Asimilacion refers to the process by which individuals or groups integrate and adapt to a new culture, often adopting its language, customs, and values while losing some aspects of their original identity. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in shaping multicultural societies and influences social cohesion and identity formation. Discover how asimilacion impacts your community and personal experiences in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
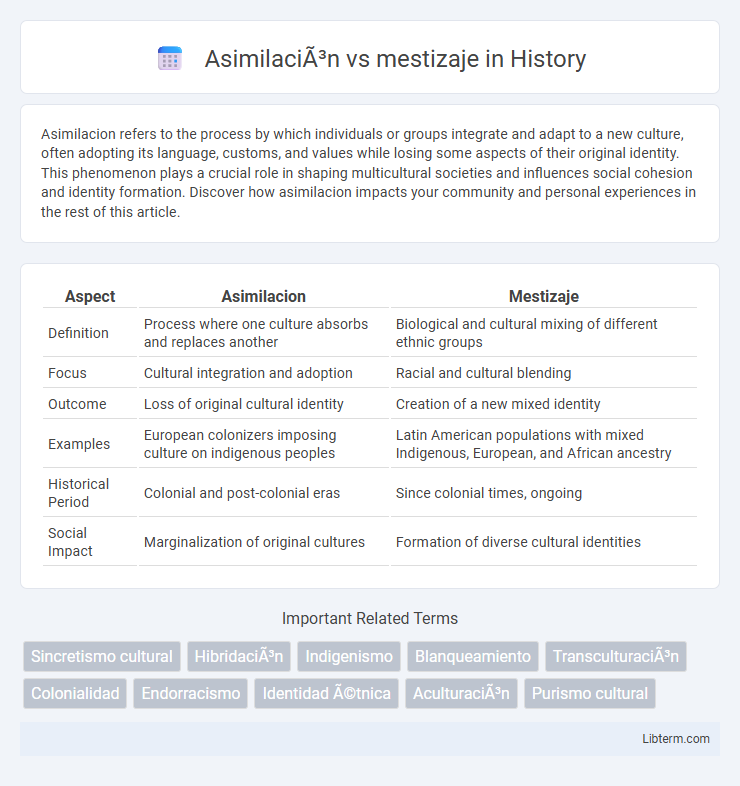
| Aspect | Asimilacion | Mestizaje |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where one culture absorbs and replaces another | Biological and cultural mixing of different ethnic groups |
| Focus | Cultural integration and adoption | Racial and cultural blending |
| Outcome | Loss of original cultural identity | Creation of a new mixed identity |
| Examples | European colonizers imposing culture on indigenous peoples | Latin American populations with mixed Indigenous, European, and African ancestry |
| Historical Period | Colonial and post-colonial eras | Since colonial times, ongoing |
| Social Impact | Marginalization of original cultures | Formation of diverse cultural identities |
Definición de asimilación
Asimilacion es el proceso mediante el cual un grupo etnico adopta las caracteristicas culturales, linguisticas y sociales de otro grupo dominante, perdiendo gradualmente su identidad original. En contraste, el mestizaje implica la mezcla biologica y cultural entre distintos grupos, dando lugar a nuevas identidades hibridas. La asimilacion suele involucrar la absorcion total con reduccion de diferencias, mientras que el mestizaje celebra la diversidad y convivencia cultural.
El concepto de mestizaje
El concepto de mestizaje se refiere a la mezcla biologica y cultural entre diferentes grupos etnicos, especialmente entre indigenas, europeos y africanos en America Latina. Este proceso no solo implica la combinacion genetica, sino tambien la fusion de tradiciones, lenguas y costumbres que dan origen a nuevas identidades culturales. A diferencia de la asimilacion, que busca la absorcion total de una cultura dominante, el mestizaje valora la coexistencia y la transformacion mutua de las culturas involucradas.
