A council serves as a governing or advisory body that makes decisions and sets policies for communities, organizations, or governments. Its members collaborate to address public issues, allocate resources, and represent the interests of their constituents. Discover how your local council impacts daily life and how you can engage with its processes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
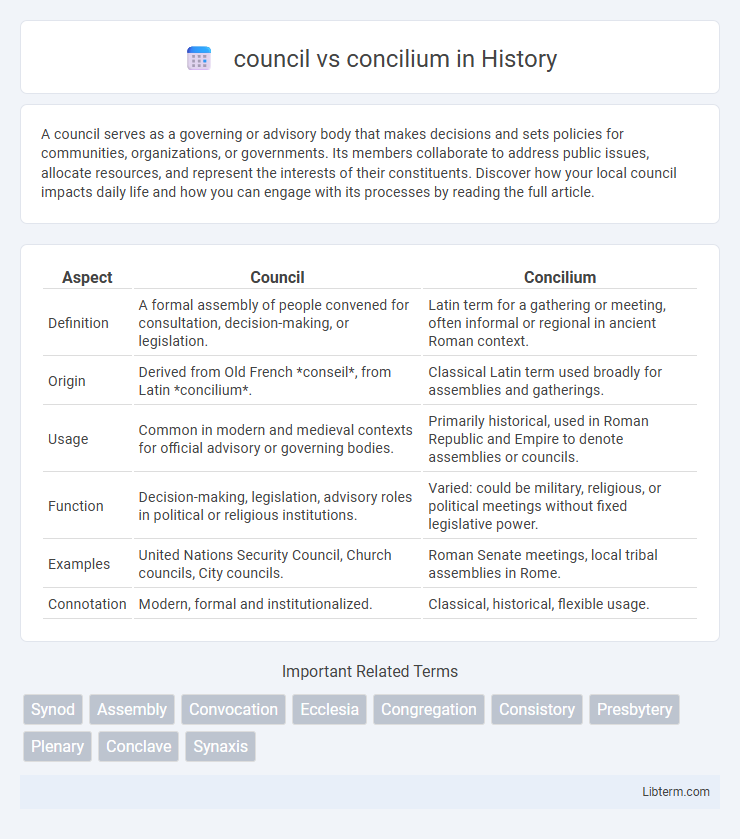
| Aspect | Council | Concilium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal assembly of people convened for consultation, decision-making, or legislation. | Latin term for a gathering or meeting, often informal or regional in ancient Roman context. |
| Origin | Derived from Old French *conseil*, from Latin *concilium*. | Classical Latin term used broadly for assemblies and gatherings. |
| Usage | Common in modern and medieval contexts for official advisory or governing bodies. | Primarily historical, used in Roman Republic and Empire to denote assemblies or councils. |
| Function | Decision-making, legislation, advisory roles in political or religious institutions. | Varied: could be military, religious, or political meetings without fixed legislative power. |
| Examples | United Nations Security Council, Church councils, City councils. | Roman Senate meetings, local tribal assemblies in Rome. |
| Connotation | Modern, formal and institutionalized. | Classical, historical, flexible usage. |
Understanding the Terms: Council and Concilium
A council refers to a formally organized group of individuals convened to deliberate, make decisions, or govern specific activities, often within governmental, organizational, or community contexts. Concilium, derived from Latin, originally means a gathering or assembly for advice or consultation, and in historical or ecclesiastical contexts, it emphasizes deliberative meetings often for theological or doctrinal purposes. Understanding these terms involves recognizing council as a structured decision-making body, while concilium highlights the advisory or consultative nature of the assembly.
Historical Origins of Council and Concilium
The terms "council" and "concilium" both originate from Latin, with "concilium" referring to a formal assembly or gathering in ancient Roman society, often convened for political, religious, or military purposes. Historical records show that "concilium" was used to describe deliberative bodies in Roman governance and ecclesiastical contexts, laying the foundation for the medieval church councils known simply as "councils." The evolution from "concilium" to "council" reflects the adaptation of Roman institutional practices into Christian and later secular European political structures.
