Carceratus is a genus of diverse wasps known for their unique parasitic behavior targeting other insects. Their ecological role in controlling pest populations makes them essential to maintaining a balanced environment. Discover more about Carceratus and how your understanding of these fascinating wasps can enhance natural pest management in the article ahead.
Table of Comparison
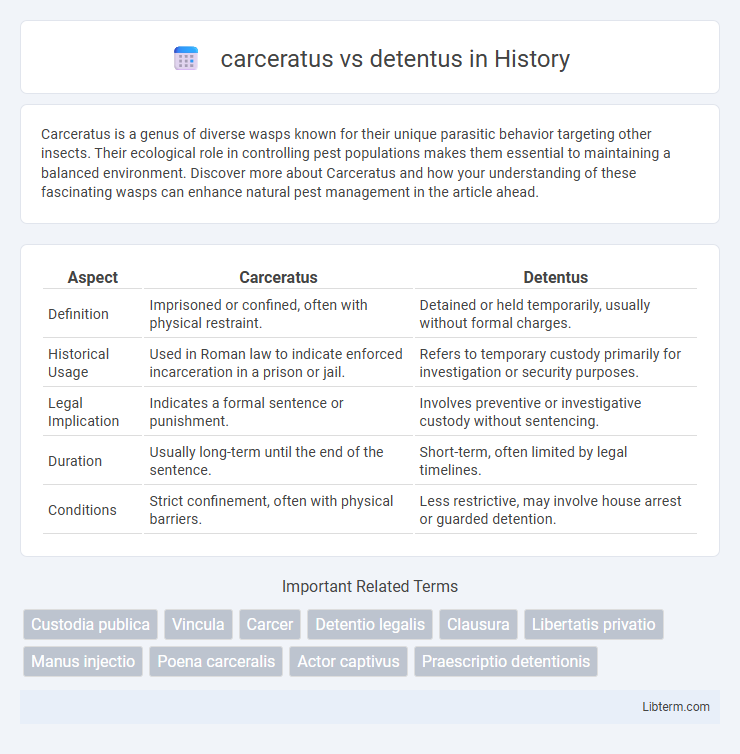
| Aspect | Carceratus | Detentus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Imprisoned or confined, often with physical restraint. | Detained or held temporarily, usually without formal charges. |
| Historical Usage | Used in Roman law to indicate enforced incarceration in a prison or jail. | Refers to temporary custody primarily for investigation or security purposes. |
| Legal Implication | Indicates a formal sentence or punishment. | Involves preventive or investigative custody without sentencing. |
| Duration | Usually long-term until the end of the sentence. | Short-term, often limited by legal timelines. |
| Conditions | Strict confinement, often with physical barriers. | Less restrictive, may involve house arrest or guarded detention. |
Introduction: Understanding Carceratus vs Detentus
Carceratus and Detentus are distinct legal terms referring to different forms of imprisonment or detention under the law. Carceratus typically implies formal incarceration within a prison or correctional facility, emphasizing punitive confinement following a legal judgment. Detentus generally denotes a broader concept of detention, which may include temporary holding or custodial measures before trial or without formal sentencing.
Etymology and Historical Background
Carceratus derives from the Latin word "carcer," meaning prison or enclosure, signifying a state of being imprisoned or confined. Detentus originates from "detinere," which means to hold back or restrain, emphasizing the act of detention or temporary confinement. Historically, carceratus referred to formal imprisonment in a prison structure, while detentus indicated a broader scope of restraint, including military or civil custody without formal incarceration.
Legal Definitions: Carceratus Explained
Carceratus refers to a person legally imprisoned or detained as a result of a formal judicial process, emphasizing lawful custody based on a court order or legal mandate. In contrast, detentus generally denotes an individual held in custody without formal charges or a clear legal basis, often implying temporary or extrajudicial detention. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for legal contexts involving rights, due process, and the legitimacy of confinement.
Legal Definitions: Detentus Explained
Detentus refers to a person who is held in custody without formal arrest or criminal charges, often in administrative or civil contexts. Unlike carceratus, which denotes imprisonment following legal conviction, detentus status typically involves restraint based on security or preventive detention grounds. Legal frameworks distinguish detentus to emphasize temporary or non-penal custody, ensuring specific procedural safeguards and review mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Carceratus and Detentus
Carceratus and detentus both refer to forms of deprivation of liberty, but carceratus implies confinement in a prison or jail, emphasizing physical incarceration. Detentus denotes being held or detained, which can occur in various settings beyond prisons, such as police custody or administrative detention. The key difference lies in carceratus's focus on penal imprisonment versus detentus's broader application to temporary or preventative holding measures.
Usage in Modern Legal Systems
Carceratus and detentus represent distinct legal concepts related to custody in modern legal systems, where carceratus typically refers to imprisonment following a legal sentence, emphasizing long-term or formal incarceration, while detentus denotes temporary or administrative detention often used in pre-trial contexts. Modern jurisprudence differentiates these terms to clarify the rights and procedural guarantees afforded to individuals, with detentus often subjected to stricter temporal limits and oversight to prevent unlawful deprivation of liberty. The clear legal distinction impacts case law, prison administration, and human rights considerations, particularly in ensuring compliance with constitutional protections against arbitrary detention.
Implications for Prisoners’ Rights
Carceratus and detentus represent distinct legal statuses with significant implications for prisoners' rights, particularly concerning due process and conditions of confinement. Carceratus typically refers to incarceration following a formal conviction, granting prisoners specific legal protections and access to rehabilitation programs, whereas detentus often denotes detention without trial, limiting access to legal recourse and increasing vulnerability to human rights abuses. Understanding these differences is crucial for advocating fair treatment and ensuring compliance with international human rights standards in correctional institutions.
Jurisprudence: Landmark Cases Involving Carceratus and Detentus
Landmark jurisprudence cases involving carceratus and detentus have shaped the legal distinctions between wrongful imprisonment and unlawful detention based on intent and circumstances. The case of *Foster v. State* established critical parameters distinguishing carceratus, where physical restraint is enforced violently or secretly, from detentus, involving lawful custody lacking proper authorization. Jurisprudential analysis in *Williams v. Commonwealth* further reinforced the necessity of mens rea in proving carceratus, whereas detentus often hinges on procedural errors or jurisdictional deficiencies impacting the legality of detention.
Comparative Analysis Across Jurisdictions
Carceratus and detentus represent distinct legal concepts primarily relating to forms of custody, with carceratus typically referring to imprisonment within penal institutions, whereas detentus encompasses various forms of lawful detention including administrative holds. Comparative analysis across jurisdictions reveals that civil law systems rigidly define carceratus through codified statutes emphasizing punitive confinement, while common law jurisdictions adopt broader interpretations of detentus incorporating preventive measures like bail or house arrest. Variations also exist in procedural safeguards, duration limits, and rights afforded to individuals under each category, reflecting divergent legal traditions and human rights frameworks.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Relevance of Carceratus vs Detentus
The distinction between carceratus and detentus continues to hold critical importance in modern legal systems, shaping the definitions of lawful imprisonment and personal liberty. Clarifying these terms ensures precise judicial outcomes and protects individual rights against unlawful confinement. Ongoing legal debates emphasize the necessity of distinguishing carceratus as formal imprisonment and detentus as restraint without full incarceration for accurate application of human rights standards.
carceratus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com