Legends serve as powerful narratives that preserve cultural heritage and impart timeless wisdom through symbolic storytelling. These stories often blend historical facts with myth, enriching your understanding of ancient traditions and moral values. Explore the rest of the article to uncover fascinating legends from around the world that continue to inspire and educate.
Table of Comparison
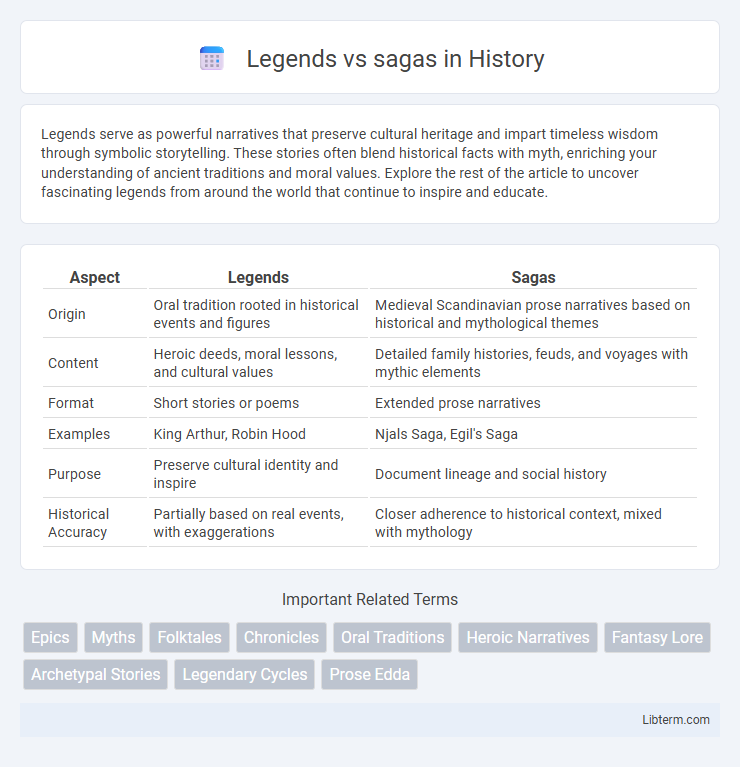
| Aspect | Legends | Sagas |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Oral tradition rooted in historical events and figures | Medieval Scandinavian prose narratives based on historical and mythological themes |
| Content | Heroic deeds, moral lessons, and cultural values | Detailed family histories, feuds, and voyages with mythic elements |
| Format | Short stories or poems | Extended prose narratives |
| Examples | King Arthur, Robin Hood | Njals Saga, Egil's Saga |
| Purpose | Preserve cultural identity and inspire | Document lineage and social history |
| Historical Accuracy | Partially based on real events, with exaggerations | Closer adherence to historical context, mixed with mythology |
Introduction: Defining Legends and Sagas
Legends are traditional narratives rooted in historical events or figures, often embellished to emphasize heroism or moral lessons. Sagas originate from Old Norse literature and are epic tales that combine history, mythology, and genealogy, primarily focused on Scandinavian and Icelandic culture. Both genres preserve cultural identity but differ in scope, with legends being more universally varied and sagas tied closely to specific regional histories.
Historical Origins of Legends and Sagas
Legends originated from oral traditions rooted in specific cultures, often blending historical events with mythic elements to explain ancestors' deeds or natural phenomena. Sagas, primarily emerging from Old Norse literature, are prose narratives that chronicle the historical and genealogical exploits of Scandinavian heroes, nobles, and early medieval societies. Both genres serve as vital historical sources, preserving early cultural values and societal structures through storytelling.
Key Characteristics of Legends
Legends are traditional stories rooted in historical events or figures, often embellished to highlight heroic deeds or cultural values. They typically blend fact and fiction, emphasizing themes like bravery, moral lessons, and supernatural elements linked to real people or places. Legends serve to preserve cultural heritage, offering insights into the beliefs and societal norms of the time.
Distinctive Features of Sagas
Sagas are extensive narrative prose rooted in medieval Icelandic literature, characterized by detailed genealogies, historical events, and a focus on heroic deeds and family honor. They often emphasize realism and complex character development, contrasting with legends that typically involve more supernatural elements and moral lessons. Sagas also maintain a distinct style marked by terse, understated narration and a strong connection to actual places and societal structures of the time.
Major Themes Explored in Legends
Legends primarily explore themes of heroism, cultural identity, and moral lessons, often rooted in historical events with fictional embellishments. These narratives emphasize the valor and virtues of protagonists, reinforcing societal values and collective memory. Themes of divine intervention, fate, and the struggle between good and evil are recurrent, illustrating the human condition through mythic storytelling.
Common Motifs in Sagas
Sagas frequently feature common motifs such as heroic quests, family feuds, and encounters with supernatural beings that highlight themes of honor, fate, and resilience. These narratives often emphasize genealogies and detailed descriptions of lineage to establish social status and historical context. The recurrence of motifs like vengeance, loyalty, and the struggle between pagan and Christian values reflects the cultural and moral framework of the Norse and Icelandic societies that produced them.
Cultural Significance: Legends vs Sagas
Legends often serve as moral or heroic narratives deeply embedded in the collective identity of a culture, symbolizing values and ideals that shape societal norms. Sagas, primarily rooted in Norse and Icelandic traditions, preserve historical memories and genealogies, blending factual events with mythic elements to reinforce cultural continuity and heritage. Both forms act as repositories of communal knowledge, yet legends emphasize allegorical lessons, while sagas prioritize historical lineage and social structure.
Storytelling Styles and Narrative Structures
Legends typically focus on historical events or heroic figures, using linear narrative structures that emphasize factual storytelling and moral lessons. Sagas feature complex, multi-generational plots with intertwining characters and episodic storytelling, often blending myth and history to create rich cultural narratives. Both forms employ vivid imagery and oral tradition techniques, but sagas prioritize expansive, detailed storytelling while legends remain concise and thematically focused.
Famous Examples of Legends and Sagas
Legends like King Arthur and Robin Hood epitomize heroic figures deeply rooted in historical traditions, blending fact and mythology. Famous sagas such as the Icelandic "Njals Saga" and the Norse "Saga of the Volsungs" offer detailed narratives of Viking age heroes and genealogies, preserving cultural heritage through prose. These examples highlight the enduring impact of legends and sagas in shaping collective memory and national identity across centuries.
Lasting Impact on Modern Literature and Media
Legends and sagas have profoundly shaped modern literature and media by providing archetypal narratives and rich cultural contexts that continue to inspire storytelling. Legends often emphasize heroic deeds and moral lessons, influencing genres like fantasy and adventure, while sagas contribute complex family histories and epic themes, prevalent in historical fiction and film. Their enduring motifs and character archetypes remain central to contemporary narratives, ensuring cultural heritage and imaginative exploration persist across global media platforms.
Legends Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com