A scheduling order is a critical tool used by courts to outline deadlines for various phases of litigation, ensuring the process moves efficiently and predictably. It helps manage timelines for discovery, motions, and trial preparation, minimizing delays and promoting fair case management. Explore the article to understand how a scheduling order can impact your legal proceedings and optimize case outcomes.
Table of Comparison
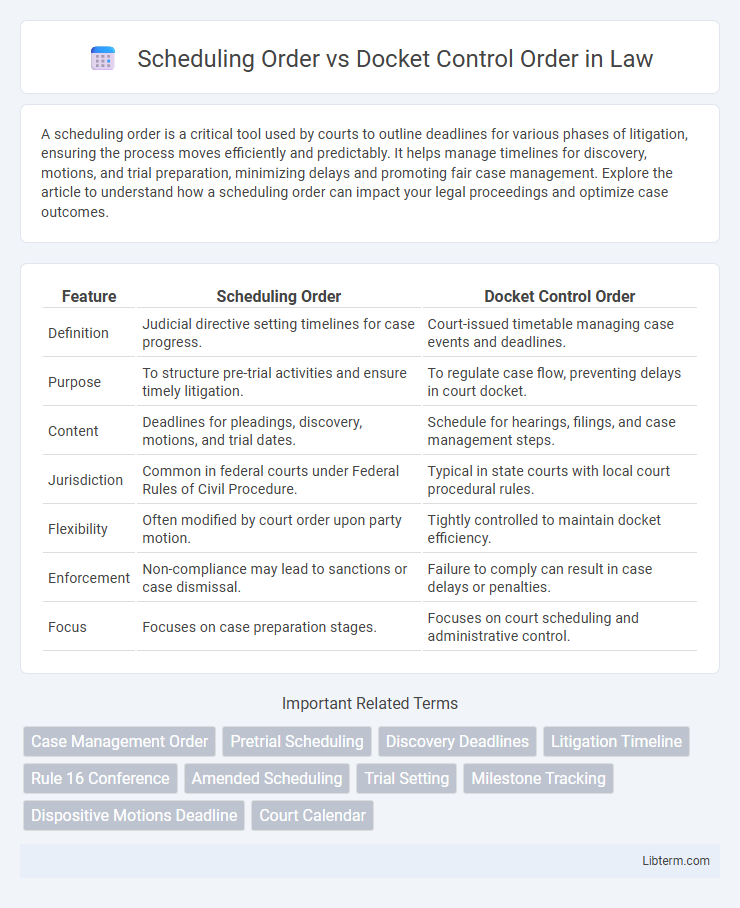
| Feature | Scheduling Order | Docket Control Order |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial directive setting timelines for case progress. | Court-issued timetable managing case events and deadlines. |
| Purpose | To structure pre-trial activities and ensure timely litigation. | To regulate case flow, preventing delays in court docket. |
| Content | Deadlines for pleadings, discovery, motions, and trial dates. | Schedule for hearings, filings, and case management steps. |
| Jurisdiction | Common in federal courts under Federal Rules of Civil Procedure. | Typical in state courts with local court procedural rules. |
| Flexibility | Often modified by court order upon party motion. | Tightly controlled to maintain docket efficiency. |
| Enforcement | Non-compliance may lead to sanctions or case dismissal. | Failure to comply can result in case delays or penalties. |
| Focus | Focuses on case preparation stages. | Focuses on court scheduling and administrative control. |
Understanding Scheduling Orders
Scheduling Orders establish clear timelines for key pretrial activities, including deadlines for discovery, motion filings, and expert witness disclosures, ensuring an organized litigation process. These orders are tailored to the specific complexities of a case, providing flexibility to accommodate various procedural needs and court requirements. Understanding the scope and function of Scheduling Orders is essential for effective case management and compliance with the court's procedural framework.
Defining Docket Control Orders
Docket Control Orders are court-issued directives that establish specific deadlines and procedural timelines to efficiently manage case progression. These orders coordinate the scheduling of hearings, filings, and other case events to ensure timely resolution. Unlike general Scheduling Orders, Docket Control Orders emphasize strict adherence to deadlines and detailed case management to minimize delays and case congestion.
Key Differences Between Scheduling and Docket Control Orders
Scheduling Orders establish specific deadlines for case activities such as motions, discovery, and trial dates, providing a structured timeline to ensure timely progress. Docket Control Orders oversee the overall management of the court's calendar, focusing on priority setting and equitable distribution of cases to prevent congestion. The key difference lies in Scheduling Orders targeting individual case timelines, while Docket Control Orders regulate the court's docket flow and resource allocation.
Legal Purpose of Scheduling Orders
Scheduling Orders establish specific deadlines and procedural timelines in a case to ensure efficient progression through litigation phases, including discovery cutoffs and motion filing dates. These orders help courts manage caseloads and prevent delays by providing a clear framework for parties to follow. Unlike Docket Control Orders, which primarily monitor court calendar management, Scheduling Orders play a critical legal role in enforcing procedural discipline and fostering timely case resolution.
Legal Purpose of Docket Control Orders
Docket Control Orders serve to streamline litigation by setting firm deadlines for each phase of a case, thereby minimizing delays and promoting judicial efficiency. Unlike Scheduling Orders that generally outline a timeline for discovery and motions, Docket Control Orders have the legal purpose of enforcing compliance with court procedures and maintaining strict control over the progress of a case. Courts rely on Docket Control Orders to ensure timely case management and to prevent unnecessary adjournments, safeguarding the right to a fair and expeditious trial.
Timeline Management in Litigation
Scheduling Orders establish a comprehensive timeline for all pretrial activities, including deadlines for discovery, motions, and expert reports, ensuring systematic progression in litigation. Docket Control Orders focus on managing court dates and hearings, prioritizing the efficient use of judicial resources by setting specific timelines for case events. Effective timeline management in litigation relies on the interplay of both orders to maintain case flow and prevent delays.
Impact on Case Progression
Scheduling Orders establish firm deadlines for key case events such as discovery and motions, ensuring a structured timeline that propels consistent case progression. Docket Control Orders offer detailed oversight of court calendars, managing hearing dates and trial sessions to prevent delays and streamline judicial efficiency. Together, these orders minimize procedural bottlenecks, enhancing predictability and expediting resolution within the case lifecycle.
Challenges in Modifying Orders
Modifying a Scheduling Order poses challenges due to strict deadlines and the need for good cause, often requiring substantial justification to avoid disrupting trial preparation. In contrast, Docket Control Orders are more rigidly enforced to maintain court efficiency, making amendments difficult without court approval and risk of sanctions. Both orders demand careful navigation of procedural rules to prevent delays and ensure procedural fairness throughout the litigation process.
Best Practices for Compliance
Scheduling orders outline specific deadlines for case milestones, while docket control orders manage the overall flow and priority of cases within the court system. Best practices for compliance include meticulously tracking all deadlines in a centralized case management system and regularly reviewing docket entries to avoid missed filings or hearings. Employing automated alerts and maintaining clear communication with all parties ensures adherence to both scheduling and docket control requirements.
Importance in Legal Proceedings
Scheduling Orders establish critical deadlines for discovery, motions, and trial dates, ensuring timely case progression and preventing unnecessary delays. Docket Control Orders manage the court's calendar by controlling the timing of hearings and case filings, promoting judicial efficiency and resource allocation. Both orders are essential in legal proceedings to maintain order, enforce timelines, and facilitate fair administration of justice.
Scheduling Order Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com