Pronoia holders benefit from exclusive access to unique investment opportunities within decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems, leveraging token-based governance and rewards. These holders often enjoy increased staking rewards, voting power in protocol decisions, and early participation in new projects. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can maximize the advantages of pronoia ownership in today's crypto markets.
Table of Comparison
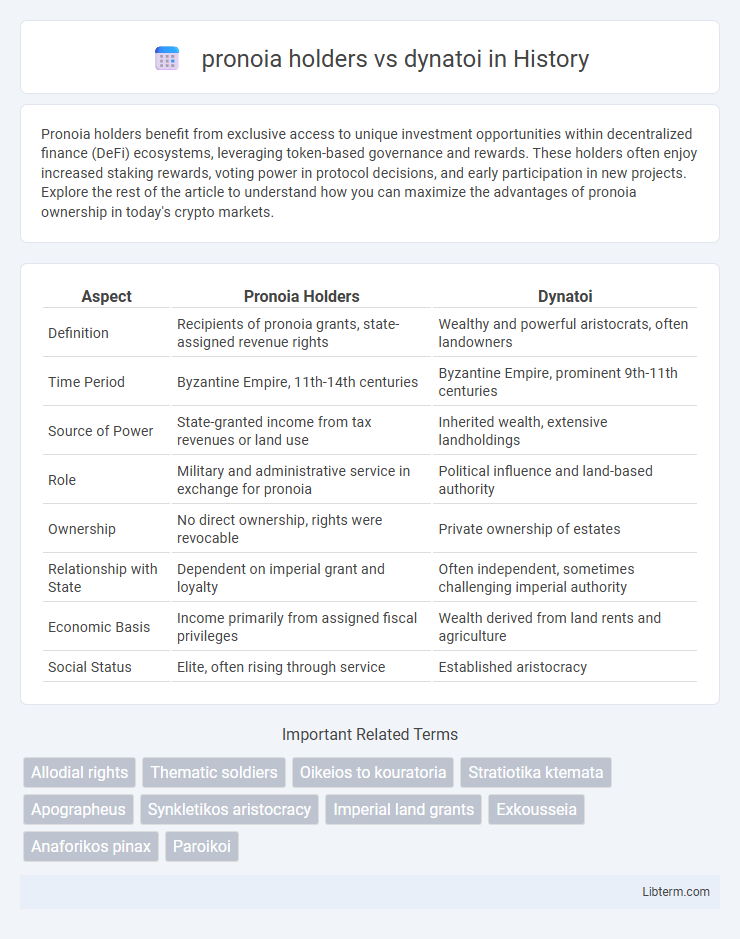
| Aspect | Pronoia Holders | Dynatoi |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recipients of pronoia grants, state-assigned revenue rights | Wealthy and powerful aristocrats, often landowners |
| Time Period | Byzantine Empire, 11th-14th centuries | Byzantine Empire, prominent 9th-11th centuries |
| Source of Power | State-granted income from tax revenues or land use | Inherited wealth, extensive landholdings |
| Role | Military and administrative service in exchange for pronoia | Political influence and land-based authority |
| Ownership | No direct ownership, rights were revocable | Private ownership of estates |
| Relationship with State | Dependent on imperial grant and loyalty | Often independent, sometimes challenging imperial authority |
| Economic Basis | Income primarily from assigned fiscal privileges | Wealth derived from land rents and agriculture |
| Social Status | Elite, often rising through service | Established aristocracy |
Defining Pronoia Holders and Dynatoi
Pronoia holders were Byzantine landowners granted estates by the emperor in exchange for military or administrative services, often compensated through tax revenues from the land rather than direct ownership. Dynatoi referred to the powerful aristocratic families in the Byzantine Empire who accumulated significant wealth and influence, often through inherited landholdings and high-ranking positions within the imperial administration. The distinction lies in pronoia holders having conditional, service-based rights to land, while dynatoi represented entrenched hereditary elites controlling extensive properties and political power.
Historical Origins of Pronoia and Dynatoi
Pronoia holders emerged during the Byzantine Empire as recipients of land grants in exchange for military or administrative service, institutionalizing a mutually beneficial relationship between the central government and local elites. Dynatoi, meaning "powerful ones," referred to wealthy landowners and aristocrats who often leveraged their influence to amass significant estates, challenging imperial authority. The historical origins of pronoia and dynatoi reveal a shift from centralized control to a more decentralized land tenure system, impacting socio-political dynamics in medieval Byzantium.
