The Emirate system, rooted in historical governance, blends traditional leadership with modern administrative roles to manage regions effectively. Rich cultural heritage and economic development characterize each Emirate, influencing your business and travel experiences significantly. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Emirate dynamics shape regional growth and opportunities.
Table of Comparison
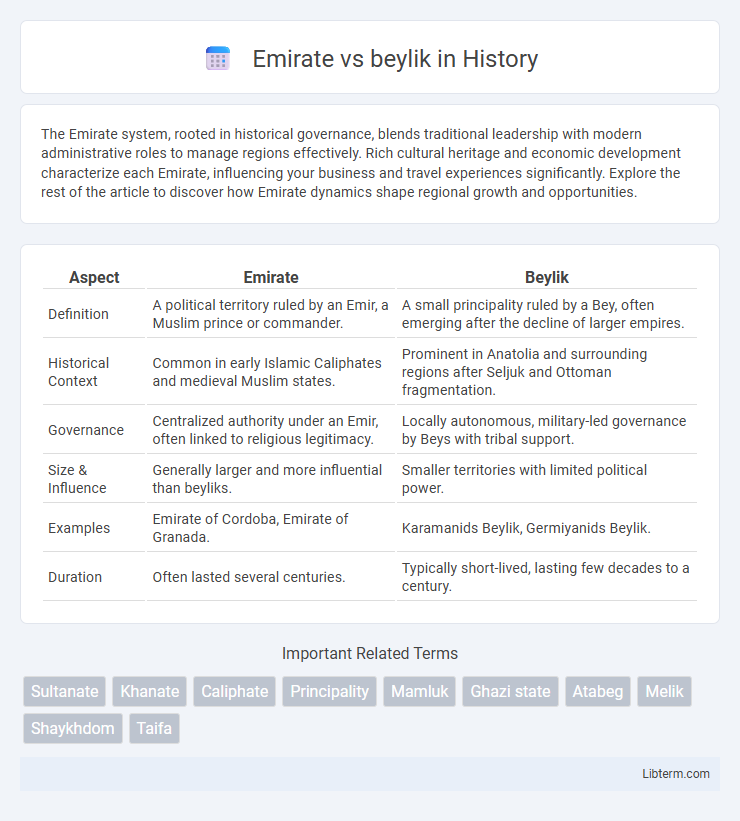
| Aspect | Emirate | Beylik |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A political territory ruled by an Emir, a Muslim prince or commander. | A small principality ruled by a Bey, often emerging after the decline of larger empires. |
| Historical Context | Common in early Islamic Caliphates and medieval Muslim states. | Prominent in Anatolia and surrounding regions after Seljuk and Ottoman fragmentation. |
| Governance | Centralized authority under an Emir, often linked to religious legitimacy. | Locally autonomous, military-led governance by Beys with tribal support. |
| Size & Influence | Generally larger and more influential than beyliks. | Smaller territories with limited political power. |
| Examples | Emirate of Cordoba, Emirate of Granada. | Karamanids Beylik, Germiyanids Beylik. |
| Duration | Often lasted several centuries. | Typically short-lived, lasting few decades to a century. |
Overview: Emirate vs Beylik
An emirate is a political territory ruled by an emir, typically signifying a Muslim principality with centralized authority and often hereditary leadership. A beylik, in contrast, refers to a smaller Turkish emirate or principality, especially prevalent in Anatolia during the medieval Seljuk and Ottoman periods, characterized by more localized governance and tribal affiliations. Both entities reflect Islamic governance structures but differ mainly in size, scope, and historical context within the Muslim world.
Historical Origins of Emirates and Beyliks
Emirates and beyliks both originated during the medieval Islamic period but differ in governance and territorial control. Emirates were typically ruled by emirs, who held sovereign authority often recognized by larger caliphates, such as the Umayyad or Abbasid dynasties, governing defined regions with administrative and military power. Beyliks emerged primarily in Anatolia and the Balkans after the decline of the Seljuk Empire, governed by beys who exercised localized control, often establishing independent or semi-independent principalities.
