Chisels are versatile hand tools used for carving or cutting hard materials such as wood, stone, or metal with precision and control. Each chisel features a sharp blade and a sturdy handle designed to withstand force, making it essential for craftsmanship and detailed work. Discover how choosing the right chisel can enhance your projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
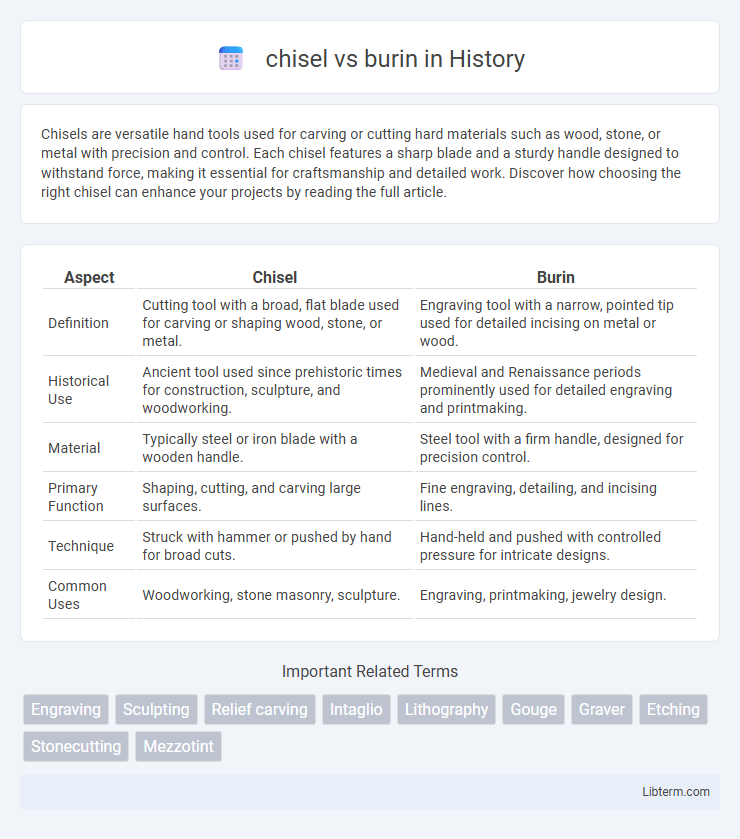
| Aspect | Chisel | Burin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cutting tool with a broad, flat blade used for carving or shaping wood, stone, or metal. | Engraving tool with a narrow, pointed tip used for detailed incising on metal or wood. |
| Historical Use | Ancient tool used since prehistoric times for construction, sculpture, and woodworking. | Medieval and Renaissance periods prominently used for detailed engraving and printmaking. |
| Material | Typically steel or iron blade with a wooden handle. | Steel tool with a firm handle, designed for precision control. |
| Primary Function | Shaping, cutting, and carving large surfaces. | Fine engraving, detailing, and incising lines. |
| Technique | Struck with hammer or pushed by hand for broad cuts. | Hand-held and pushed with controlled pressure for intricate designs. |
| Common Uses | Woodworking, stone masonry, sculpture. | Engraving, printmaking, jewelry design. |
Introduction to Chisel and Burin
A chisel is a versatile hand tool with a sharp metal blade used for carving or cutting hard materials like wood, stone, or metal, commonly employed in woodworking and sculpture. A burin, also known as a graver, is a specialized engraving tool with a hardened steel tip designed for precision incisions on metal or wood surfaces, predominantly used in printmaking and fine metalwork. Both tools enable detailed craftsmanship but differ significantly in shape, purpose, and technique.
Historical Origins and Development
Chisels and burins both trace their origins to ancient toolmaking, with chisels emerging during the Neolithic period as essential implements for woodworking and stone carving. Burins, distinguished by their fine, pointed tips, originated in the Upper Paleolithic era, primarily developed for detailed engraving on bone, antler, and ivory. The evolution of these tools reflects specialized adaptations in craftsmanship, where chisels enabled broader shaping and burins facilitated precise incisions in artistic and functional artifacts.
Key Differences in Design
Chisels feature a flat or beveled cutting edge designed for versatility in woodworking, whereas burins possess a sharp, pointed tip engineered for precise engraving and fine detail work. The bevel angle of a chisel typically ranges between 25 to 30 degrees, optimizing it for controlled material removal, while burins have a more acute angle to enable intricate line work on metal or wood surfaces. Handle design also contrasts, with chisels often having a longer, straight grip for forceful strikes and burins equipped with ergonomic handles to facilitate delicate hand movements.
Materials and Construction
Chisels are typically crafted from hardened steel with a beveled edge designed for cutting and shaping a variety of materials like wood, stone, and metal. Burins, often made from carbon steel or tool steel, feature a sharp, pointed tip ideal for intricate engraving on metals and wood. The construction of chisels emphasizes durability and edge retention, while burins prioritize fine control and precision engraving capabilities.
Primary Functions and Uses
Chisels are primarily designed for carving and cutting wood, stone, or metal by removing small pieces with a beveled edge, making them ideal for shaping and smoothing surfaces. Burins, also known as gravers, are specialized tools used mainly in engraving and fine detailing on metal or wood, featuring a sharp pointed tip for creating precise lines and intricate designs. The primary function of a chisel emphasizes broader material removal and shaping, while burins focus on detailed, controlled incisions and artistic embellishments.
Techniques: How to Use Each Tool
Chisels are typically used by applying controlled mallet strikes to carve or shape wood, stone, or metal, allowing for rough shaping or detailed work depending on the blade size and angle. Burins, on the other hand, are primarily employed in engraving and intaglio techniques, where the tool is pushed or pulled with steady hand pressure to incise fine lines and intricate details into hard materials like metal or wood. Mastery of each tool involves understanding the appropriate grip, angle, and force to achieve precision, with chisels requiring more forceful, repetitive impacts and burins relying on delicate, continuous pressure.
Advantages of Using a Chisel
Chisels offer greater versatility and control for woodworkers and sculptors due to their wider range of sizes and blade shapes compared to burins. The tool's ergonomic handle design reduces hand fatigue, enabling longer work sessions and increased precision. Chisels are also easier to sharpen and maintain, ensuring consistent performance across various materials like wood, stone, and metal.
Benefits of Using a Burin
A burin offers precise control and fine detail work ideal for engraving and delicate carving. Its sharp, narrow tip allows artists to create clean, crisp lines with greater accuracy compared to a chisel. This tool minimizes material waste and enhances the quality of intricate designs, making it essential for detailed metalwork and printmaking.
Chisel vs Burin: Which to Choose?
Chisels offer versatility with various blade widths and handle designs suited for woodworking and sculpting, making them ideal for broader cuts and shaping tasks. Burins, featuring a sharp, pointed tip and often used in engraving or fine detail work, provide precision for intricate lines on metal or wood surfaces. Choosing between a chisel and burin depends on the project's requirements: opt for chisels when removing larger material volumes and burins for detailed engraving and fine carving.
Conclusion and Expert Recommendations
Chisels provide versatility for woodworking and general carving, while burins excel in precision engraving on metal, offering finer detail control. Experts recommend selecting tools based on material and project requirements, favoring chisels for bulk shaping and burins for intricate line work. Optimal results often come from combining both tools, leveraging their unique strengths for comprehensive craftsmanship.
chisel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com