Roles in Byzantine Society and Administration
Pronoia holders were granted land or revenue rights by the Byzantine state in exchange for military service, forming a key component of the military-administrative system that supported provincial governance. Dynatoi represented the wealthiest and most influential aristocrats who often controlled large estates and held high-ranking administrative or military offices, exerting significant power within both local and imperial hierarchies. The interplay between pronoia holders and dynatoi shaped the balance of authority in Byzantine society, with pronoia serving as a mechanism for the state to reward loyalty while dynatoi consolidated regional control.
Land Ownership and Economic Power
Pronoia holders were granted rights to collect taxes and manage lands by Byzantine emperors, but they did not hold full legal ownership, limiting their direct control over estates and economic resources. In contrast, dynatoi comprised powerful aristocratic families with hereditary land ownership, enabling them to consolidate vast estates and exert significant economic influence within the empire. This distinction allowed dynatoi to maintain entrenched wealth and political power, while pronoia holders served as imperial agents with conditional benefits tied to military or administrative service.
Military Obligations and Service
Pronoia holders in the Byzantine Empire were granted land in exchange for military service, requiring them to provide troops or personal combat in defense of the empire, reflecting a feudal-like system tied directly to military obligations. Dynatoi, as powerful landed aristocrats, often held large estates but sometimes evaded direct military service, leveraging their wealth and influence to fulfill obligations through hired soldiers or political maneuvering. The pronoia system created a more structured and accountable military service compared to the dynatoi, who prioritized land accumulation and social status over consistent battlefield engagement.
Political Influence and Court Relations
Pronoia holders secured significant political influence by managing military and administrative tasks under Byzantine imperial authority, contrasting with the dynatoi who wielded hereditary aristocratic power often challenging central control. The pronoia system reinforced loyalty to the emperor through granted land and revenues, fostering closer court relations and dependence on imperial favor. In contrast, dynatoi established independent power bases often competing with the imperial court for dominance, impacting the balance of political authority in Byzantium.
Social Status and Privileges
Pronoia holders in the Byzantine Empire were granted land and income by the state in exchange for military service, which elevated their social status above ordinary citizens but below the established aristocracy known as the dynatoi. The dynatoi, composed of wealthy landowners and high-ranking officials, enjoyed extensive privileges including political influence, large estates, and hereditary titles that secured their dominance in Byzantine society. While pronoia holders had temporary and conditional rights tied to their service, the dynatoi's privileges were more permanent and institutionalized, reinforcing a rigid social hierarchy.
Conflicts and Rivalries Between Groups
Pronoia holders in the Byzantine Empire often clashed with the dynatoi, the powerful landed aristocracy, over control of land and military privileges, fueling persistent conflicts throughout the 10th and 11th centuries. The dynatoi sought to consolidate estates and influence, while pronoia holders, granted land and revenue rights by the state, resisted efforts to diminish their autonomy or absorb their holdings. These rivalries destabilized provincial governance and weakened imperial authority by exacerbating factionalism between imperial appointees and entrenched local elites.
Impact on Byzantine Reforms and Policies
Pronoia holders and dynatoi played contrasting roles in Byzantine reforms, with pronoia holders often supporting imperial policies by managing land grants in exchange for military service, thus stabilizing provincial administration and revenue. Dynatoi, as powerful aristocratic families, frequently resisted central reforms, leveraging their influence to retain local control and challenge imperial authority. The tension between pronoia holders and dynatoi significantly shaped Byzantine fiscal and military policies, prompting emperors to balance decentralization with efforts to curb aristocratic dominance.
Legacy of Pronoia Holders and Dynatoi in Byzantine History
Pronoia holders in Byzantine history were granted conditional land rights tied to military or administrative service, fostering loyalty and decentralizing imperial control. Dynatoi, the powerful landed aristocrats, often expanded their hereditary estates, challenging central authority and contributing to regional power consolidation. The legacy of pronoia holders and dynatoi shaped Byzantine socio-political structures by balancing imperial governance with aristocratic influence, impacting land tenure systems and military organization.
pronoia holders Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com