Key Differences in Governance Structure
Emirates are typically governed by a hereditary emir who wields centralized authority over a defined territory, often with formalized administrative institutions and diplomatic recognition. Beyliks, by contrast, are smaller principalities led by a bey, whose power may be more localized and less institutionalized, often operating within larger imperial frameworks such as the Ottoman Empire. Governance in emirates tends to be more hierarchical and stable, while beyliks exhibit greater variability in autonomy and administrative complexity.
Geographic Influence and Expansion
Emirates and beyliks both played significant roles in medieval territorial governance, with emirates often controlling larger, strategically important regions characterized by urban centers and vital trade routes. Beyliks typically emerged as smaller, more localized principalities with influence concentrated in rural or frontier areas, facilitating gradual regional expansion through military campaigns and alliances. The geographic influence of emirates frequently encompassed diverse landscapes and multicultural populations, whereas beyliks adapted to specific local conditions, enabling nimble and targeted territorial growth.
Social Organization and Class Systems
Emirates typically featured centralized rule under an emir, with a hierarchical social organization heavily influenced by Islamic law and tribal affiliations, where ruling elites and military commanders held significant power over commoners and slaves. Beyliks, often smaller and semi-autonomous principalities, exhibited more flexible social structures that integrated local customs and tribal networks, allowing diverse classes such as artisans, merchants, and tribal leaders to play key roles. Both systems emphasized the distinction between ruling elites and subordinate classes, but beyliks showed more fluidity in social mobility due to their regional autonomy and economic diversity.
Military Structure and Strategies
Emirates typically featured highly centralized military structures led by emirs who commanded elite cavalry units and employed intricate siege tactics reflecting their control over vast territories. Beyliks operated smaller, more flexible forces often relying on local militias and skilled archers, emphasizing guerrilla warfare and rapid, strategic raids to defend their limited domains. The military strategies of emirates favored large-scale, organized campaigns, while beyliks adapted to asymmetric warfare to maximize their resources and maintain regional influence.
Role in Islamic and Regional Politics
An emirate, typically governed by an emir, functions as a sovereign political entity with established authority over a defined territory, playing a significant role in Islamic governance and regional politics through centralized administration and military leadership. In contrast, a beylik, often led by a bey, usually represents a smaller principality or tribal domain with more localized influence, impacting regional politics through alliances, control of trade routes, and military campaigns within the broader Islamic framework. Both entities contributed to the political fragmentation and dynamism of the Muslim world, shaping the balance of power between central caliphates and emerging local authorities.
Economic Foundations and Trade
Emirates and beyliks historically differed in their economic foundations, where emirates often controlled key trade routes and urban centers facilitating large-scale commerce and tax collection. Beyliks typically relied on localized economies based on agriculture, small-scale crafts, and limited trade activities within their territories. These distinctions shaped their economic power, with emirates engaging in extensive trade networks connecting regions, while beyliks maintained more self-sufficient and regionally focused economies.
Cultural Contributions and Legacies
Emirates and beyliks both played significant roles in shaping regional cultures through their patronage of arts, architecture, and literature, with emirates often establishing grand mosques, libraries, and educational institutions that became cultural hubs. Beyliks contributed to the preservation and promotion of local traditions and crafted unique artistic expressions, blending Turkic, Persian, and Islamic influences. The legacies of emirates are visible in monumental structures and urban development, while beyliks left a lasting impact through folk arts, regional governance models, and the nurturing of localized cultural identities.
Decline and Transformation Over Time
Emirates often experienced decline due to centralized authority weakening under external pressures and internal fragmentation, leading to loss of control and territorial reduction. Beyliks, smaller and more flexible political units, frequently transformed by adapting to local dynamics and integrating with emerging empires such as the Ottoman Empire, which absorbed many beyliks through conquest or alliance. Over time, this process facilitated the transition from fragmented emirate rule to more structured provincial governance within larger imperial frameworks.
Emirate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com