Naturalism explores the belief that everything arises from natural causes and laws, rejecting supernatural explanations. This philosophy deeply influences literature, art, and science by focusing on realistic depiction and the environment's impact on human behavior. Discover how Naturalism shapes our understanding of the world and influences various fields in the full article.
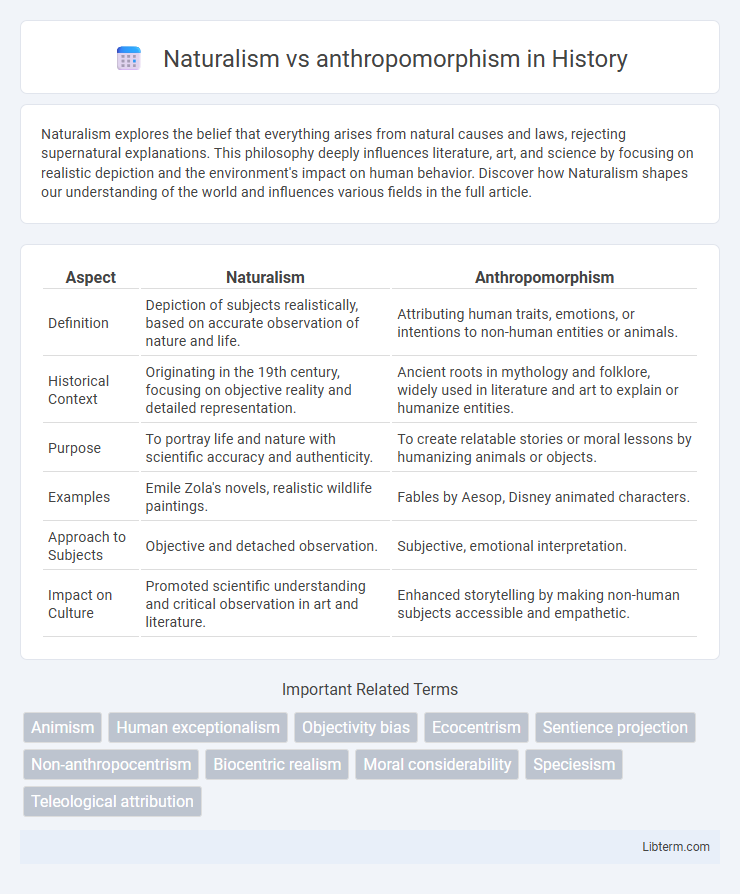
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Naturalism | Anthropomorphism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Depiction of subjects realistically, based on accurate observation of nature and life. | Attributing human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities or animals. |
| Historical Context | Originating in the 19th century, focusing on objective reality and detailed representation. | Ancient roots in mythology and folklore, widely used in literature and art to explain or humanize entities. |
| Purpose | To portray life and nature with scientific accuracy and authenticity. | To create relatable stories or moral lessons by humanizing animals or objects. |
| Examples | Emile Zola's novels, realistic wildlife paintings. | Fables by Aesop, Disney animated characters. |
| Approach to Subjects | Objective and detached observation. | Subjective, emotional interpretation. |
| Impact on Culture | Promoted scientific understanding and critical observation in art and literature. | Enhanced storytelling by making non-human subjects accessible and empathetic. |
Understanding Naturalism: Definitions and Principles
Naturalism is a philosophical viewpoint asserting that everything arises from natural causes and laws without supernatural intervention, emphasizing observable phenomena and empirical evidence. It holds that human beings and animals are part of the natural world, governed by the same biological and physical processes. This principle contrasts with anthropomorphism, which attributes human characteristics to non-human entities, often distorting scientific understanding by imposing human perspectives on nature.
Anthropomorphism Explained: Human Traits in Non-Human Entities
Anthropomorphism involves attributing human traits, emotions, and intentions to non-human entities such as animals, objects, or natural phenomena, enhancing their relatability and understandability. This cognitive bias impacts literature, psychology, and robotics, where human-like characteristics aid in emotional connection and communication. Naturalism, contrastingly, emphasizes objective observation and explanation of behavior based on biological and environmental factors without human-like interpretation.
