Longue duree explores the deep, enduring structures shaping societies and history beyond immediate events or short-term changes. This approach reveals the underlying economic, social, and cultural forces that influence long-term developments. Discover how understanding longue duree can transform your perspective on historical analysis by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
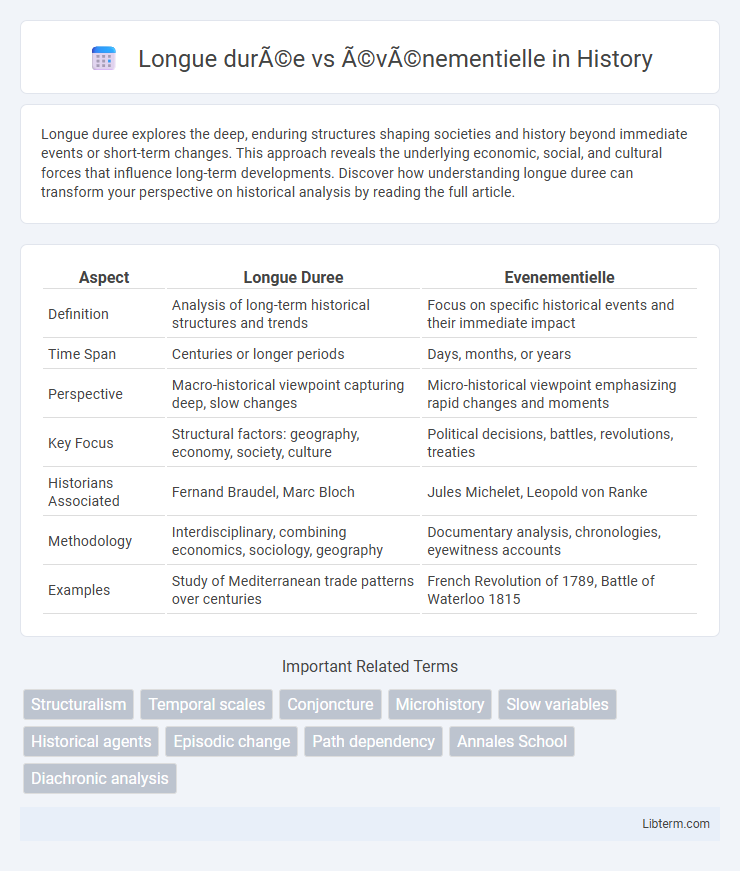
| Aspect | Longue Duree | Evenementielle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analysis of long-term historical structures and trends | Focus on specific historical events and their immediate impact |
| Time Span | Centuries or longer periods | Days, months, or years |
| Perspective | Macro-historical viewpoint capturing deep, slow changes | Micro-historical viewpoint emphasizing rapid changes and moments |
| Key Focus | Structural factors: geography, economy, society, culture | Political decisions, battles, revolutions, treaties |
| Historians Associated | Fernand Braudel, Marc Bloch | Jules Michelet, Leopold von Ranke |
| Methodology | Interdisciplinary, combining economics, sociology, geography | Documentary analysis, chronologies, eyewitness accounts |
| Examples | Study of Mediterranean trade patterns over centuries | French Revolution of 1789, Battle of Waterloo 1815 |
Introduction to Longue Durée and Événementielle
Longue duree emphasizes the analysis of long-term historical structures and social patterns that shape societies over centuries, contrasting sharply with evenementielle, which focuses on short-term events and specific incidents. The concept of longue duree, popularized by historian Fernand Braudel, prioritizes deep-rooted economic, social, and cultural forces that persist beyond individual events. Evenementielle concentrates on discrete moments or occurrences, often highlighting political decisions, battles, or significant historical milestones.
Defining Longue Durée in Historical Analysis
Longue duree in historical analysis emphasizes the study of long-term structural factors such as geographic, economic, and social trends that shape societies over centuries. This approach contrasts with evenementielle, which concentrates on short-term events and individual actions. By focusing on enduring patterns, longue duree enables historians to understand the deep-rooted causes and persistent influences behind historical developments.
