Retention strategies are crucial for maintaining a loyal customer base and maximizing long-term business growth. Effective retention involves understanding customer needs, delivering consistent value, and fostering strong relationships to reduce churn and increase satisfaction. Discover actionable tips and techniques to boost your retention rates in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
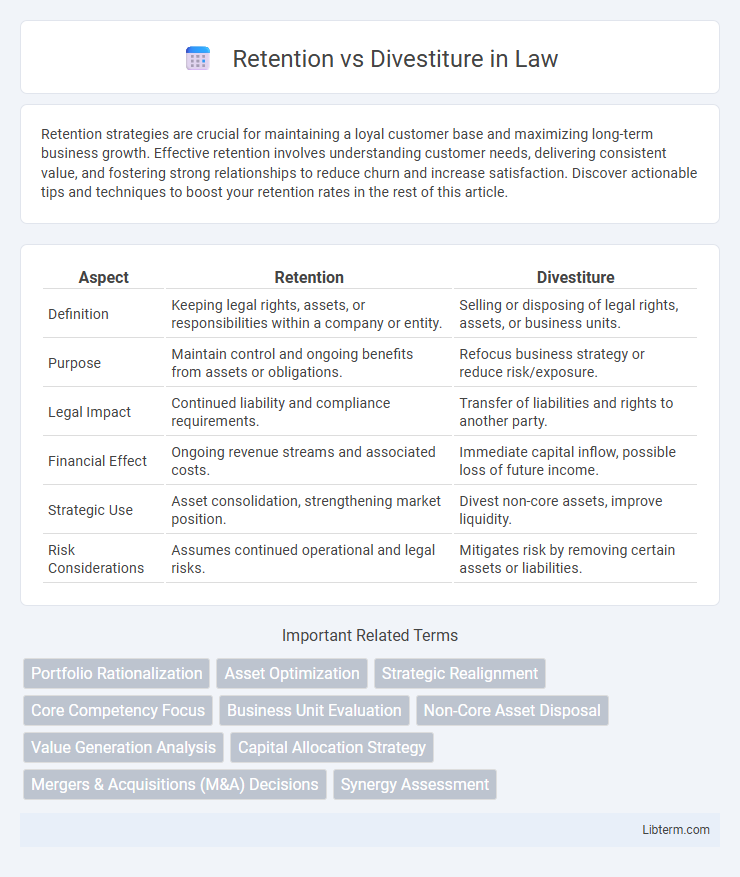
| Aspect | Retention | Divestiture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Keeping legal rights, assets, or responsibilities within a company or entity. | Selling or disposing of legal rights, assets, or business units. |
| Purpose | Maintain control and ongoing benefits from assets or obligations. | Refocus business strategy or reduce risk/exposure. |
| Legal Impact | Continued liability and compliance requirements. | Transfer of liabilities and rights to another party. |
| Financial Effect | Ongoing revenue streams and associated costs. | Immediate capital inflow, possible loss of future income. |
| Strategic Use | Asset consolidation, strengthening market position. | Divest non-core assets, improve liquidity. |
| Risk Considerations | Assumes continued operational and legal risks. | Mitigates risk by removing certain assets or liabilities. |
Understanding Retention and Divestiture
Retention involves maintaining ownership or control over assets, products, or business units that align with a company's strategic goals and offer long-term value. Divestiture refers to the process of selling or liquidating assets or divisions that no longer fit the company's core objectives or hinder operational efficiency. Effective decision-making in retention versus divestiture relies on evaluating financial performance, market potential, and alignment with corporate strategy.
Key Differences Between Retention and Divestiture
Retention involves maintaining ownership and operational control of assets or business units to capitalize on long-term value, while divestiture entails selling or liquidating assets to improve financial health or focus on core competencies. Retention supports strategic growth and stability by leveraging existing resources, contrasting with divestiture's goal of reducing risk and reallocating capital. Financial metrics like return on investment and impact on cash flow differ significantly, with retention emphasizing sustained profit generation and divestiture prioritizing immediate liquidity and efficiency.
Strategic Rationale for Retention
Retention supports long-term competitive advantage by preserving core competencies and market share in strategic business units. Companies prioritize retention to leverage existing assets, customer relationships, and brand equity, ensuring sustained revenue streams and growth potential. This approach aligns with corporate objectives to maintain stability, optimize operational efficiency, and capitalize on emerging market opportunities.
When Divestiture Becomes Necessary
Divestiture becomes necessary when a business unit underperforms consistently, drains resources, or no longer aligns with the company's strategic goals. Retaining such assets risks financial losses and distracts management from core operations, making divestment a strategic move to enhance overall portfolio value. Market shifts, regulatory changes, or the emergence of more profitable opportunities often trigger the decision to divest.
Financial Impacts of Retention vs Divestiture
Retention maintains consistent revenue streams and preserves asset value, reducing costs associated with market re-entry and transaction fees. Divestiture generates immediate capital influx, improving liquidity and balance sheet metrics, but may result in long-term revenue loss and potential restructuring expenses. Financial analysis must weigh ongoing operational cash flows against one-time divestiture proceeds to optimize shareholder value.
Operational Considerations for Each Strategy
Retention strategies require thorough evaluation of operational capabilities, including resource allocation, process efficiency, and ongoing cost management to sustain competitive advantage. Divestiture demands careful planning around asset valuation, workforce realignment, and minimizing disruption to core business operations during the transition. Both strategies necessitate robust risk assessment and strategic communication to maintain stakeholder confidence and operational continuity.
Market Conditions Influencing the Decision
Market conditions such as economic stability, competitive intensity, and consumer demand dynamics critically influence the retention versus divestiture decision. In a stable or growing market with high demand, businesses tend to retain assets to capitalize on potential long-term gains. Conversely, in volatile or declining markets, divestiture can mitigate risks and reallocate resources to more profitable ventures.
Risk Factors: Retention vs Divestiture
Retention involves maintaining assets or business units, which carries risks such as ongoing operational costs, market volatility, and potential regulatory changes that can impact profitability. Divestiture, by contrast, reduces exposure to these risks by eliminating underperforming or non-core assets but introduces risks related to valuation challenges, potential loss of future revenue, and transitional disruptions. Careful risk assessment in retention vs divestiture decisions ensures alignment with strategic goals while managing financial and market uncertainties.
Case Studies: Successful Retention and Divestiture
Case studies on retention highlight companies like IBM, which retained core business units during digital transformation, driving sustained growth and innovation. Successful divestiture examples include General Electric's sale of its appliance division, unlocking shareholder value and streamlining operations. These cases showcase strategic decision-making that balances focus on core competencies with portfolio optimization.
Best Practices for Decision-Making
Effective retention vs divestiture decisions require comprehensive financial analysis, market trend assessment, and alignment with long-term strategic goals. Employing data-driven metrics such as return on investment (ROI), cash flow projections, and competitive positioning helps prioritize assets with sustainable value. Engaging cross-functional teams and leveraging scenario planning enhances decision accuracy and mitigates risks associated with asset portfolio management.
Retention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com