Mens rea, meaning "guilty mind," is a crucial element in criminal law that determines a defendant's mental state at the time of committing a crime. It differentiates between intentional wrongdoing and accidental acts, significantly affecting the severity of charges and penalties. Explore this article to understand how mens rea influences legal responsibility and your rights within the justice system.
Table of Comparison
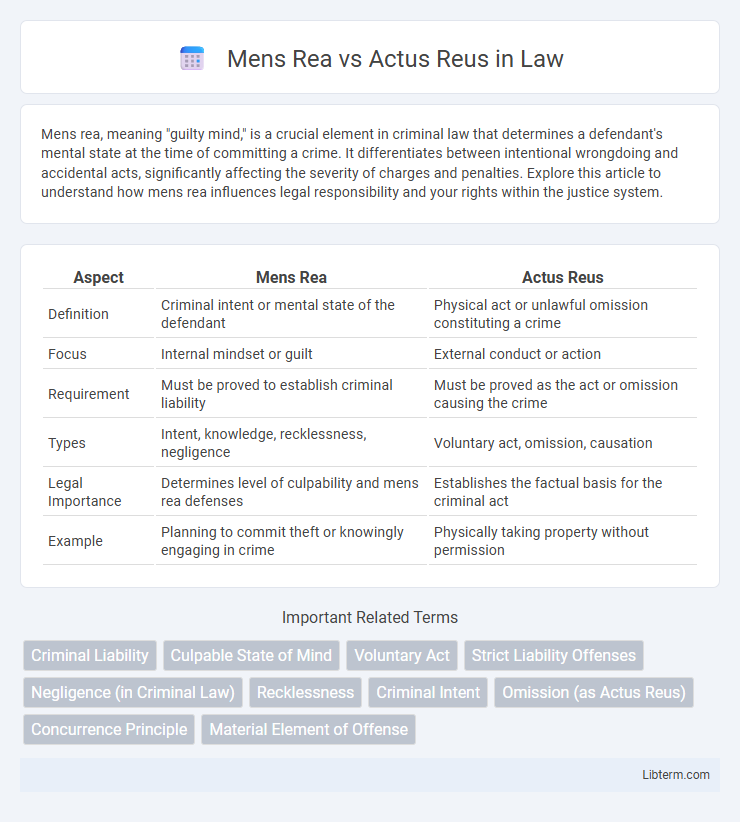
| Aspect | Mens Rea | Actus Reus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Criminal intent or mental state of the defendant | Physical act or unlawful omission constituting a crime |
| Focus | Internal mindset or guilt | External conduct or action |
| Requirement | Must be proved to establish criminal liability | Must be proved as the act or omission causing the crime |
| Types | Intent, knowledge, recklessness, negligence | Voluntary act, omission, causation |
| Legal Importance | Determines level of culpability and mens rea defenses | Establishes the factual basis for the criminal act |
| Example | Planning to commit theft or knowingly engaging in crime | Physically taking property without permission |
Introduction to Mens Rea and Actus Reus
Mens Rea, Latin for "guilty mind," refers to the mental state or intent behind a criminal act, essential in establishing culpability in criminal law. Actus Reus, meaning "guilty act," involves the physical action or conduct that constitutes a criminal offense. Together, Mens Rea and Actus Reus form the foundational elements needed to prove most crimes, linking intent with the actual commission of the unlawful act.
Defining Mens Rea: The Guilty Mind
Mens rea, the Latin term for "guilty mind," refers to the mental state or intent behind committing a criminal act, encompassing knowledge, recklessness, or purpose to cause harm. It plays a crucial role in establishing criminal liability, as proving mens rea demonstrates that the defendant acted with a culpable state of mind. Distinct from actus reus, which focuses on the physical act, mens rea emphasizes the defendant's awareness and intention during the offense.
Defining Actus Reus: The Guilty Act
Actus reus refers to the physical component of a crime, encompassing the voluntary actions, omissions, or conduct that breach the law. It is essential to establish actus reus to prove that the accused engaged in the criminal act, demonstrating the external manifestation of guilt. Unlike mens rea, which focuses on intent, actus reus centers on whether the defendant's behavior violated legal statutes.
Key Differences Between Mens Rea and Actus Reus
Mens Rea refers to the mental state or intent behind committing a crime, representing the defendant's culpability, while Actus Reus pertains to the actual physical act or unlawful conduct. The key difference lies in Mens Rea addressing the "guilty mind" element, whereas Actus Reus involves the "guilty act" element required for criminal liability. Both components must generally be proven beyond a reasonable doubt in criminal law to establish a defendant's guilt.
Types of Mens Rea in Criminal Law
Mens Rea, the mental element of a crime, includes various types such as intention, recklessness, knowledge, and negligence, which determine the defendant's state of mind at the time of the offense. Intention involves purposeful conduct to bring about a specific result, while recklessness refers to conscious disregard of a substantial risk. Knowledge implies awareness that certain circumstances exist or that a result is practically certain, whereas negligence occurs when a person fails to be aware of a substantial and unjustifiable risk.
Elements of Actus Reus in Criminal Offenses
The elements of Actus Reus in criminal offenses include a voluntary physical act or unlawful omission that causes a prohibited result, demonstrating the external component of a crime. It requires conduct that breaches the law, such as an affirmative action or failure to act when there is a legal duty. Establishing Actus Reus is essential to proving guilt, as it connects the defendant's behavior to the criminal outcome.
The Role of Mens Rea in Determining Criminal Liability
Mens Rea, the mental state or intent behind a criminal act, plays a crucial role in establishing criminal liability by determining whether the defendant had the necessary culpability at the time of the offense. It differentiates between intentional wrongdoing and accidental conduct, influencing the severity of charges and potential punishment. The interplay between mens rea and actus reus, the physical act itself, ensures that only those with a guilty mind combined with a guilty act are held liable under criminal law.
Examples Illustrating Actus Reus and Mens Rea
Actus reus refers to the physical act of committing a crime, such as theft involving the unauthorized taking of property or assault characterized by the intentional infliction of bodily harm. Mens rea involves the mental state or intent behind the act, exemplified by knowingly planning a robbery or recklessly causing harm without intent. Understanding the distinction is crucial in criminal law, where both the wrongful act and culpable mental state must be proven for conviction.
Legal Defenses Related to Mens Rea and Actus Reus
Legal defenses related to mens rea often revolve around the defendant's mental state, such as insanity, intoxication, or mistake of fact, which can negate the required culpable intent for criminal liability. Defenses tied to actus reus focus on disproving the physical act element, including alibi, consent, or lack of voluntary action, demonstrating that the defendant did not commit the prohibited conduct. Effective legal strategy requires distinguishing between these elements to challenge both the mental and physical components of a crime.
Conclusion: The Importance of Mens Rea and Actus Reus in Justice
The principles of mens rea and actus reus are fundamental to ensuring a just legal system by establishing both the mental intent and the physical act as essential components of criminal liability. Recognizing mens rea prevents wrongful convictions of individuals lacking criminal intent, while proving actus reus confirms the occurrence of the prohibited act. Together, these elements uphold fairness and accuracy in justice by balancing culpability with actual conduct.
Mens Rea Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com