Decline commonly refers to a gradual decrease or reduction in quality, quantity, or strength over time. This can impact various aspects of life or business, such as sales, health, or performance, requiring strategic adjustments to mitigate negative effects. Explore the full article to understand how to effectively recognize and manage decline in your specific context.
Table of Comparison
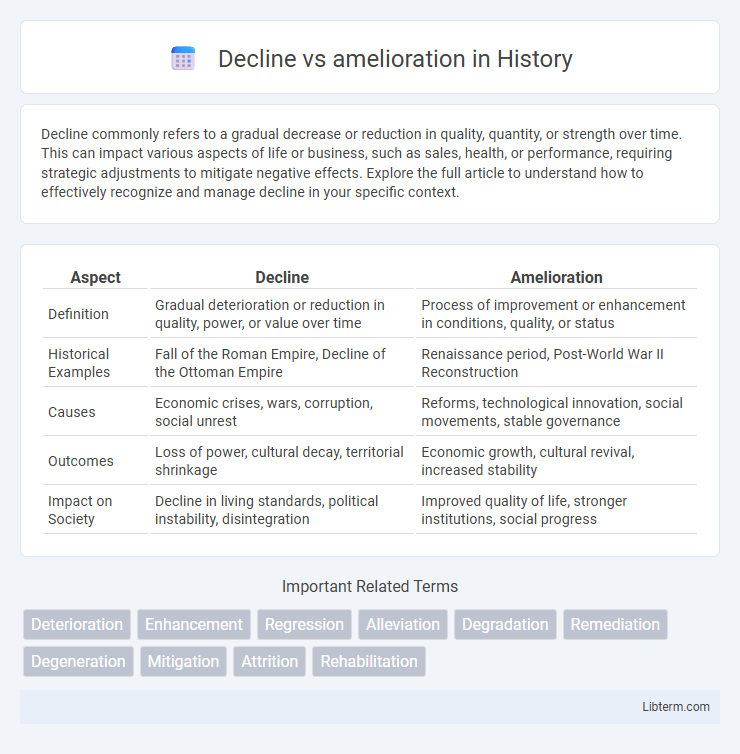
| Aspect | Decline | Amelioration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual deterioration or reduction in quality, power, or value over time | Process of improvement or enhancement in conditions, quality, or status |
| Historical Examples | Fall of the Roman Empire, Decline of the Ottoman Empire | Renaissance period, Post-World War II Reconstruction |
| Causes | Economic crises, wars, corruption, social unrest | Reforms, technological innovation, social movements, stable governance |
| Outcomes | Loss of power, cultural decay, territorial shrinkage | Economic growth, cultural revival, increased stability |
| Impact on Society | Decline in living standards, political instability, disintegration | Improved quality of life, stronger institutions, social progress |
Understanding Decline and Amelioration
Understanding decline involves recognizing the degradation or worsening of conditions, such as economic downturns, environmental damage, or social instability. Amelioration refers to the process of improvement or mitigation of negative effects through targeted interventions like policy reforms, technological innovations, or community programs. Analyzing the indicators and drivers behind both decline and amelioration enables effective strategies for sustainable development and resilience building.
Historical Perspectives on Decline
Historical perspectives on decline emphasize the interpretation of societal, economic, and political deteriorations over time, often linked to the fall of empires such as Rome or the Ming dynasty. Scholars analyze factors including resource depletion, internal corruption, external invasions, and technological stagnation to explain these downturns. Understanding decline involves examining complex cause-effect relationships within the broader context of cultural and institutional shifts.
Key Drivers of Amelioration
Key drivers of amelioration include effective policy implementation, technological innovation, and community engagement, which collectively enhance environmental quality and social well-being. Economic incentives such as subsidies and grants promote sustainable practices that reduce pollution and resource depletion. Public awareness campaigns and education initiatives empower individuals to adopt eco-friendly behaviors, accelerating the positive trend toward environmental restoration.
Societal Impacts of Decline
Societal impacts of decline encompass reduced economic productivity, increased unemployment rates, and deterioration of public health systems. Social cohesion weakens as communities face rising poverty, crime, and educational disparities. Infrastructure degradation and diminishing government resources further exacerbate inequality and hinder sustainable development.
Measuring Progress and Regression
Measuring progress and regression involves quantifying the degree of decline versus amelioration in specific contexts such as health, environmental quality, or social development. Key metrics include statistical indicators like rate of recovery, percentage improvement, or frequency of relapse, enabling precise assessment of positive or negative trends. Accurate data collection and analysis tools enhance the ability to track changes over time, facilitating informed decision-making for interventions and policy adjustments.
Factors Influencing Amelioration
Factors influencing amelioration include favorable environmental conditions, effective intervention strategies, and robust support systems that promote recovery and improvement. Positive genetic predispositions and adaptive behaviors also play significant roles in enhancing the amelioration process. Socioeconomic resources and access to healthcare are critical in accelerating functional gains and overall well-being.
Case Studies: Decline vs Amelioration
Case studies analyzing decline versus amelioration reveal critical insights into urban development, public health, and environmental management. For example, Detroit's economic decline highlights systemic challenges in industrial shifts and population loss, while revitalization efforts in Pittsburgh demonstrate successful amelioration through economic diversification and infrastructure investment. Comparative analysis of these cases underscores the role of policy intervention, community engagement, and adaptive strategies in reversing decline and promoting sustainable improvement.
Psychological Effects of Decline
Psychological effects of decline often include increased feelings of helplessness, anxiety, and depression due to perceived loss of control and diminished capacity. Cognitive decline can lead to reduced self-esteem and social withdrawal, further exacerbating mental health challenges. Early intervention and support are critical in mitigating the psychological impact of decline and promoting resilience.
Strategies for Fostering Amelioration
Strategies for fostering amelioration involve targeted interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, which enhances adaptive coping mechanisms and promotes mental resilience. Implementing community support programs and skill development workshops addresses environmental factors contributing to decline, thereby facilitating recovery and growth. Regular assessment and personalized treatment plans optimize outcomes by tailoring approaches to individual needs.
Future Outlook: Navigating Between Decline and Amelioration
Future outlook scenarios in economic and environmental models emphasize key indicators signaling either decline or amelioration. Strategic policy-making and innovation in sustainable technologies play pivotal roles in shifting trajectories toward amelioration, mitigating risks associated with decline. Monitoring data trends in resource consumption, emission levels, and social resilience informs adaptive measures designed to secure long-term stability and growth.
Decline Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com