Augur is a decentralized prediction market platform built on the Ethereum blockchain, allowing users to forecast events and earn rewards for accurate predictions. It leverages smart contracts to enable trustless, transparent, and censorship-resistant markets on a wide range of topics. Discover how Augur can transform your approach to forecasting by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
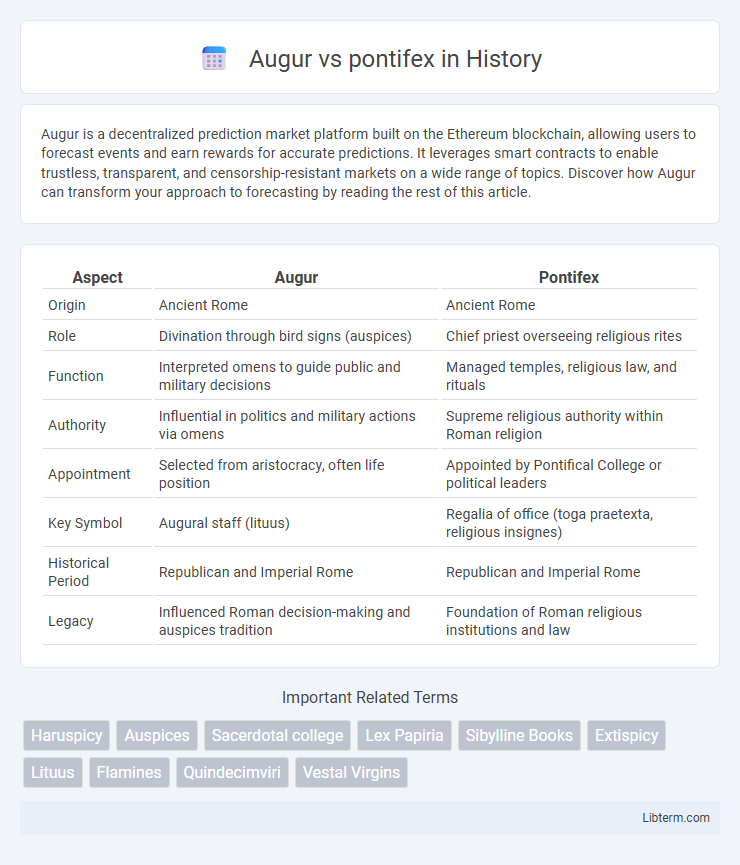
| Aspect | Augur | Pontifex |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Rome | Ancient Rome |
| Role | Divination through bird signs (auspices) | Chief priest overseeing religious rites |
| Function | Interpreted omens to guide public and military decisions | Managed temples, religious law, and rituals |
| Authority | Influential in politics and military actions via omens | Supreme religious authority within Roman religion |
| Appointment | Selected from aristocracy, often life position | Appointed by Pontifical College or political leaders |
| Key Symbol | Augural staff (lituus) | Regalia of office (toga praetexta, religious insignes) |
| Historical Period | Republican and Imperial Rome | Republican and Imperial Rome |
| Legacy | Influenced Roman decision-making and auspices tradition | Foundation of Roman religious institutions and law |
Understanding Augur and Pontifex: A Brief Overview
Augurs were ancient Roman priests specializing in interpreting the will of the gods by studying the flight patterns of birds, a practice known as augury, crucial for public and military decisions. Pontifices, on the other hand, served as high-ranking religious officials responsible for overseeing the Roman state religion, maintaining the pax deorum, and regulating sacred rituals and laws. Both roles were vital in Roman religion, with augurs focused on divination and pontifices on religious law and administration.
Historical Origins of Augurs and Pontifices
Augurs and pontifices originated in ancient Rome as key religious officials governing spiritual and civic duties. Augurs specialized in interpreting the will of the gods through bird flights and natural omens, while pontifices maintained religious law, rituals, and the Roman calendar. Their distinct roles formed the foundation of Roman religious and political authority from the early Republic through the Empire.
