by individuals or families. The distribution of these lands played a crucial role in Roman agrarian reforms and social structures, influencing wealth concentration and civilian-military relationships throughout Roman history.
Legal Distinctions Between *Ager Assignatus* and *Ager Privatus*
The legal distinction between *ager assignatus* and *ager privatus* centers on ownership and purpose: *ager assignatus* refers to land assigned by the state for specific public uses such as military veterans' settlements or infrastructure projects, whereas *ager privatus* denotes privately owned land with unrestricted ownership rights. *Ager assignatus* often entails state-imposed obligations, limitations on transfer, and usage conditions governed by public law, contrasting with *ager privatus* where property rights are protected under private law allowing sale, inheritance, and full control. Roman law codified these differences to balance public interest with private property rights, ensuring that *ager assignatus* served utilitarian functions without compromising individual ownership freedoms inherent in *ager privatus*.
Methods of Assignation and Privatization
Ager assignatus refers to land allocated through state-sponsored distribution methods such as centuriation or legal allotments to citizens or veterans, whereas ager privatus denotes privately owned land acquired via purchase, inheritance, or long-term occupation. Assignation of ager assignatus typically involves formal procedures governed by Roman law, including public surveys and official registrations, while ager privatus is established through private agreements and recognized property rights confirmed by legal documentation. The distinction highlights state control and organized settlement in ager assignatus, contrasting with individual ownership and market transactions characterizing ager privatus.
Social and Economic Implications
Ager assignatus, land designated by the state for specific public uses or allocated to military veterans, contrasted with ager privatus, privately owned land subject to individual control and market transactions. Socially, ager assignatus reinforced state authority and supported public welfare or rewards, limiting private accumulation, while ager privatus facilitated economic growth through private investment and trade. Economically, ager assignatus often ensured equitable access to resources and promoted social stability, whereas ager privatus enabled wealth creation and social stratification through land commodification.
Role in Roman Agrarian Reforms
Ager assignatus referred to public land allocated specifically to individual Roman citizens through agrarian reforms aimed at redistributing land to veterans and the urban poor, promoting social stability and military loyalty. Ager privatus denoted privately owned land that was secured through purchase or inheritance, exempt from direct state redistribution but often subject to legal disputes during reforms. The distinction between ager assignatus and ager privatus was central to Rome's agrarian policies, as reformers sought to balance public land allocation with the protection of private property rights.
Case Studies and Historical Examples
Ager assignatus refers to publicly assigned land often allocated to veterans in ancient Rome, contrasting with ager privatus, which denotes privately owned land subject to individual property rights. The Roman Land Commission's distribution of ager assignatus after the Punic Wars illustrates state-directed land redistribution to reward soldiers and promote colonization, whereas ager privatus cases, such as Cicero's legal disputes over estate ownership, highlight private landholding and property law evolution. These distinctions profoundly shaped land tenure systems, influencing socio-political dynamics and legal precedents in Roman history.
Lasting Impact on Roman Society
Ager assignatus referred to land officially allocated to Roman citizens, often veterans, reinforcing social hierarchies and political control, while ager privatus represented privately owned land subject to fewer restrictions. The distribution of ager assignatus facilitated military loyalty and urban stabilization, shaping socioeconomic structures by limiting elite land monopolies. In contrast, ager privatus allowed wealth accumulation among the elite, perpetuating class disparities and influencing Roman legal frameworks surrounding property rights.
ager assignatus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com