Understanding Événementielle: The Study of Events
Evenementielle focuses on the analysis and interpretation of discrete historical events, emphasizing their immediate impact and specific contexts. This approach contrasts with the longue duree by centering on short-term occurrences and the dynamics that drive change within a particular timeframe. Understanding evenementielle involves examining causality, agency, and the unfolding of events to reveal their significance in shaping historical narratives.
Origins and Theoretical Foundations
The concept of longue duree, introduced by historian Fernand Braudel, emphasizes the analysis of slow, underlying social, economic, and environmental structures shaping history over centuries. In contrast, evenementielle focuses on discrete, often political or military events that mark significant but shorter-term historical changes. Longue duree's theoretical foundation derives from the Annales School, prioritizing deep temporal frameworks and interdisciplinary methods, while evenementielle aligns with traditional historiography concentrating on causality and chronology of individual events.
Key Proponents and Influencers
Fernand Braudel, a prominent advocate of the longue duree approach, emphasized the importance of long-term social, economic, and environmental structures in shaping history. In contrast, historians like Leopold von Ranke focused on evenementielle, prioritizing short-term events and political episodes as critical moments driving historical change. The longue duree framework deeply influenced the Annales School, while evenementielle remains foundational in traditional narrative historiography.
Methodological Differences
Longue duree analysis emphasizes the study of long-term historical structures, focusing on persistent social, economic, and cultural patterns that evolve over centuries, while evenementielle prioritizes short-term events and discrete episodes to interpret historical changes. Methodologically, longue duree relies on interdisciplinary data sources such as geography, demography, and economics to trace gradual transformations, whereas evenementielle employs detailed archival research and chronological event sequencing to understand immediate causes and effects. The contrast highlights longue duree's structural, macro-historical approach versus evenementielle's event-driven, micro-historical focus, influencing the scope and depth of historical interpretation.
Strengths and Limitations of Longue Durée
The longue duree approach excels in providing deep historical insights by emphasizing long-term social, economic, and environmental structures that shape events over centuries, offering a comprehensive understanding beyond isolated incidents. Its strength lies in revealing patterns and underlying causes often missed in event-focused studies, making it invaluable for analyzing gradual change and continuity. However, this method's limitation is its potential to overlook the significance of short-term events and individual agency, sometimes leading to deterministic interpretations that underplay immediate historical impacts.
Strengths and Limitations of Événementielle
Evenementielle research excels at capturing immediate, specific occurrences and detailed situational factors, providing rich, context-sensitive data for short-term analysis. Its limitations include a lack of depth in understanding long-term structural patterns and underlying social processes, often leading to fragmented insights disconnected from broader historical context. This approach may overlook the slower, cumulative influences emphasized in longue duree studies, reducing its ability to explain enduring social dynamics.
Case Studies: Comparative Applications
Case studies comparing longue duree and evenementielle approaches reveal distinct analytical strengths; longue duree emphasizes deep historical structures shaping societal trends over centuries, while evenementielle focuses on discrete, impactful incidents within shorter time frames. In economic history, longue duree highlights persistent patterns such as institutional evolution in feudal societies, whereas evenementielle case studies examine pivotal events like the 1929 stock market crash and its immediate consequences. Combining both perspectives offers a richer understanding of causality and transformation in fields like political revolutions and cultural shifts.
Integrating Longue Durée and Événementielle Approaches
Integrating longue duree and evenementielle approaches enhances historical analysis by combining deep structural perspectives with specific event dynamics, providing a comprehensive understanding of both enduring trends and pivotal moments. This synthesis allows researchers to contextualize short-term events within long-term social, economic, and cultural frameworks, revealing intricate causal relationships. Employing database cross-referencing and temporal mapping tools further optimizes the integration of macro-scale changes and micro-scale occurrences for multidimensional insights.
Longue durée Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com