Maintaining confidentiality protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, preserving trust and legal compliance. Effective confidentiality practices are essential for safeguarding personal data and business secrets. Explore the article to understand how you can strengthen your confidentiality measures.
Table of Comparison
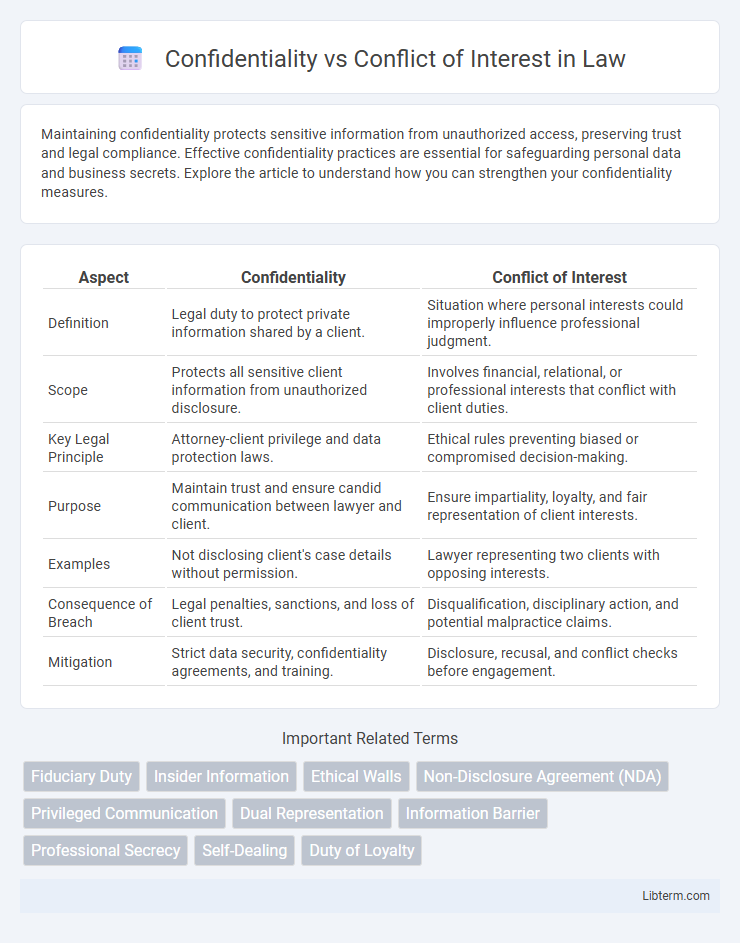
| Aspect | Confidentiality | Conflict of Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal duty to protect private information shared by a client. | Situation where personal interests could improperly influence professional judgment. |
| Scope | Protects all sensitive client information from unauthorized disclosure. | Involves financial, relational, or professional interests that conflict with client duties. |
| Key Legal Principle | Attorney-client privilege and data protection laws. | Ethical rules preventing biased or compromised decision-making. |
| Purpose | Maintain trust and ensure candid communication between lawyer and client. | Ensure impartiality, loyalty, and fair representation of client interests. |
| Examples | Not disclosing client's case details without permission. | Lawyer representing two clients with opposing interests. |
| Consequence of Breach | Legal penalties, sanctions, and loss of client trust. | Disqualification, disciplinary action, and potential malpractice claims. |
| Mitigation | Strict data security, confidentiality agreements, and training. | Disclosure, recusal, and conflict checks before engagement. |
Understanding Confidentiality: Definition and Importance
Confidentiality refers to the ethical and legal duty to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure, ensuring trust between parties involved. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of professional relationships, especially in fields such as healthcare, law, and finance, by safeguarding personal data and proprietary details. Understanding confidentiality helps prevent breaches that could lead to legal consequences, reputational damage, and harm to individuals or organizations.
Defining Conflict of Interest in Professional Settings
Conflict of interest in professional settings occurs when personal interests potentially interfere with the objective judgment or duties owed to a client or employer. It undermines trust and can lead to decisions that favor personal gain over organizational or client loyalty. Identifying and managing conflicts of interest is essential to maintaining ethical standards and protecting confidential information.
Key Differences Between Confidentiality and Conflict of Interest
Confidentiality involves safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure, ensuring trust and privacy in professional relationships. Conflict of interest arises when personal interests potentially interfere with impartial decision-making or professional duties, risking bias or undue influence. The key difference lies in confidentiality protecting information security, while conflict of interest addresses ethical objectivity and integrity in actions.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Breaching Confidentiality
Breaching confidentiality in legal practice can lead to severe ethical violations and disciplinary actions, including disbarment and civil liability for damages incurred by the client. Conflict of interest often exacerbates confidentiality breaches by compromising the lawyer's ability to protect sensitive information impartially. Maintaining strict confidentiality safeguards client trust, upholds ethical standards outlined by professional bodies like the ABA Model Rules, and prevents legal repercussions stemming from unauthorized disclosure.
Identifying and Managing Conflicts of Interest
Identifying and managing conflicts of interest requires a clear understanding of confidentiality boundaries and ethical obligations to prevent biased decision-making. Organizations implement robust disclosure policies and ongoing monitoring systems to detect potential conflicts early, ensuring that sensitive information is protected while maintaining transparency. Effective conflict management includes recusal procedures, third-party reviews, and continuous training to uphold integrity and trust in professional relationships.
Confidentiality in Client-Professional Relationships
Confidentiality in client-professional relationships ensures that sensitive information shared by the client remains protected and undisclosed without permission, establishing trust and ethical integrity. Professionals are legally and ethically bound to safeguard client data against unauthorized access, fostering a secure environment for open communication. Maintaining strict confidentiality mitigates risks of information breaches and supports compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Common Scenarios: When Confidentiality Meets Conflict of Interest
Common scenarios where confidentiality meets conflict of interest include corporate mergers, where employees possess sensitive information that could benefit competing parties, and legal practices, where attorneys must navigate client confidentiality while avoiding representation that may harm rival clients. In healthcare, professionals face conflicts when patient confidentiality clashes with obligations to family members or insurance providers. These situations demand rigorous ethical guidelines and transparent disclosure to uphold trust and legal compliance.
Best Practices for Maintaining Confidentiality and Managing Conflicts
Maintaining confidentiality requires implementing strict data protection protocols, restricting information access to authorized personnel, and conducting regular training on privacy policies to safeguard sensitive client and organizational information. Managing conflicts of interest involves transparent disclosure of any personal or financial interests that could influence professional judgment, establishing clear guidelines for decision-making processes, and enforcing recusal policies when conflicts arise. Combining these best practices ensures ethical integrity, fosters trust, and complies with legal standards across industries.
Consequences of Violating Confidentiality vs. Ignoring Conflicts of Interest
Violating confidentiality can lead to legal penalties, loss of professional licenses, and irreversible damage to client trust, significantly harming reputation and business viability. Ignoring conflicts of interest may result in biased decision-making, compromised integrity, legal disputes, and financial losses due to impaired judgment. Both breaches undermine ethical standards, but confidentiality violations typically incur more immediate legal consequences, whereas conflicts of interest erode long-term credibility and stakeholder confidence.
Strategies for Balancing Confidentiality and Conflict of Interest in the Workplace
Effective strategies for balancing confidentiality and conflict of interest in the workplace include establishing clear policies that define sensitive information boundaries and disclosure requirements. Implementing regular training programs on ethical decision-making enhances employee awareness of confidentiality obligations while identifying potential conflicts early. Utilizing confidential reporting systems and appointing compliance officers ensures ongoing monitoring and resolution of conflicts without compromising private information.
Confidentiality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com