A diplomat plays a crucial role in fostering international relations and resolving conflicts through negotiation and dialogue. Skilled in communication and cultural understanding, diplomats work to safeguard their country's interests while promoting global cooperation. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how diplomacy shapes our world and impacts your daily life.
Table of Comparison
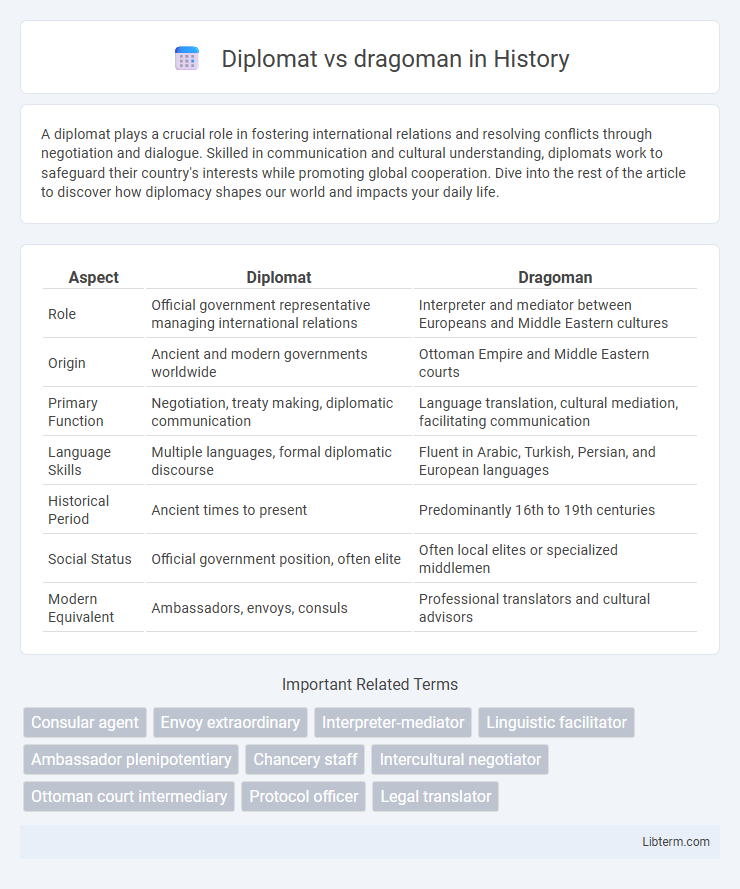
| Aspect | Diplomat | Dragoman |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Official government representative managing international relations | Interpreter and mediator between Europeans and Middle Eastern cultures |
| Origin | Ancient and modern governments worldwide | Ottoman Empire and Middle Eastern courts |
| Primary Function | Negotiation, treaty making, diplomatic communication | Language translation, cultural mediation, facilitating communication |
| Language Skills | Multiple languages, formal diplomatic discourse | Fluent in Arabic, Turkish, Persian, and European languages |
| Historical Period | Ancient times to present | Predominantly 16th to 19th centuries |
| Social Status | Official government position, often elite | Often local elites or specialized middlemen |
| Modern Equivalent | Ambassadors, envoys, consuls | Professional translators and cultural advisors |
Introduction: Diplomat vs Dragoman
Diplomats are official representatives of a country responsible for managing international relations, negotiating treaties, and protecting national interests abroad. Dragomans historically served as interpreters and cultural mediators between diplomats and local populations, especially in the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East. Understanding the distinct roles of diplomats and dragomans highlights the evolution of international communication and diplomacy practices.
Historical Origins of Diplomats and Dragomans
Diplomats originated in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt, where envoys negotiated peace treaties and alliances between city-states. Dragomans emerged primarily in the Ottoman Empire as official interpreters and mediators skilled in multiple languages, facilitating communication between Ottoman officials and European diplomats. The historical roles of diplomats and dragomans highlight their distinct functions: diplomats representing sovereign states in formal negotiations, while dragomans served as linguistic and cultural intermediaries in diplomatic contexts.