Historical Roots: From Ancient Myths to Modern Science
Naturalism, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, emphasizes understanding the world through observable phenomena and scientific inquiry, contrasting with anthropomorphism, which attributes human traits to deities and animals as seen in myths from civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt. During the Enlightenment, naturalism gained momentum with figures like Galileo and Newton, promoting empirical evidence over mythological interpretations. Modern science continues this trajectory, relying on natural laws and rejecting anthropomorphic explanations in fields such as biology and cosmology.
Naturalism in Literature and Art
Naturalism in literature and art emphasizes a realistic depiction of everyday life, focusing on accurate representation without idealization or exaggeration. It highlights environment, heredity, and social conditions as fundamental influences on human behavior, often portraying characters shaped by their surroundings and biological instincts. Unlike anthropomorphism, which attributes human traits to animals or objects, naturalism strictly observes nature and human experience without projecting human emotions or intentions onto non-human subjects.
The Psychological Appeal of Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism appeals psychologically by attributing human traits, emotions, and intentions to non-human entities, facilitating empathy and understanding. This cognitive bias helps individuals relate to animals, objects, and natural phenomena by creating familiar narratives that simplify complex or ambiguous stimuli. Naturalism, in contrast, emphasizes objective observation and avoids projecting human characteristics, aiming for an accurate representation of non-human life and reality without emotional or subjective interpretation.
Naturalism vs Anthropomorphism in Animal Studies
Naturalism in animal studies emphasizes observing and interpreting animal behavior based on biological and ecological realities without attributing human emotions or intentions. Anthropomorphism, by contrast, involves ascribing human-like traits, emotions, or motives to animals, which can distort scientific understanding and lead to biased conclusions. Rigorous animal research prioritizes naturalistic approaches to maintain objectivity, improve species-specific insights, and foster ethical treatment grounded in factual animal behavior.
Impact on Environmental Ethics and Conservation
Naturalism emphasizes understanding ecosystems through objective scientific observation, fostering environmental ethics rooted in preserving biodiversity and ecological balance. Anthropomorphism assigns human traits to nature, which can enhance empathy and public support for conservation but risks oversimplifying complex ecological processes. Balancing both approaches can improve conservation strategies by combining scientific rigor with emotional engagement, promoting sustainable environmental stewardship.
Cultural Perspectives: East vs West
Naturalism in Eastern cultures often emphasizes harmony with nature, reflecting philosophical traditions like Taoism and Shinto that view humans as integral parts of the natural world, while Western perspectives tend to separate humans from nature, leading to anthropomorphic interpretations where animals and natural forces are imbued with human traits. In the West, anthropomorphism is frequently used in literature and art to make nature relatable and to assert human dominance or moral lessons, whereas Eastern cultures tend to avoid overt humanization of natural elements, focusing instead on symbolic and holistic relationships. These differing cultural perspectives influence environmental ethics, storytelling, and the representation of nature in media across East and West.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Naturalism faces criticism for neglecting the subjective and symbolic qualities of human experience, often reducing complex phenomena to purely physical explanations. Anthropomorphism is challenged for projecting human traits onto non-human entities, leading to misinterpretations and anthropocentric bias in scientific observations. Both approaches struggle with balancing empirical accuracy and meaningful representation, complicating the interpretation of animal behavior, environmental processes, and cultural narratives.
Which Perspective Shapes Our Worldview?
Naturalism emphasizes understanding the world through observable phenomena and scientific explanation, shaping a worldview grounded in empirical evidence and material reality. Anthropomorphism attributes human traits and emotions to animals or objects, influencing perception by projecting human experiences onto non-human entities. The dominance of either perspective affects how individuals interpret nature, ethics, and their relationship with the environment.
Naturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com