Sovereignty defines a state's ultimate authority to govern itself without external interference, encompassing political, legal, and territorial control. Understanding sovereignty is crucial for grasping international relations, national independence, and the dynamics of global power. Explore this article to discover how sovereignty shapes your country's role on the world stage.
Table of Comparison
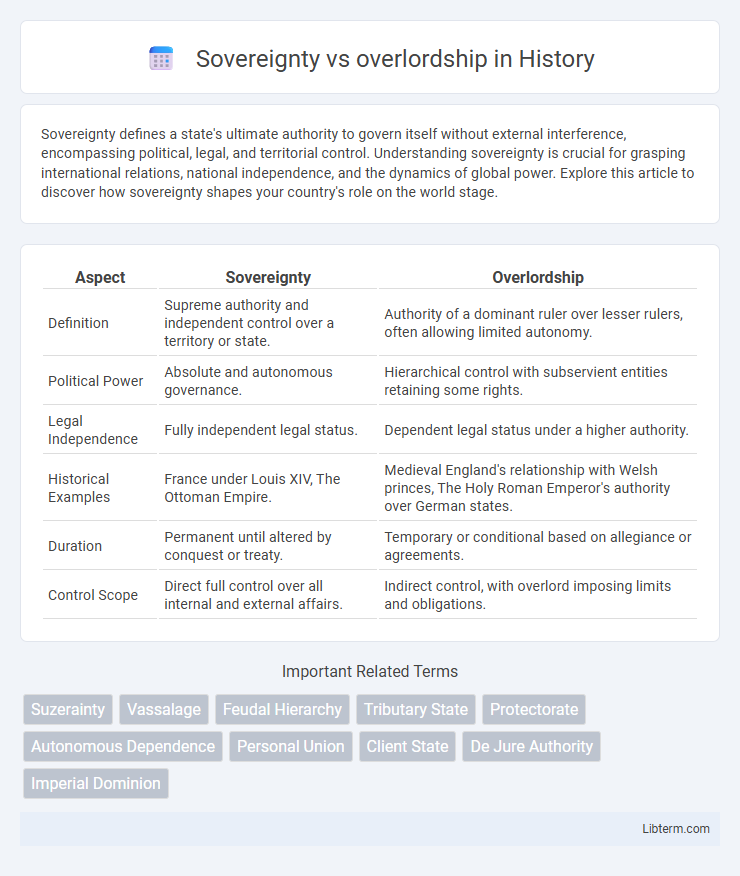
| Aspect | Sovereignty | Overlordship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supreme authority and independent control over a territory or state. | Authority of a dominant ruler over lesser rulers, often allowing limited autonomy. |
| Political Power | Absolute and autonomous governance. | Hierarchical control with subservient entities retaining some rights. |
| Legal Independence | Fully independent legal status. | Dependent legal status under a higher authority. |
| Historical Examples | France under Louis XIV, The Ottoman Empire. | Medieval England's relationship with Welsh princes, The Holy Roman Emperor's authority over German states. |
| Duration | Permanent until altered by conquest or treaty. | Temporary or conditional based on allegiance or agreements. |
| Control Scope | Direct full control over all internal and external affairs. | Indirect control, with overlord imposing limits and obligations. |
Understanding Sovereignty: Definition and Origins
Sovereignty refers to the supreme authority of a state to govern itself without external interference, originating from the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648 which established the foundations of the modern nation-state system. It embodies the legal and political autonomy to enact laws, enforce order, and conduct foreign policy independently. Understanding sovereignty involves recognizing its role as a fundamental principle in international law that distinguishes independent states from territories under overlordship or external control.
The Concept of Overlordship Explained
Overlordship refers to a hierarchical relationship in which a dominant power exercises control or authority over subordinate states or territories, often allowing limited self-governance while demanding allegiance and tribute. This concept contrasts with sovereignty, where a state possesses full, independent authority without external interference. Historically, overlordship facilitated political and military dominance without formal annexation, enabling overlords to wield influence through vassalage, suzerainty, or colonial structures.
