Kimono is a traditional Japanese garment known for its elegant design and cultural significance, often made from silk and featuring intricate patterns. Wearing a kimono represents an artful expression of heritage and craftsmanship, reflecting centuries of history and social symbolism. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a kimono can transform your understanding of Japanese culture and fashion.
Table of Comparison
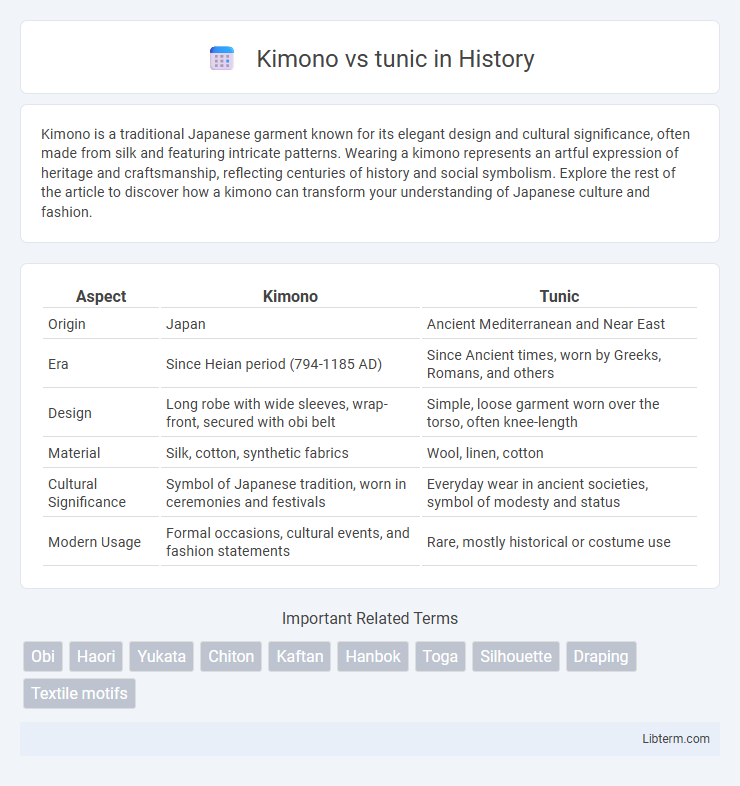
| Aspect | Kimono | Tunic |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Japan | Ancient Mediterranean and Near East |
| Era | Since Heian period (794-1185 AD) | Since Ancient times, worn by Greeks, Romans, and others |
| Design | Long robe with wide sleeves, wrap-front, secured with obi belt | Simple, loose garment worn over the torso, often knee-length |
| Material | Silk, cotton, synthetic fabrics | Wool, linen, cotton |
| Cultural Significance | Symbol of Japanese tradition, worn in ceremonies and festivals | Everyday wear in ancient societies, symbol of modesty and status |
| Modern Usage | Formal occasions, cultural events, and fashion statements | Rare, mostly historical or costume use |
Introduction: Defining Kimono and Tunic
A kimono is a traditional Japanese garment characterized by its T-shaped, straight-lined robes wrapped around the body, typically made from silk with intricate patterns. A tunic, originating from ancient civilizations like Rome and Greece, is a simple, loose-fitting garment that extends to the hips or knees, often made from cotton or linen. Both serve as versatile clothing pieces but differ significantly in cultural significance, design, and fabric choice.
Historical Origins and Evolution
The kimono, originating in Japan during the Heian period (794-1185), evolved from the kosode, characterized by its T-shaped, straight-lined robes worn as everyday clothing by aristocrats. In contrast, tunics trace back to ancient civilizations such as Rome and Greece, serving as a fundamental garment for both men and women, adapting over centuries into various cultural styles and lengths. While the kimono remains a ceremonial symbol of Japanese heritage, the tunic's evolution influenced numerous Western and global fashion trends, demonstrating distinct historical trajectories rooted in cultural significance.
Key Design Elements and Structure
Kimonos feature T-shaped, straight-lined robes with wide sleeves and a wrap-around front secured by an obi belt, emphasizing symmetry and a flat silhouette. Tunics typically have a looser fit with side seams, shorter sleeves, and a simple pullover style or side buttons, offering more varied shapes and casual wearability. The kimono's layered fabric design contrasts with the tunic's single-layer construction, highlighting differing cultural aesthetics and functional purposes.
Cultural Significance and Meaning
Kimonos hold deep cultural significance in Japan, symbolizing tradition, social status, and various ceremonies, often featuring intricate designs that reflect seasons and personal identity. Tunics, historically worn across many cultures such as Ancient Rome and India, represent versatile everyday attire and a connection to cultural heritage through simpler, practical designs. Both garments embody unique cultural narratives, with kimonos emphasizing formal elegance and tunics highlighting functional, historical roots.
Fabric Choices and Patterns
Kimonos are traditionally crafted from luxurious silk, featuring intricate patterns like florals, cranes, and seasonal motifs symbolizing Japanese culture and aesthetics. Tunics often utilize breathable fabrics such as cotton, linen, or lightweight blends, showcasing simpler, geometric or ethnic-inspired patterns suitable for casual or contemporary wear. Fabric choice in kimonos emphasizes elegance and tradition, while tunics prioritize comfort and versatility.
Typical Occasions for Wearing
Kimonos are traditionally worn during formal Japanese ceremonies, festivals, weddings, and tea ceremonies, embodying cultural heritage and elegance. Tunics are versatile garments suitable for casual outings, office wear, and informal gatherings due to their comfortable and adaptable design. The distinct occasions highlight the kimono's ceremonial significance versus the tunic's everyday practicality.
Regional Variations and Styles
Kimonos originate from Japan and are characterized by their T-shaped, straight-lined robes with wide sleeves and long sashes called obi, featuring intricate patterns that reflect regional and seasonal motifs. Tunics, prevalent across various cultures including the Mediterranean, Middle East, and South Asia, vary widely in fabric, length, and decoration, often tailored to local climate and cultural customs. Regional variations in kimonos emphasize formality and tradition, while tunic styles offer greater diversity, adapting to both everyday wear and ceremonial purposes across different societies.
Modern Fashion Adaptations
Modern fashion adaptations of the kimono emphasize lightweight fabrics, bold prints, and versatile layering, transforming this traditional Japanese garment into a chic everyday piece embraced globally. Tunics have evolved into sleek, minimalist styles featuring asymmetric cuts and breathable materials, catering to contemporary preferences for comfort and functionality. Both garments inspire designers by blending cultural heritage with modern aesthetics, influencing runway collections and streetwear alike.
Kimono vs Tunic: Styling Tips
Kimono styling emphasizes flowing silhouettes with wide sleeves and bold prints, perfect for layering over slim-fit pants or a fitted dress to balance volume. Tunics, typically more structured and shorter, pair well with leggings or skinny jeans, highlighting a casual yet polished look. Opt for lightweight fabrics and minimal accessories when wearing kimonos, while tunics can be enhanced with statement belts and layered necklaces for added dimension.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Kimono and Tunic
Choosing between a kimono and a tunic depends on the occasion and desired style; kimonos offer a traditional, elegant drape with wide sleeves perfect for formal or cultural events, while tunics provide versatile, casual comfort suited for everyday wear. Fabric choice also influences selection, with silk or brocade common in kimonos and cotton or linen favored in tunics. Understanding these distinctions ensures a wardrobe choice that balances aesthetic appeal and functional comfort.
Kimono Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com