Roles and Duties: Augur vs. Pontifex
Augurs in ancient Rome specialized in interpreting the will of the gods by observing natural signs, particularly the flight patterns of birds, to guide public and military decisions. Pontifices held broader religious authority, overseeing the administration of sacred laws, rituals, and the Roman state calendar while maintaining the integrity of religious practices. The augur's role was primarily divinatory, while the pontifex acted as a chief priest, ensuring institutional religious order and legal oversight.
Religious Authority and Influence
Augurs wielded significant religious authority by interpreting the will of the gods through the observation of birds, shaping political and military decisions in ancient Rome. Pontifices, as chief priests, maintained and regulated sacred law, temple rituals, and the Roman calendar, exerting broad influence over religious practices and state ceremonies. The interplay between augurs and pontifices solidified the integration of religion and governance, reinforcing Rome's social and political structure.
Rituals and Ceremonies: Contrasting Functions
Augurs specialized in interpreting the will of the gods through observing bird flight patterns, guiding public decision-making rituals and inaugurations in ancient Rome. Pontifices managed religious law and oversaw the formal calendar of festivals and ceremonies, ensuring state rituals conformed to traditional practices. The augur's role was divinatory and predictive, while the pontifex wielded authoritative control over ritual correctness and the maintenance of sacred rites.
Political Power within Ancient Rome
Augurs and Pontifices were crucial religious officials in Ancient Rome whose political power significantly influenced governance and society. Augurs specialized in interpreting the will of the gods through bird flight patterns, guiding political decisions and public policies by sanctioning auspices, while Pontifices held broader authority over religious law, state rituals, and the calendar, directly controlling key aspects of Rome's legal and political frameworks. The Pontifex Maximus, as the chief Pontifex, wielded substantial political influence, often intertwining religious duties with legislative power, shaping Rome's political hierarchy and decision-making processes.
Selection and Appointment Process
The selection and appointment process for Augurs involved co-optation within the college, where existing members chose new ones based on religious expertise and reputation, often from patrician families. In contrast, Pontifices were typically appointed by the college of Pontiffs or elected by popular assemblies, reflecting both religious authority and political influence. These distinct appointment methods highlighted the Augurs' focus on divination and augury ceremonies, whereas Pontifices managed broader religious law and public rites.
Symbolic Differences: Attire and Tools
Augurs wore a distinctive toga adorned with a lituus, a curved staff symbolizing their role in interpreting omens from the flight patterns of birds, while Pontifices donned simpler garments but carried the *libri pontificales*, sacred books essential for overseeing religious law and rituals. The lituus, emblematic of augural authority, contrasted sharply with the pontifex's ceremonial implements like the *aspersorium* used for ritual purification. These attire and tool differences underscored their distinct symbolic functions: augurs as diviners of divine will through natural signs, pontifices as guardians of religious tradition and legal order.
Impact on Roman Society and Governance
The Augur's role in interpreting the will of the gods through avian omens significantly influenced Roman political and military decisions, embedding religious legitimacy into governance. Pontifex, as a chief priest within the College of Pontiffs, oversaw the regulation of religious law and rituals, thereby maintaining social order and legal continuity. Together, these religious offices intertwined divine authority with state functions, reinforcing Rome's theocratic governance and stabilizing societal norms.
Legacy and Influence in Modern Times
The legacy of Augurs and Pontifices profoundly shapes modern religious and legal traditions, with Augurs influencing practices in divination and interpreting omens, while Pontifices established foundational structures for ecclesiastical authority and public law in ancient Rome. Augurs' role in guiding decision-making through auspices remains a reference point in studies of ancient ritual and governance. Pontifex positions evolved into the papal office, directly impacting contemporary Catholic Church hierarchy and canon law, cementing their enduring influence on institutional religion and cultural heritage.
Augur Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com