Anthropology explores the origins, behavior, and cultural development of humans across time and space, offering deep insights into societal structures and evolution. By studying diverse cultures and human biology, it helps you understand the complexities of human existence and social interaction. Discover how anthropology can broaden your perspective in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
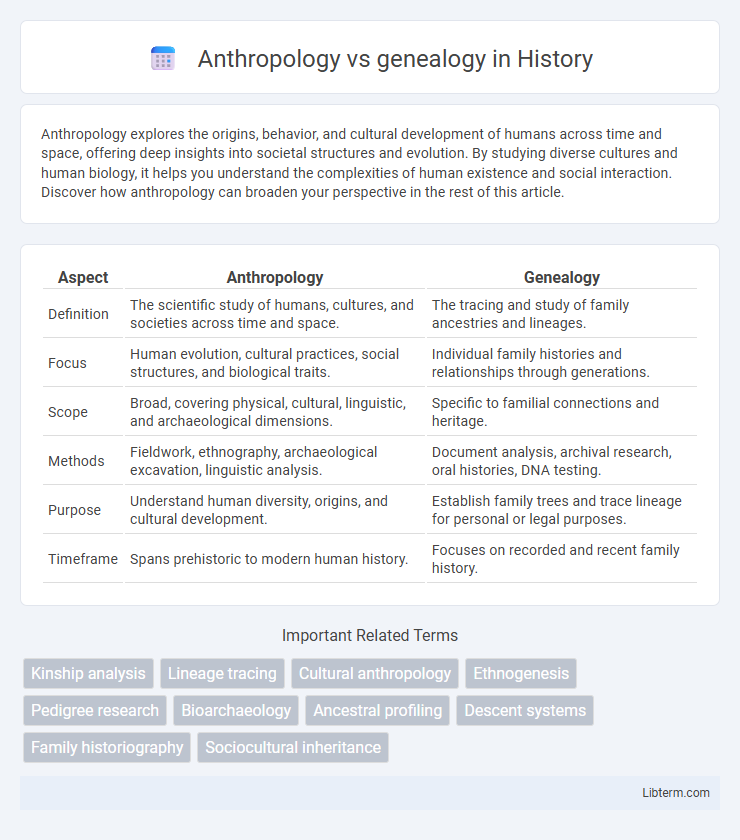
| Aspect | Anthropology | Genealogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The scientific study of humans, cultures, and societies across time and space. | The tracing and study of family ancestries and lineages. |
| Focus | Human evolution, cultural practices, social structures, and biological traits. | Individual family histories and relationships through generations. |
| Scope | Broad, covering physical, cultural, linguistic, and archaeological dimensions. | Specific to familial connections and heritage. |
| Methods | Fieldwork, ethnography, archaeological excavation, linguistic analysis. | Document analysis, archival research, oral histories, DNA testing. |
| Purpose | Understand human diversity, origins, and cultural development. | Establish family trees and trace lineage for personal or legal purposes. |
| Timeframe | Spans prehistoric to modern human history. | Focuses on recorded and recent family history. |
Understanding Anthropology: A Broad Perspective
Anthropology explores human societies, cultures, and biological aspects across time, emphasizing the complexity of human behavior and evolution. Genealogy focuses specifically on tracing family lineages and ancestral connections through historical records and genetic data. Understanding anthropology provides a broad perspective on human development beyond individual family histories, incorporating cultural, social, and biological dimensions.
Genealogy Explained: Tracing Family Roots
Genealogy involves tracing family roots by studying historical records, such as birth certificates, marriage licenses, and census data, to construct detailed family trees. It focuses on identifying ancestors and understanding lineage connections across generations. Unlike anthropology, which studies human cultures and societies broadly, genealogy provides personalized insights into individual ancestry and heritage.
Key Differences Between Anthropology and Genealogy
Anthropology studies human societies, cultures, and biological aspects across time, emphasizing holistic analysis through ethnography and archaeology, whereas genealogy specifically traces individual family lineages and ancestral relationships using historical records. Anthropology employs a broad interdisciplinary approach to understand human behavior and evolution, while genealogy is primarily focused on constructing family trees and verifying bloodline connections. The key difference lies in anthropology's comprehensive cultural and biological scope compared to genealogy's narrower aim of documenting familial descent.
Research Methods in Anthropology
Research methods in anthropology emphasize qualitative approaches such as participant observation, ethnographic fieldwork, and in-depth interviews to understand cultures and social behaviors. Anthropologists often use a holistic perspective, integrating biological, archaeological, linguistic, and cultural data to analyze human societies over time. Unlike genealogy, which primarily relies on documentary and archival records to trace family lineage, anthropology incorporates diverse data sources to explore broader human experiences and social dynamics.
Tools and Techniques in Genealogy
Genealogy utilizes tools such as DNA testing kits, online databases, and archival records to trace family lineages and uncover ancestral connections. Techniques include pedigree charting, record analysis, and genetic genealogy to establish relationships and verify historical data. Specialized software platforms integrate these tools, enhancing accuracy and enabling systematic documentation of family history.
The Role of Culture in Anthropology
Anthropology examines human cultures, behaviors, and societies to understand the diverse ways people live and interact, highlighting culture as a central element shaping identity and social structures. Genealogy, by contrast, traces lineage and ancestral relationships, focusing primarily on biological descent rather than cultural context. The role of culture in anthropology provides insight into customs, beliefs, and traditions that influence human experience beyond mere genetic connections.
The Importance of Records in Genealogy
Records are essential in genealogy for tracing lineage, verifying family connections, and preserving historical accuracy. Unlike anthropology, which studies cultures and human behavior broadly, genealogy relies heavily on birth certificates, marriage records, census data, and other official documents to reconstruct family trees. Accurate record-keeping ensures the integrity of genealogical research and helps uncover personal and historical identities.
Outcomes and Applications of Anthropological Studies
Anthropological studies produce outcomes that deepen understanding of human cultures, behaviors, and societal evolution, enabling applications in fields such as public health, education, and cultural preservation. These findings aid policymakers in crafting culturally sensitive programs and support forensic investigations by providing insights into human variation and ancestry. Unlike genealogy, which traces individual lineage, anthropology offers broader societal and evolutionary perspectives crucial for addressing contemporary global challenges.
Practical Benefits of Genealogical Research
Genealogical research offers practical benefits such as uncovering family history, enhancing personal identity, and connecting with living relatives, which can aid in medical history awareness and inheritance planning. Unlike anthropology, which studies human societies broadly, genealogy provides concrete data on individual ancestors and lineage, making it valuable for legal documentation and cultural preservation. Access to online databases and DNA testing tools has significantly improved the accuracy and accessibility of genealogical findings for personal and professional use.
Integrating Anthropology and Genealogy for Holistic Insights
Integrating anthropology and genealogy provides holistic insights by combining cultural, social, and biological perspectives with detailed family histories and ancestral connections. Anthropological methods enhance genealogical research through context about societal structures, migration patterns, and cultural practices that shape lineage narratives. This interdisciplinary approach enriches understanding of identity, heritage, and human evolution by connecting individual ancestry with broader human behavior and historical processes.
Anthropology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com