Urbanization transforms rural landscapes into bustling cities, driving economic growth and innovation while posing challenges like overcrowding and resource strain. Efficient urban planning and sustainable development are essential to manage these impacts and improve quality of life. Explore the rest of the article to discover how urbanization shapes our future and what it means for your community.
Table of Comparison
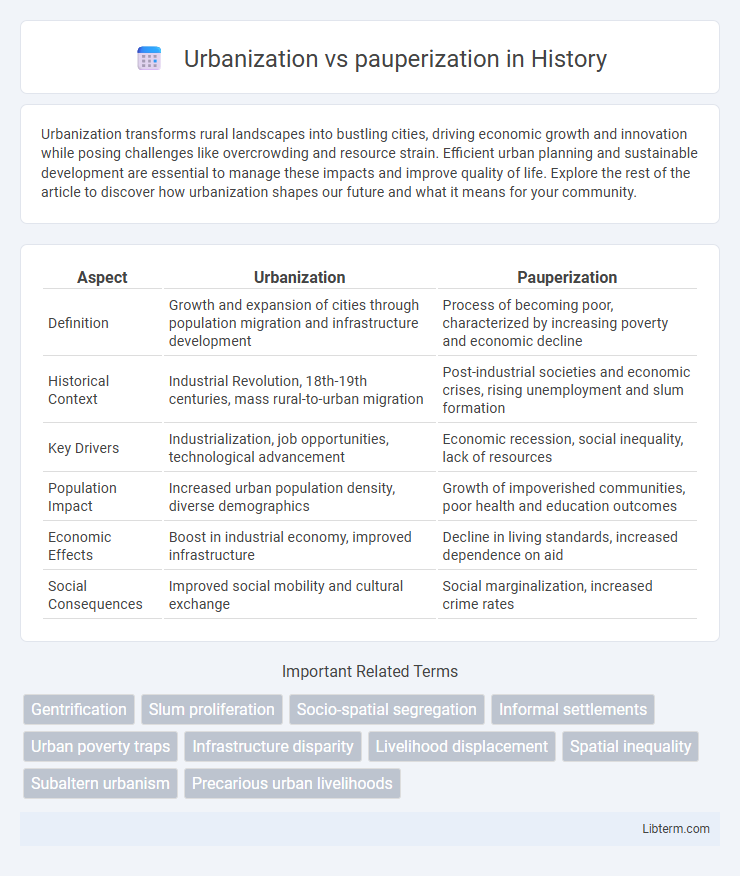
| Aspect | Urbanization | Pauperization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growth and expansion of cities through population migration and infrastructure development | Process of becoming poor, characterized by increasing poverty and economic decline |
| Historical Context | Industrial Revolution, 18th-19th centuries, mass rural-to-urban migration | Post-industrial societies and economic crises, rising unemployment and slum formation |
| Key Drivers | Industrialization, job opportunities, technological advancement | Economic recession, social inequality, lack of resources |
| Population Impact | Increased urban population density, diverse demographics | Growth of impoverished communities, poor health and education outcomes |
| Economic Effects | Boost in industrial economy, improved infrastructure | Decline in living standards, increased dependence on aid |
| Social Consequences | Improved social mobility and cultural exchange | Social marginalization, increased crime rates |
Understanding Urbanization: Definitions and Dynamics
Urbanization refers to the increasing concentration of populations in urban areas, driven by factors such as industrialization, economic opportunities, and improved infrastructure. This process often leads to the expansion of cities and changes in land use, social structures, and economic activities. However, urbanization can sometimes exacerbate pauperization, where rapid city growth outpaces resource availability, resulting in increased poverty, inadequate housing, and strained public services.
The Historical Context of Urban Growth
The rapid urbanization during the Industrial Revolution transformed rural societies into sprawling metropolitan centers, intensifying the dynamics of pauperization as vast numbers of laborers migrated in search of work but often faced inadequate housing and poor sanitation. The historical context reveals how the unchecked urban growth outpaced infrastructure development, exacerbating poverty and social inequalities in burgeoning cities. This phenomenon was particularly pronounced in 19th-century Europe, where industrial hubs like Manchester and London exemplified the dual forces of urban expansion and increased pauperization.