Orígenes históricos de ambos procesos
Asimilacion and mestizaje originate from distinct historical contexts in colonial Latin America; asimilacion involved the absorption of Indigenous peoples into dominant European cultures through legal and social frameworks imposed by colonial powers. Mestizaje emerged as a biological and cultural process of racial and ethnic mixing between Indigenous peoples and Europeans, reflecting complex social dynamics and identity formations. The roots of asimilacion lie in assimilationist policies aiming at cultural homogenization, whereas mestizaje stems from the lived realities of intercultural unions and hybrid identities in post-colonial societies.
Diferencias clave entre asimilación y mestizaje
Asimilacion implica la incorporacion total de una cultura a otra, donde el grupo minoritario pierde sus caracteristicas culturales originales para adaptarse completamente al grupo dominante. Mestizaje se refiere al proceso biocultural de mezcla entre diferentes grupos etnicos y raciales, resultando en nuevas identidades hibridas que conservan elementos de ambas culturas. Las diferencias clave radican en que la asimilacion busca homogeneidad cultural, mientras que el mestizaje celebra la diversidad y la creacion de nuevas formas culturales.
Impacto cultural en comunidades indígenas
Asimilacion implica la perdida de elementos culturales propios al adoptar la cultura dominante, lo que resulta en la erosion de idiomas, tradiciones y practicas indigenas. Mestizaje, en cambio, promueve una mezcla cultural que puede preservar ciertos rasgos autoctonos mientras integra otros, generando identidades hibridas. El impacto cultural en comunidades indigenas varia segun el grado de resistencia o adaptacion, afectando su cohesion social, patrimonio cultural y derechos territoriales.
Efectos sociales de la asimilación
The social effects of assimilation include the erosion of indigenous cultural identities and languages, leading to a loss of traditional customs and social structures. This process often results in marginalized communities facing discrimination and reduced access to resources within dominant societies. Assimilation can create homogeneous social environments but at the cost of cultural diversity and social cohesion.
Mestizaje como herramienta de identidad
Mestizaje serves as a powerful tool for identity formation by blending indigenous, European, and African ancestries, creating a unique cultural and ethnic synthesis central to many Latin American societies. This process fosters a shared sense of belonging and pride, distinguishing mestizo identity from purely assimilative approaches that often imply the erasure of original cultural roots. Embracing mestizaje emphasizes inclusion and celebration of diversity within a collective national identity.
Políticas y legislación relacionadas
Politicas de asimilacion en paises latinoamericanos buscaron eliminar identidades indigenas mediante la imposicion de la cultura dominante, implementando leyes de educacion y lenguaje uniformes. En contraste, las politicas de mestizaje promovieron la integracion de diferentes grupos etnicos y culturales, apoyadas por legislaciones que fomentaban la mezcla como identidad nacional. Ambas estrategias influyeron en la construccion de ciudadania y derechos sociales, afectando profundamente la diversidad cultural y los movimientos indigenas.
Ejemplos contemporáneos en América Latina
Contemporary examples of asimilacion in Latin America include Indigenous communities in urban Mexico adopting Spanish language and customs to navigate economic opportunities, while mestizaje is evident in countries like Mexico and Brazil, where mixed Indigenous, European, and African ancestries shape national identities and cultural expressions. In Argentina, mestizaje manifests through the blending of European immigrants and Indigenous peoples, impacting social practices and local traditions. Urban areas of Colombia also exhibit asimilacion as Afro-Colombian populations adopt dominant cultural norms to access education and employment.
Desafíos y debates actuales
Asimilacion involves the absorption of minority cultures into a dominant culture, often leading to loss of original identities, while mestizaje emphasizes cultural blending and coexistence. Current debates highlight challenges such as preserving indigenous languages and traditions amidst pressure to conform, and addressing systemic inequalities that hinder true multicultural integration. Scholars argue that mestizaje offers a more inclusive framework, yet tensions persist over issues of cultural appropriation and social justice in diverse societies.
Asimilación Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com