A nuncupative will is an oral declaration of a person's final wishes made in the presence of witnesses, often used in emergency situations where writing is not possible. This type of will is typically limited in validity and scope, varying by jurisdiction and requiring strict adherence to legal requirements to be recognized. Explore the article further to understand how a nuncupative will may impact your estate planning and what safeguards to consider.
Table of Comparison
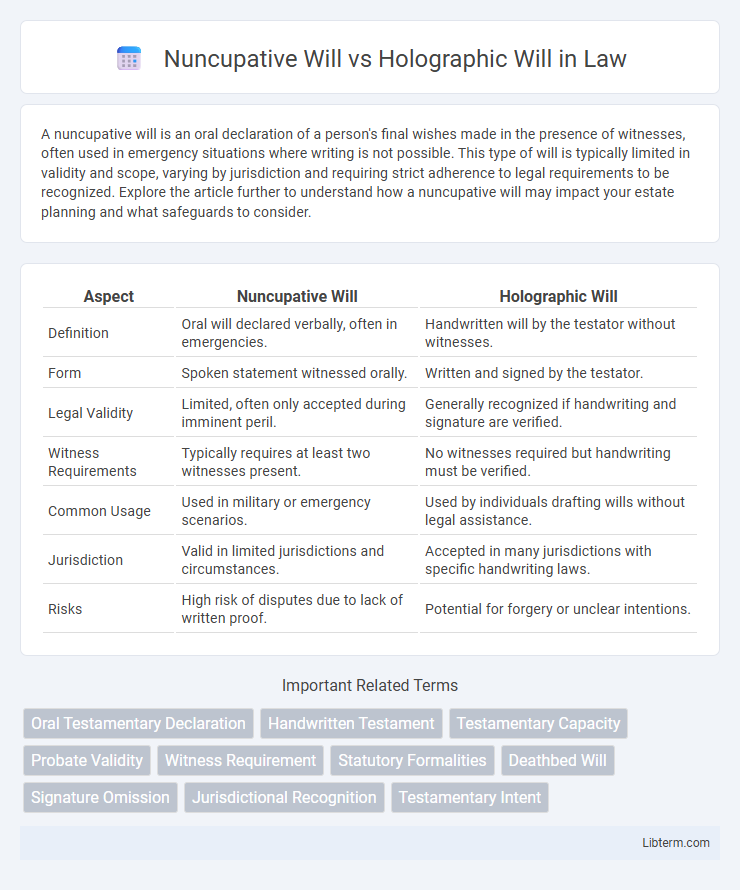
| Aspect | Nuncupative Will | Holographic Will |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Oral will declared verbally, often in emergencies. | Handwritten will by the testator without witnesses. |
| Form | Spoken statement witnessed orally. | Written and signed by the testator. |
| Legal Validity | Limited, often only accepted during imminent peril. | Generally recognized if handwriting and signature are verified. |
| Witness Requirements | Typically requires at least two witnesses present. | No witnesses required but handwriting must be verified. |
| Common Usage | Used in military or emergency scenarios. | Used by individuals drafting wills without legal assistance. |
| Jurisdiction | Valid in limited jurisdictions and circumstances. | Accepted in many jurisdictions with specific handwriting laws. |
| Risks | High risk of disputes due to lack of written proof. | Potential for forgery or unclear intentions. |
Introduction to Nuncupative and Holographic Wills
Nuncupative wills are oral declarations of a person's testamentary intentions made in the presence of witnesses, often permitted only under specific emergency situations such as imminent death. Holographic wills are handwritten documents that express a testator's wishes, requiring the individual's signature but generally not necessitating witnesses, making them distinct in their formal requirements. Both types of wills serve as alternatives to formal written wills, providing flexible options for estate planning in unique circumstances.
Definition of Nuncupative Will
A nuncupative will is an oral will declared by the testator in the presence of witnesses, typically during imminent peril or emergency situations, and is often limited by specific legal requirements such as witness numbers and property value thresholds. Unlike holographic wills, which are handwritten and signed by the testator, nuncupative wills rely entirely on verbal testimony and are recognized in fewer jurisdictions due to their susceptibility to fraud. Courts generally require strict adherence to statutory formalities to validate nuncupative wills, emphasizing their temporary nature and exception status within estate planning.