Pauperization: Unraveling the Concept
Pauperization refers to the process of becoming impoverished, often characterized by a decline in living standards, limited access to resources, and social exclusion. It frequently emerges in urban settings where rapid urbanization outpaces economic opportunities, leading to the proliferation of slums and informal settlements. Understanding pauperization is crucial for addressing urban poverty and implementing effective social policies to improve socioeconomic conditions.
How Urbanization Drives Socioeconomic Disparities
Rapid urbanization intensifies socioeconomic disparities by concentrating wealth and resources in metropolitan hubs while marginalizing low-income populations to informal settlements with inadequate access to education, healthcare, and employment. The influx of rural migrants into cities often leads to overcrowded slums, exacerbating poverty and limiting upward mobility despite economic growth. Urban infrastructure development typically favors affluent districts, reinforcing spatial segregation and perpetuating cycles of pauperization among vulnerable communities.
Urban Migration: Opportunity or Pathway to Pauperization?
Urban migration often presents a complex interplay between opportunity and pauperization, as millions of rural inhabitants move to cities seeking better employment and improved living standards. Rapid urbanization frequently outpaces infrastructure development, leading to the growth of informal settlements with inadequate housing, sanitation, and access to essential services. This dynamic can trap migrants in cycles of poverty, highlighting the critical need for inclusive urban planning and social policies that transform migration into genuine economic and social mobility opportunities.
Infrastructure Challenges Amid Rapid Urbanization
Rapid urbanization often outpaces the development of essential infrastructure, leading to significant challenges in housing, transportation, and sanitation systems. Insufficient infrastructure investment results in overcrowded slums, limited access to clean water, and inadequate public services, exacerbating pauperization among urban populations. Addressing infrastructure deficits through sustainable urban planning and integrated development policies is critical to mitigating poverty and promoting equitable growth.
The Role of Policy in Mitigating Pauperization
Effective urban policies play a crucial role in mitigating pauperization by promoting inclusive economic growth and improving access to affordable housing, education, and healthcare in rapidly urbanizing areas. Strategic investments in social infrastructure and targeted poverty alleviation programs reduce disparities caused by urban migration, preventing the concentration of poverty in slums and informal settlements. Enforcing land-use regulations and supporting sustainable development initiatives enhance urban resilience, ensuring equitable opportunities for all residents amidst ongoing urbanization.
Case Studies: Global Cities Facing Urbanization and Pauperization
Global cities such as Mumbai, Rio de Janeiro, and Johannesburg exemplify the intertwined challenges of urbanization and pauperization, where rapid population growth strains infrastructure and intensifies socio-economic disparities. Case studies reveal how informal settlements expand due to insufficient affordable housing, catalyzing pockets of extreme poverty alongside urban development. Urban policy frameworks in these cities emphasize the importance of integrated approaches to address housing deficits, improve public services, and foster inclusive economic opportunities to mitigate pauperization.
Sustainable Urban Planning to Combat Social Inequality
Sustainable urban planning integrates affordable housing, green spaces, and efficient public transportation to mitigate the effects of pauperization amid rapid urbanization. Implementing mixed-use developments and promoting inclusive economic opportunities can reduce social inequality by fostering community resilience and access to essential services. Emphasizing participatory governance ensures marginalized populations contribute to urban policies, enhancing equity and long-term sustainability.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Urban Growth and Social Equity
Rapid urbanization in developing cities often exacerbates pauperization, intensifying poverty and social exclusion in informal settlements. Future urban planning must integrate sustainable development strategies and inclusive policies to promote equitable access to housing, education, and employment opportunities. Leveraging smart city technologies and community-based initiatives can enhance resource distribution and foster resilience among vulnerable populations, ensuring balanced urban growth aligned with social equity goals.
Urbanization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com