Impartiality ensures decisions are made fairly without favoritism or bias, fostering trust and credibility in various settings such as the workplace or legal systems. It creates an environment where diverse perspectives are respected and evaluated based on objective criteria. Explore the rest of this article to understand how cultivating impartiality can enhance your judgment and relationships.
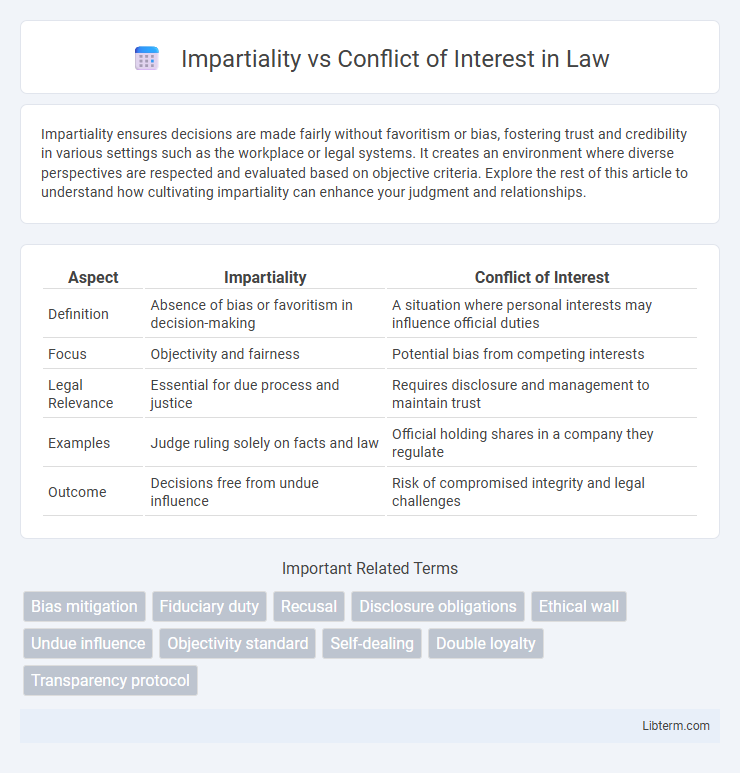
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Impartiality | Conflict of Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Absence of bias or favoritism in decision-making | A situation where personal interests may influence official duties |
| Focus | Objectivity and fairness | Potential bias from competing interests |
| Legal Relevance | Essential for due process and justice | Requires disclosure and management to maintain trust |
| Examples | Judge ruling solely on facts and law | Official holding shares in a company they regulate |
| Outcome | Decisions free from undue influence | Risk of compromised integrity and legal challenges |
Understanding Impartiality: Definition and Importance
Impartiality refers to the unbiased and fair treatment of all parties, ensuring decisions are made based on objective criteria rather than personal interests or relationships. It is crucial in maintaining trust, credibility, and integrity in professional and legal contexts, preventing favoritism and discrimination. Understanding impartiality helps identify and mitigate conflicts of interest that may compromise ethical standards and decision-making processes.
What Constitutes a Conflict of Interest
A conflict of interest arises when personal, financial, or professional relationships compromise or appear to compromise an individual's ability to act impartially. It includes situations where decisions benefit oneself, family, or close associates at the expense of fairness and objectivity. Recognizing and disclosing these conflicts is essential to maintain integrity and trust in professional and organizational environments.
Key Differences Between Impartiality and Conflict of Interest
Impartiality refers to the unbiased and fair treatment of all parties without favoritism or prejudice, ensuring objective decision-making. A conflict of interest arises when personal, financial, or professional relationships could compromise one's judgment or influence decisions. The key difference lies in impartiality being the ideal state of neutrality, while a conflict of interest represents a potential threat to this neutrality.
Common Examples of Conflict of Interest
Common examples of conflict of interest include financial investments in competing companies, accepting gifts or favors from clients, and holding dual roles that influence decision-making outcomes. These situations compromise impartiality by creating biased judgments or favoritism. Transparency and clear policies help maintain objectivity and prevent conflicts from undermining trust.
How Impartiality Promotes Ethical Decision-Making
Impartiality fosters ethical decision-making by ensuring decisions are based on objective criteria rather than personal biases or external influences, thus maintaining fairness and integrity. It minimizes conflicts of interest by promoting transparency and accountability, which strengthens trust among stakeholders and upholds professional standards. Organizations that prioritize impartiality reduce the risk of unethical conduct and reinforce a culture of ethical responsibility.
Warning Signs of Potential Bias in the Workplace
Warning signs of potential bias in the workplace include favoritism in decision-making, inconsistent application of policies, and undue influence from personal relationships or external interests. Employees showing reluctance to disclose financial or personal connections that could affect their judgment may indicate conflicts of interest. Identifying these red flags early helps maintain impartiality and upholds ethical standards within the organization.
Legal Implications of Conflict of Interest
Conflict of interest in legal settings undermines the impartiality required for fair decision-making, potentially leading to biased judgments and compromised ethical standards. Legal implications include disciplinary actions, nullification of decisions, and potential civil or criminal liability for parties involved in undisclosed conflicts. Courts emphasize strict disclosure requirements to preserve judicial integrity and public trust in the legal process.
Strategies to Foster Impartiality in Organizations
Ensuring impartiality in organizations involves implementing clear policies that define and manage conflicts of interest, requiring employees to disclose any personal or financial interests that could influence their professional judgment. Regular training programs on ethics and unbiased decision-making cultivate a culture of transparency and accountability. Utilizing independent review committees and establishing whistleblower protections further reinforce objective decision-making and minimize undue influence.
Managing and Disclosing Conflicts of Interest
Managing conflicts of interest requires transparent disclosure and proactive measures to separate personal interests from professional responsibilities, ensuring decisions remain unbiased and objective. Organizations must implement strict policies mandating timely reporting of potential conflicts, coupled with oversight mechanisms like recusal or independent review to uphold impartiality. Effective conflict of interest management strengthens trust, mitigates risks of ethical breaches, and safeguards organizational integrity.
Best Practices for Upholding Integrity and Fairness
Maintaining impartiality requires transparent disclosure of any potential conflicts of interest and strict adherence to established ethical guidelines to prevent bias in decision-making processes. Implementing regular training and robust monitoring systems ensures all parties uphold integrity and fairness, promoting accountability and trust. Best practices include recusal in situations of personal interest and fostering a culture of openness to safeguard objective judgment.
Impartiality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com