Roles and Responsibilities Compared
Diplomats primarily represent their nation's interests abroad by negotiating treaties, managing political relations, and protecting citizens, often involving high-level decision-making and policy formulation. Dragomans historically served as interpreters and cultural mediators in diplomatic missions, facilitating communication between different language groups and ensuring accurate translation of documents and conversations. While diplomats undertake strategic and administrative duties, dragomans focused on linguistic expertise and regional knowledge critical to effective cross-cultural diplomacy.
Linguistic Skills: Translator or Negotiator?
Diplomats often require advanced negotiation skills paired with proficient linguistic abilities to navigate complex international relations effectively. Dragomans, historically, specialized as translators and cultural mediators, possessing deep knowledge of multiple languages and regional customs to facilitate communication between diverse groups. While both roles demand language proficiency, diplomats emphasize strategic negotiation, whereas dragomans focus primarily on accurate translation and interpretation within cross-cultural contexts.
Training and Qualifications: Then and Now
Historically, diplomats required formal education in law, languages, and international relations, while dragomans specialized in mastering multiple regional languages and cultural protocols to act as intermediaries in the Ottoman Empire. Contemporary diplomats undergo rigorous training through diplomatic academies and receive comprehensive instruction in global policy, negotiation, and foreign languages, reflecting modern international standards. Dragomans, largely obsolete today, are replaced by professional interpreters and cultural advisors with specialized language and regional expertise.
Influence on International Relations
Diplomats and dragomans both played crucial roles in shaping international relations, with diplomats engaging directly in state-to-state negotiations and policy-making. Dragomans served as indispensable intermediaries, leveraging cultural and linguistic expertise to facilitate communication between diverse parties, particularly in the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East. Their unique positions enabled smoother dialogue and conflict resolution, significantly influencing diplomatic outcomes and cross-cultural understanding during historical periods of complex geopolitical interaction.
Cultural Mediation and Representation
Diplomats primarily engage in formal political negotiations and represent their nation's interests abroad, while dragomans historically served as cultural mediators and interpreters between different linguistic and ethnic groups, facilitating communication and fostering mutual understanding. Dragomans possess deep knowledge of local customs, languages, and social nuances, essential for bridging cultural divides in diplomatic contexts. This cultural mediation role made dragomans indispensable in early international relations, contrasting with diplomats whose focus is more on official policy and state representation.
Evolution of the Professions Over Time
The roles of diplomat and dragoman evolved significantly from ancient to modern times, with diplomats shifting from primarily noble envoys to professional state representatives engaging in complex international relations. Dragomans, once essential as linguistic and cultural intermediaries in Ottoman and Middle Eastern diplomacy, gradually diminished as professional translation and diplomatic services developed. This evolution reflects broader changes in global communication, state sovereignty, and bureaucratic specialization.
Diplomat and Dragoman in Modern Context
Diplomats in the modern context serve as official representatives of their governments, engaging in negotiations, policy advocacy, and international relations to promote national interests. Dragomans, historically interpreters and intermediaries in Middle Eastern diplomacy, now are largely obsolete but their role in cultural and linguistic mediation underscores the importance of communication skills in diplomacy. Contemporary diplomacy increasingly values the specialized expertise and language proficiency once associated with dragomans to navigate complex global interactions effectively.
Conclusion: Bridging Worlds, Old and New
Diplomats and dragomans both serve as crucial intermediaries in international relations, with diplomats focusing on formal negotiations and policy-making while dragomans historically facilitated communication between cultures through translation and cultural mediation. The evolution from dragoman to diplomat highlights the shift from personalized, language-based mediation to structured diplomacy driven by state interests and international law. Bridging worlds old and new requires combining the deep cultural understanding of dragomans with the strategic expertise of diplomats to navigate today's global complexities effectively.
Diplomat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com