Issue estoppel prevents the re-litigation of a specific issue that has already been conclusively decided in a previous legal proceeding between the same parties, ensuring judicial efficiency and consistency. This doctrine safeguards your rights by barring parties from contesting matters that have been definitively resolved, thereby avoiding unnecessary duplication of legal efforts. Explore the rest of this article to understand how issue estoppel operates and its impact on your legal cases.
Table of Comparison
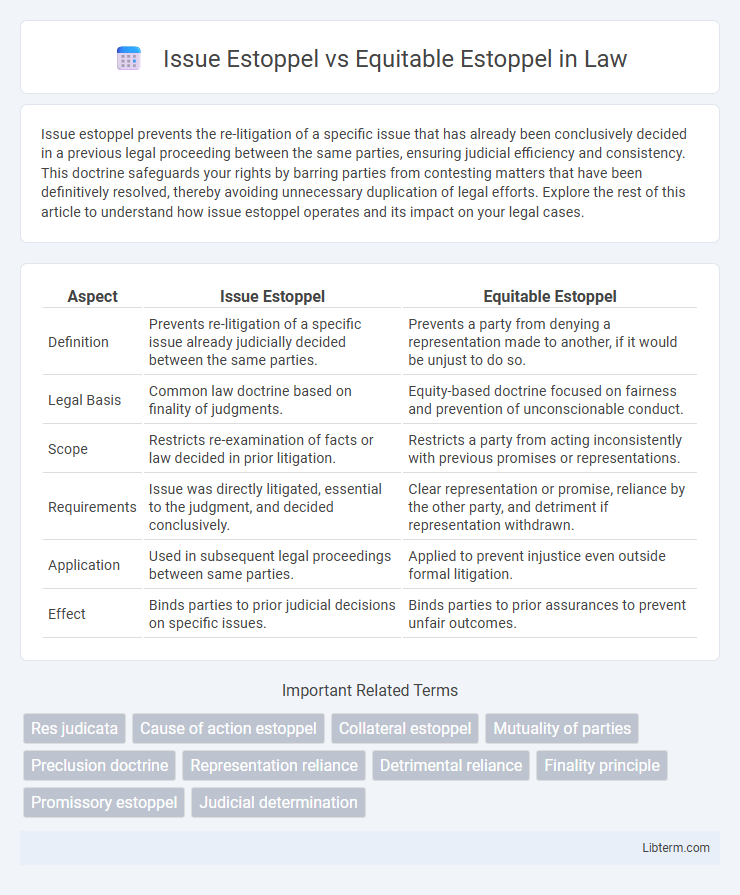
| Aspect | Issue Estoppel | Equitable Estoppel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prevents re-litigation of a specific issue already judicially decided between the same parties. | Prevents a party from denying a representation made to another, if it would be unjust to do so. |
| Legal Basis | Common law doctrine based on finality of judgments. | Equity-based doctrine focused on fairness and prevention of unconscionable conduct. |
| Scope | Restricts re-examination of facts or law decided in prior litigation. | Restricts a party from acting inconsistently with previous promises or representations. |
| Requirements | Issue was directly litigated, essential to the judgment, and decided conclusively. | Clear representation or promise, reliance by the other party, and detriment if representation withdrawn. |
| Application | Used in subsequent legal proceedings between same parties. | Applied to prevent injustice even outside formal litigation. |
| Effect | Binds parties to prior judicial decisions on specific issues. | Binds parties to prior assurances to prevent unfair outcomes. |
Introduction to Estoppel in Law
Estoppel in law prevents parties from asserting contradictory claims that would unfairly harm the opposing party. Issue estoppel bars re-litigation of specific facts or issues already decided in a previous case between the same parties. Equitable estoppel prevents a party from going back on a promise or representation when the other party has relied on it to their detriment.
Defining Issue Estoppel: Key Features
Issue estoppel prevents re-litigation of a specific issue that was already decided in a previous legal proceeding between the same parties, ensuring finality and consistency in judgments. It applies when the issue was directly decided, essential to the previous judgment, and involved the same parties or their privies. This doctrine differs from equitable estoppel by focusing strictly on judicial determinations rather than relying on representations or conduct to prevent unfairness.