Linguistic Differences Between Council and Concilium
The term "council" originates from the Latin word "concilium," but in modern English, "council" typically refers to an assembly or advisory group within a civic or organizational context, whereas "concilium" is a Latin noun used primarily in historical or ecclesiastical settings. Linguistically, "council" has evolved with adaptations in pronunciation and spelling to fit English phonology, while "concilium" retains its classical Latin form and declension patterns. The semantic shift reflects cultural and institutional usage differences, with "council" signifying a formal committee or governing body and "concilium" often denoting a wider assembly or gathering, especially in religious or academic discourse.
Usage in Religious Contexts
The terms "council" and "concilium" both refer to assemblies or gatherings, but "concilium" is the Latin root often used historically in ecclesiastical settings to denote formal church meetings such as the early ecumenical councils. In religious contexts, "council" is the preferred English term for official synods or assemblies, like the Council of Nicaea, shaping doctrine and church discipline. The semantic distinction highlights "concilium" as the source term, while "council" captures the practical, ongoing institutional functions within Christianity.
Council vs Concilium in Government and Politics
In government and politics, "Council" typically refers to a formal assembly of elected or appointed officials who deliberate and make decisions on administrative, legislative, or advisory matters within a specific jurisdiction. "Concilium," a Latin term, historically denotes a gathering or meeting, often with a broader or more informal connotation, used in contexts ranging from Roman political assemblies to ecclesiastical synods. Modern usage favors "Council" for official governmental bodies, emphasizing structured governance and decision-making processes.
Key Functions and Purposes
A council typically functions as a governing or advisory body responsible for making decisions, setting policies, and overseeing administrative matters within political, organizational, or community contexts. Concilium, often used in historical or ecclesiastical settings, refers to a formal assembly convened primarily for deliberation, doctrinal decisions, and resolving conflicts or disputes within religious or institutional frameworks. Both serve key purposes of collective decision-making and governance, but councils emphasize ongoing administration, while concilium focuses on formal consensus and authoritative rulings.
Examples of Famous Councils and Conciliums
The Council of Trent (1545-1563) stands as a prominent example of a council, where Catholic Church leaders addressed Reformation challenges and clarified doctrines. The First Council of Nicaea (325 AD), a famous concilium, established foundational Christian beliefs like the Nicene Creed. Both councils and conciliums serve pivotal roles in doctrinal decisions and ecclesiastical governance, shaping religious history through collective deliberation.
Council vs Concilium: Regional Preferences
Council is predominantly used in English-speaking countries, especially in the United Kingdom, United States, and Commonwealth nations, reflecting formal assemblies or governing bodies. Concilium, derived from Latin, is more common in European regions with Romance languages, such as Italy and Spain, where it retains historical and ecclesiastical connotations. Regional preferences highlight council's widespread administrative application, while concilium is often reserved for scholarly or religious contexts within Latin-influenced cultures.
Modern-Day Relevance and Application
Council refers to a formal assembly or advisory group often used in contemporary governance, local government, and organizational decision-making processes, emphasizing structured debate and policy formulation. Concilium, derived from Latin, historically signifies a broader assembly or gathering with deliberative functions, now primarily referenced in ecclesiastical or academic contexts to denote authoritative meetings or synods. Modern-day applications of council dominate civic administration and corporate governance, while concilium maintains specialized usage in religious and scholarly discussions, reflecting its traditional and formal connotations.
Choosing the Right Term: Council or Concilium?
Choosing the right term between "council" and "concilium" depends on the context and the audience's familiarity with Latin or formal ecclesiastical language. "Council" is the standard English term used broadly for assemblies or deliberative bodies in governmental, organizational, or religious contexts. "Concilium," derived directly from Latin, is typically reserved for specific historical or ecclesiastical references, especially in Roman Catholic contexts, emphasizing formal church gatherings or synods.
council Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com