Definition of Holographic Will
A holographic will is a handwritten and unwitnessed testamentary document created entirely in the testator's handwriting, valid in certain jurisdictions relying on the authenticity of the handwriting itself. Unlike nuncupative wills, which are oral and typically allowed only in emergency situations or for military personnel, holographic wills provide a tangible, personalized record of the testator's final wishes. The legality and acceptance of holographic wills depend on specific state or country laws, often requiring clear evidence that the entire document was handwritten and signed by the testator.
Legal Requirements for Nuncupative Wills
Nuncupative wills require the testator to declare their final wishes orally in the presence of at least two or more credible witnesses, often during imminent death or military service, meeting strict legal conditions to be considered valid. These wills must be made by individuals incapable of drafting written documents, and the oral statements must be confirmed shortly after death within a specified timeframe, typically ranging from days to weeks, depending on jurisdiction. Unlike holographic wills, which must be handwritten and signed by the testator, nuncupative wills rely heavily on witness testimony and the immediacy of circumstances surrounding the testator's final moments.
Legal Requirements for Holographic Wills
Holographic wills must be entirely handwritten and signed by the testator to meet legal requirements, ensuring their authenticity and validity in many jurisdictions. Unlike nuncupative wills, which are oral and typically accepted only under strict conditions, holographic wills avoid the need for witnesses yet still require clear intent and testamentary capacity. Courts often scrutinize the handwriting and signature to confirm that the will reflects the testator's true intentions without undue influence.
Key Differences Between Nuncupative and Holographic Wills
Nuncupative wills are oral declarations made in the presence of witnesses, typically under emergency conditions, while holographic wills are handwritten documents signed by the testator without witnesses. Nuncupative wills are often subject to strict limitations regarding asset types and geographic jurisdiction, unlike holographic wills which generally hold more legal validity if properly executed. The key differences lie in formality, evidentiary requirements, and vulnerability to contestation, with holographic wills providing clearer proof of intent compared to nuncupative wills.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuncupative Wills
Nuncupative wills, which are oral and made during imminent peril, offer the advantage of quick execution without formalities, beneficial in emergency situations where written wills are impractical. However, their disadvantages include limited validity in many jurisdictions, high susceptibility to fraud, and challenges in proving authenticity due to the lack of physical documentation. Unlike holographic wills, which are handwritten and typically accepted with fewer formalities, nuncupative wills often face stricter evidentiary scrutiny and restricted use to specific scenarios such as military service or imminent death.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Holographic Wills
Holographic wills, handwritten and signed by the testator, offer the advantage of being simple to create without the need for witnesses, reducing formalities and legal costs. However, their disadvantages include a higher risk of disputes due to potential ambiguity, lack of clear validation, and possible non-recognition in some jurisdictions. Unlike nuncupative wills, which are oral and generally reserved for emergency situations, holographic wills provide a tangible document but require careful drafting to ensure enforceability.
Jurisdictions Recognizing Nuncupative and Holographic Wills
Nuncupative wills, oral declarations made in imminent danger, are recognized in limited jurisdictions such as certain states in the U.S., including Virginia and North Carolina, primarily under strict conditions and typically for personal property. Holographic wills, handwritten and signed by the testator, receive broader acceptance internationally, with recognition in jurisdictions like California, Texas, and Quebec, where formal witnessing is not mandatory. Differences in legal treatment and admissibility requirements between nuncupative and holographic wills reflect jurisdiction-specific probate laws and policies aimed at balancing testamentary freedom and fraud prevention.
Choosing the Right Will: Which One Suits Your Needs?
Nuncupative wills, spoken and often witnessed verbally, are typically suited for urgent situations with limited formalities but pose higher risks of invalidity due to lack of documentation. Holographic wills, handwritten and signed by the testator, provide clearer evidence of intent and are generally more reliable for individuals seeking to ensure their wishes are explicitly documented without formal notarization. Choosing between them depends on the urgency, legal requirements of your jurisdiction, and the need for a documented, enforceable testament.
Nuncupative Will Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com