Defining Equitable Estoppel: Essential Elements
Equitable estoppel arises when one party makes a representation or promises a certain state of affairs, inducing another party to rely on that representation to their detriment. The essential elements include a clear and unequivocal representation, reliance by the other party, and resulting detriment due to that reliance. This doctrine prevents the first party from going back on their word, ensuring fairness and justice in contractual and property disputes.
Core Distinctions Between Issue Estoppel and Equitable Estoppel
Issue estoppel prevents re-litigation of specific factual or legal issues already decided in previous litigation between the same parties, ensuring finality and judicial efficiency. Equitable estoppel prohibits a party from acting inconsistently to the detriment of another when a representation or promise was relied upon, focusing on fairness rather than preclusive effect. The core distinction lies in issue estoppel's basis in res judicata and judicial determination, while equitable estoppel rests on principles of equity and reliance outside formal judgments.
Legal Foundations of Issue Estoppel
Issue estoppel is rooted in the doctrine of res judicata, preventing re-litigation of a specific issue already judicially determined between the same parties in a prior valid and final judgment. Its legal foundation requires that the identical issue must have been necessarily decided in the earlier proceeding, ensuring consistency and finality in judicial decisions. This principle operates strictly within the judicial context, differing from equitable estoppel, which arises from fairness considerations rather than prior judicial determinations.
Principles Underlying Equitable Estoppel
Equitable estoppel arises to prevent a party from going back on a representation or promise that has been relied upon to their detriment, emphasizing fairness and justice in its application. The core principles include a clear representation or encouragement by one party, reliance by the other party, and resulting detriment if the first party is allowed to renege. Unlike issue estoppel, which precludes re-litigation of decided issues of fact or law between the same parties, equitable estoppel focuses on preventing unconscionable conduct based on reliance on representations outside formal judicial determinations.
Case Law: Landmark Decisions on Issue Estoppel
Issue estoppel prevents re-litigation of specific issues already decided in prior legal proceedings, as established in Hunter v Chief Constable of the West Midlands Police [1982] AC 529. Landmark cases like Henderson v Henderson (1843) 3 Hare 100 laid the foundation by emphasizing finality and judicial efficiency. In contrast, equitable estoppel protects parties from unconscionable conduct or representation-induced detriment, as seen in cases such as Central London Property Trust Ltd v High Trees House Ltd [1947] KB 130.
Case Law: Significant Rulings on Equitable Estoppel
Significant rulings on equitable estoppel, such as in *Central London Property Trust Ltd v High Trees House Ltd* (1947), establish that a party may be prevented from going back on a promise that was relied upon, even in the absence of a formal contract. In *Waltons Stores (Interstate) Ltd v Maher* (1988), the High Court of Australia expanded equitable estoppel to include situations where one party's conduct causes another to reasonably assume certain facts, leading to detriment if the assumption is later denied. These cases underscore the equitable principle that protects reliance and prevents unconscionable outcomes, distinguishing equitable estoppel from the narrower doctrinal boundaries of issue estoppel in dispute resolution.
Practical Applications: Issue Estoppel vs Equitable Estoppel
Issue estoppel prevents re-litigation of specific facts or issues already decided by a competent court, ensuring consistency and finality in judicial decisions. Equitable estoppel, rooted in fairness, stops a party from asserting rights or facts contradictory to their previous conduct or representations when the other party has relied on them to their detriment. In practice, issue estoppel is applied to bar re-litigation within legal proceedings, whereas equitable estoppel is invoked to prevent injustice in situations involving representations or promises outside strict legal determinations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Estoppel in Legal Disputes
Issue estoppel prevents re-litigation of specific factual or legal issues already decided by a competent court, ensuring finality and judicial efficiency, while equitable estoppel bars a party from asserting rights or facts contrary to their previous conduct to maintain fairness and prevent injustice. Selecting the appropriate estoppel depends on whether the dispute involves res judicata principles or requires protection against unconscionable conduct. Understanding these distinctions allows legal practitioners to strategically apply estoppel doctrines to uphold justice and avoid repetitive or unfair litigation.
Issue Estoppel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com