Apprenticeships provide hands-on training that bridges the gap between education and real-world work experience, enabling you to develop valuable skills in a specific trade or profession. These programs often combine classroom instruction with practical application, enhancing both your technical expertise and employability. Explore the rest of the article to discover how apprenticeships can launch your career and offer long-term benefits.
Table of Comparison
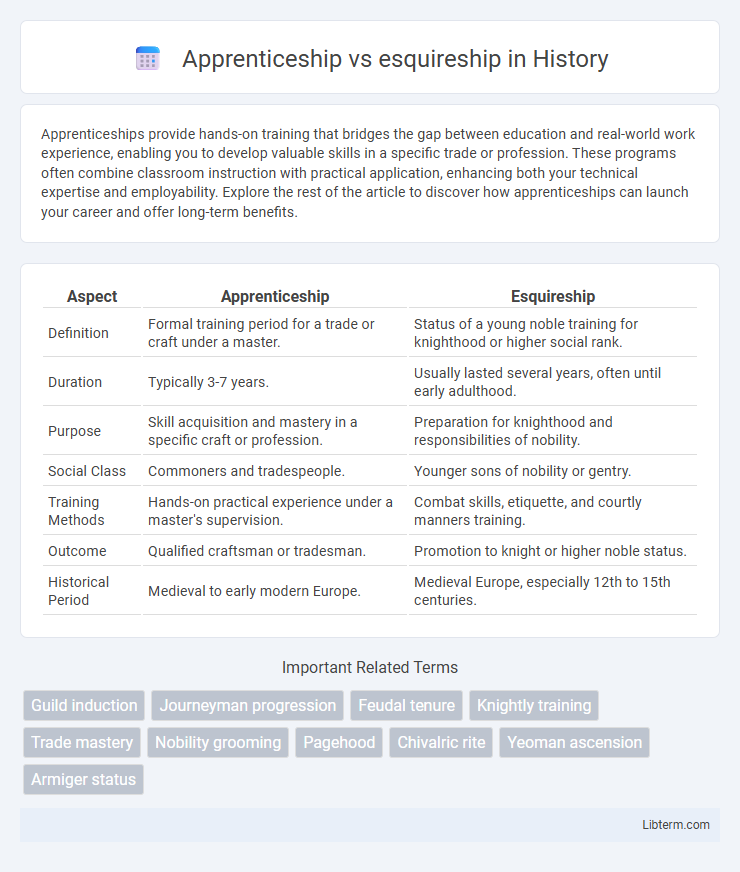
| Aspect | Apprenticeship | Esquireship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal training period for a trade or craft under a master. | Status of a young noble training for knighthood or higher social rank. |
| Duration | Typically 3-7 years. | Usually lasted several years, often until early adulthood. |
| Purpose | Skill acquisition and mastery in a specific craft or profession. | Preparation for knighthood and responsibilities of nobility. |
| Social Class | Commoners and tradespeople. | Younger sons of nobility or gentry. |
| Training Methods | Hands-on practical experience under a master's supervision. | Combat skills, etiquette, and courtly manners training. |
| Outcome | Qualified craftsman or tradesman. | Promotion to knight or higher noble status. |
| Historical Period | Medieval to early modern Europe. | Medieval Europe, especially 12th to 15th centuries. |
Understanding Apprenticeship: Definition and Scope
Apprenticeship is a structured training program combining on-the-job learning with formal education, designed to develop practical skills and industry-specific expertise. It encompasses a defined period during which apprentices work under the supervision of experienced professionals to gain hands-on experience in trades such as carpentry, electrical work, and culinary arts. The scope of apprenticeship extends beyond skill acquisition to include certification, career advancement, and meeting regulatory standards within various vocational fields.
What is Esquireship? Meaning and Historical Context
Esquireship historically signifies a rank below a knight, often granted to men of higher social status who were entitled to bear arms and had responsibilities in local governance or law enforcement. Originating in medieval England, esquires were typically landed gentry or those serving as attendants to knights, marking a socio-political status linked to the feudal system. Unlike apprenticeships centered on skill acquisition and vocational training, esquireship symbolized social hierarchy and legal privileges during the Middle Ages.
Key Differences Between Apprenticeship and Esquireship
Apprenticeship involves a structured program where individuals gain hands-on skills and practical experience in a trade or profession under the guidance of a skilled mentor. Esquireship traditionally denotes a social or legal status granted to individuals, often marking a rank of minor nobility or a licensed attorney, rather than a training process. Key differences include apprenticeship's focus on education and skill acquisition versus esquireship's emphasis on social rank or professional designation.
Pathways to Becoming an Apprentice or Esquire
Pathways to becoming an apprentice typically involve formal enrollment in vocational training programs or apprenticeships offered by trade unions or professional guilds, combining on-the-job training with classroom instruction. To become an esquire historically required serving as a squire, engaging in years of martial and courtly training under a knight, with paths often involving noble lineage or sponsorship by a lord. Modern usage of "esquire" as a professional title, especially for lawyers, necessitates completing law school, passing the bar exam, and meeting state licensing requirements.
Educational Requirements: Apprenticeship vs Esquireship
Apprenticeship requires hands-on training under a skilled professional with minimal formal education, emphasizing practical experience and on-the-job learning in trades or crafts. Esquireship, often linked to legal or noble status, mandates extensive formal education, including advanced degrees such as a Juris Doctor for lawyers, and successful completion of rigorous examinations. Apprenticeships focus on skill acquisition through mentorship, whereas esquireship demands comprehensive academic credentials and certification.
Roles and Responsibilities: Apprentice Compared to Esquire
An apprentice primarily undertakes hands-on training and learns practical skills under the supervision of experienced professionals, focusing on mastering specific tasks and gaining foundational knowledge in a trade or profession. In contrast, an esquire holds a higher status, often representing clients, providing legal advice, and performing advanced responsibilities such as drafting documents, negotiating agreements, and appearing in court. The apprentice's role is centered on learning and skill development, while the esquire assumes authoritative duties, accountability, and professional judgment within their field.
Career Prospects for Apprentices and Esquires
Career prospects for apprentices often lead to hands-on expertise and industry-specific certifications, enabling rapid entry into skilled trades or technical professions with strong demand and competitive wages. Esquires typically pursue advanced legal careers, offering opportunities for leadership roles, partnership positions, and specialized practice areas with significant earning potential and professional prestige. Both pathways provide distinct career trajectories, where apprenticeships emphasize practical skills and immediate employability, while esquires focus on legal expertise and long-term advancement within the judicial system.
Skills Developed: Practical vs Theoretical Approaches
Apprenticeship programs emphasize practical skills development through hands-on experience and real-world tasks, fostering immediate application and mastery of specific trades or professions. Esquireship education centers on theoretical knowledge, critical thinking, and legal principles, preparing candidates for analytical roles within the legal or scholarly fields. This distinction highlights the pragmatic focus of apprenticeships versus the conceptual and intellectual rigor inherent in esquireship training.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Pathway
Apprenticeship offers hands-on experience and skill development in a practical setting, fostering immediate industry readiness but may limit academic credentials. Esquireship provides comprehensive legal education with access to professional networks and potential for higher status, though it involves significant time and financial investment. Each pathway requires balancing practical experience against formal qualifications, influencing career progression and marketability in the legal profession.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between apprenticeship and esquireship depends on career goals, skill development, and industry requirements. Apprenticeships offer hands-on training and practical experience, ideal for trades and technical professions, while esquireship emphasizes formal education and legal qualifications essential for law careers. Assessing personal interests, time commitment, and long-term professional aspirations helps determine the most suitable pathway.
Apprenticeship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com