Historical Evolution of Sovereignty and Overlordship
The historical evolution of sovereignty emerged from medieval concepts of overlordship, where multiple layers of authority were held by monarchs over vassals. Overlordship involved hierarchical control with a supreme lord exercising limited power over subordinate rulers, while sovereignty developed as the principle of absolute, indivisible authority within a defined territory. This transition marked a shift from fragmented feudal governance toward centralized nation-states asserting autonomous legal and political supremacy.
Key Differences Between Sovereignty and Overlordship
Sovereignty refers to the supreme authority of a state or ruler to govern itself without external interference, ensuring complete control over its territory and laws. Overlordship denotes a relationship where one power exercises control or influence over another state or territory, often without full sovereign rights granted, indicating partial submission. Key differences include the extent of autonomy, with sovereignty granting full independence and overlordship implying subordination under a superior authority.
Sovereignty in Modern International Law
Sovereignty in modern international law refers to the full right and power of a state to govern itself without external interference, emphasizing territorial integrity and political independence. It establishes that states are legal equals with authority over their internal affairs, recognized under the United Nations Charter and customary international law. This principle limits overlordship, whereby one state exercises control over another, reinforcing a global system based on mutual respect and non-domination among sovereign entities.
Overlordship in Feudal and Colonial Contexts
Overlordship in feudal contexts denotes a hierarchical relationship where a lord exerts control over vassals by granting land in exchange for military or fiscal obligations, establishing a system of loyalty and service. In colonial contexts, overlordship manifests through imperial powers imposing authority over indigenous territories, often exploiting resources and subordinating local governance to foreign administrative structures. This dual application of overlordship underscores the dynamics of power, control, and dependency that define both medieval feudalism and colonial imperialism.
Real-World Examples: Sovereign States vs. Overlord Territories
Sovereignty refers to a state's full control over its territory and autonomy in governance, exemplified by independent countries like Japan and Canada. Overlordship, by contrast, involves external domination or influence over a territory, as seen in historical examples like the British Empire's control over India or contemporary examples such as China's influence in Hong Kong under the "one country, two systems" framework. These distinctions highlight the varying degrees of political authority and legal independence exercised by sovereign states compared to territories under overlordship.
Political and Legal Implications of Sovereignty and Overlordship
Sovereignty establishes supreme political authority within a defined territory, enabling states to enact laws, control resources, and govern without external interference, reinforcing legal independence and territorial integrity. Overlordship involves a superior entity exerting control over subordinate states or territories, often limiting their legal autonomy and political decision-making through obligations such as tribute, military support, or legal subordination. The distinction impacts international law principles, where sovereignty underpins state equality and non-intervention, whereas overlordship challenges these norms by imposing hierarchical relationships and constraints on a state's full exercise of sovereign powers.
Debates and Controversies: Where Rights Overlap or Clash
Debates over sovereignty versus overlordship intensify when national self-governance rights clash with supranational authority, raising complex issues in international law. Competing claims frequently emerge in contested regions or in cases involving colonial legacies, where historical sovereignty conflicts with imposed overlordship frameworks. Legal scholars and policymakers struggle to reconcile these overlaps, as they challenge the principles of territorial integrity and autonomous political control.
The Future of Sovereignty and Overlordship in Global Governance
The future of sovereignty and overlordship in global governance involves a dynamic balance between state autonomy and supranational authority, with increasing interdependence among nations driving collaborative decision-making. Trends in global governance emphasize decentralization and shared sovereignty through multilateral institutions like the United Nations and regional bodies, aiming to address global challenges such as climate change, cybersecurity, and pandemics. Emerging frameworks suggest a hybrid model where traditional state sovereignty coexists with new forms of overlordship that enforce international norms while respecting national sovereignty boundaries.
Sovereignty Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com