Consolidation enhances financial stability by merging assets, debts, or resources to create a stronger, more efficient entity. This process can simplify management, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. Discover how consolidation can benefit your financial strategy by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
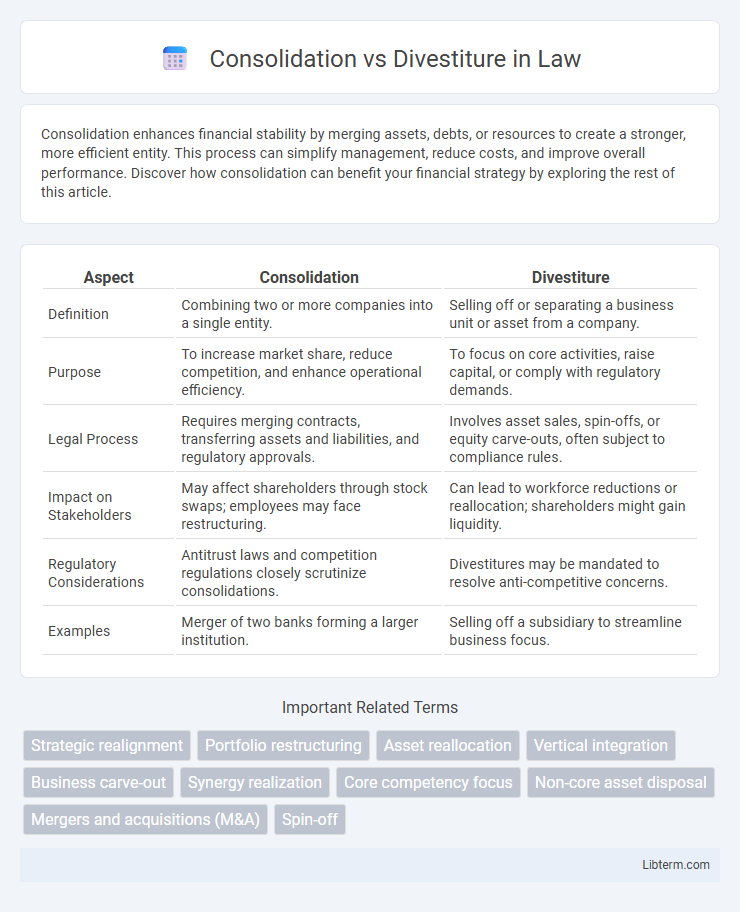
| Aspect | Consolidation | Divestiture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining two or more companies into a single entity. | Selling off or separating a business unit or asset from a company. |
| Purpose | To increase market share, reduce competition, and enhance operational efficiency. | To focus on core activities, raise capital, or comply with regulatory demands. |
| Legal Process | Requires merging contracts, transferring assets and liabilities, and regulatory approvals. | Involves asset sales, spin-offs, or equity carve-outs, often subject to compliance rules. |
| Impact on Stakeholders | May affect shareholders through stock swaps; employees may face restructuring. | Can lead to workforce reductions or reallocation; shareholders might gain liquidity. |
| Regulatory Considerations | Antitrust laws and competition regulations closely scrutinize consolidations. | Divestitures may be mandated to resolve anti-competitive concerns. |
| Examples | Merger of two banks forming a larger institution. | Selling off a subsidiary to streamline business focus. |
Introduction to Consolidation and Divestiture
Consolidation involves merging two or more companies into a single entity to enhance operational efficiency, gain market share, and achieve economies of scale. Divestiture refers to the process of a company selling off or liquidating assets, subsidiaries, or divisions to focus on core business areas and improve financial health. Both strategies play crucial roles in corporate restructuring, impacting company growth, profitability, and competitive dynamics.
Key Differences Between Consolidation and Divestiture
Consolidation involves merging two or more companies to form a new entity, enhancing market share, reducing competition, and achieving economies of scale. Divestiture refers to a company selling or spinning off assets, business units, or subsidiaries to streamline operations, raise capital, or focus on core activities. Key differences include consolidation creating unified operations and combined resources, while divestiture results in separation and transfer of ownership to improve strategic focus or financial health.
Strategic Objectives: Why Companies Consolidate or Divest
Companies pursue consolidation to achieve strategic objectives such as expanding market share, enhancing operational efficiencies, and gaining access to new technologies or customer bases. Divestiture is often driven by the need to streamline operations, focus on core competencies, reduce debt, or raise capital for strategic investments. Both strategies aim to optimize resource allocation and improve long-term competitive advantage.
Financial Implications of Consolidation vs Divestiture
Consolidation often leads to economies of scale, reduced operational costs, and enhanced market power, which can improve profit margins and shareholder value. Divestiture, on the other hand, allows companies to unlock capital by selling underperforming or non-core assets, improving liquidity and enabling focus on core business areas. Both strategies impact financial statements differently, with consolidation typically increasing assets and liabilities, while divestiture results in asset reduction and potential gain or loss recognition.
Operational Impact on Business Structure
Consolidation streamlines business structures by integrating operations, reducing redundancies, and centralizing management functions to enhance efficiency and scalability. Divestiture restructures companies by spinning off or selling divisions, which can lead to more focused operations, improved resource allocation, and agility in core business areas. Both strategies significantly alter operational workflows, but consolidation tends to create unified, larger entities while divestiture promotes leaner, specialized business units.
Risks and Challenges in Consolidation and Divestiture
Consolidation risks include integration challenges, cultural clashes, and operational disruptions that can hinder value realization and employee morale. Divestiture challenges involve asset valuation complexities, regulatory approvals, and potential loss of strategic capabilities, which may affect long-term competitiveness. Both strategies demand careful due diligence and change management to mitigate financial and organizational risks effectively.
Regulatory Considerations and Compliance
Regulatory considerations in consolidation involve rigorous antitrust reviews to prevent market monopolization, ensuring compliance with competition laws such as the Sherman Act and EU Merger Regulation. Divestiture often requires strict adherence to court-mandated orders or regulatory authorities like the Federal Trade Commission to maintain competitive market structures. Both strategies demand comprehensive compliance frameworks to manage risks related to transaction approvals, disclosure requirements, and ongoing regulatory scrutiny.
Case Studies: Successful Consolidation and Divestiture Examples
Case studies of successful consolidation include Disney's acquisition of Marvel, which strengthened its market position by integrating valuable IP and expanding its audience reach. In divestiture examples, IBM's sale of its PC division to Lenovo effectively refocused the company on higher-margin technology services, boosting profitability. These strategic moves highlight how targeted consolidation and divestiture can optimize corporate portfolios and drive sustained growth.
Decision-Making Criteria for Business Leaders
Business leaders evaluate consolidation versus divestiture based on strategic alignment, financial performance, and market positioning. Key decision-making criteria include assessing synergy potential, risk diversification, and resource allocation efficiency to drive sustainable growth. Analyzing competitive advantage and long-term value creation guides the choice between merging operations or divesting underperforming units.
Future Trends in Consolidation and Divestiture
Future trends in consolidation and divestiture indicate a strategic shift towards digital transformation and sustainability-driven portfolios. Companies increasingly leverage data analytics and AI to identify optimal acquisition targets and divestiture opportunities that enhance competitive advantage and operational efficiency. Cross-industry mergers and selective asset sales are expected to rise as organizations adapt to dynamic market conditions and regulatory environments.
Consolidation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com