A leasehold estate grants you the right to use and occupy real property for a specified period under a lease agreement, distinguishing it from freehold ownership. Understanding the terms, duration, and obligations associated with a leasehold is crucial for protecting your interests and ensuring compliance. Explore the full article to learn how leasehold estates impact your rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
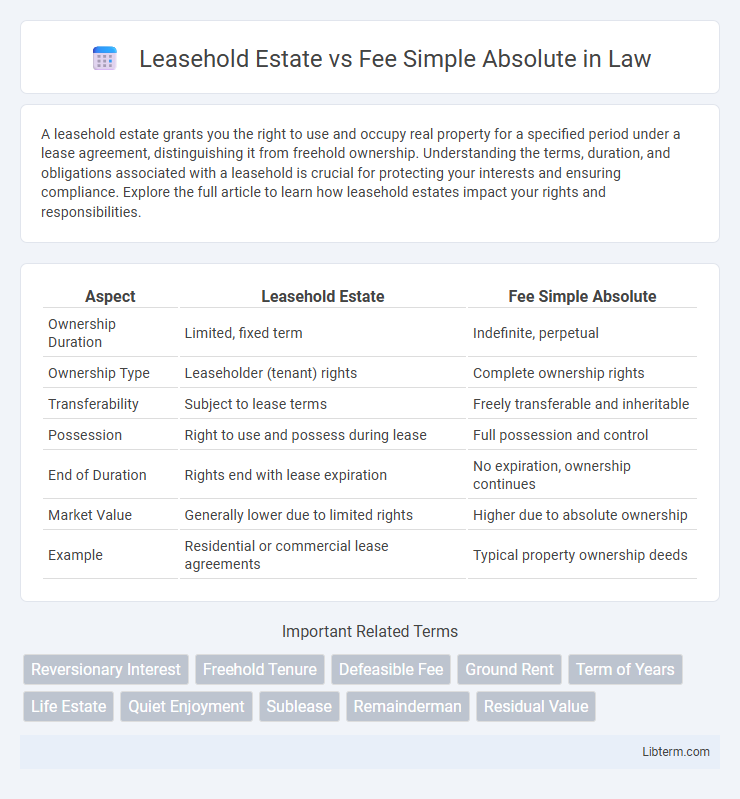
| Aspect | Leasehold Estate | Fee Simple Absolute |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Duration | Limited, fixed term | Indefinite, perpetual |
| Ownership Type | Leaseholder (tenant) rights | Complete ownership rights |
| Transferability | Subject to lease terms | Freely transferable and inheritable |
| Possession | Right to use and possess during lease | Full possession and control |
| End of Duration | Rights end with lease expiration | No expiration, ownership continues |
| Market Value | Generally lower due to limited rights | Higher due to absolute ownership |
| Example | Residential or commercial lease agreements | Typical property ownership deeds |
Introduction to Property Ownership Types
Leasehold estate grants tenants the right to use and occupy real property for a specified period under a lease agreement, without transferring ownership. Fee simple absolute represents the most complete form of property ownership, providing unlimited duration, inheritable rights, and full control over the land. Understanding these fundamental distinctions is essential for navigating property ownership, real estate transactions, and legal rights.
What is a Leasehold Estate?
A leasehold estate grants a tenant the right to occupy and use property for a specified period under a lease agreement, without transferring ownership. This interest is temporary, limited by the lease terms, and does not include the full bundle of rights associated with ownership. Unlike fee simple absolute, which conveys complete ownership with perpetual rights, leasehold estates are possessory interests that revert to the landlord upon lease expiration.
Understanding Fee Simple Absolute
Fee Simple Absolute represents the most complete form of property ownership, granting the owner unrestricted rights to use, sell, or bequeath the land indefinitely. Unlike Leasehold Estates, which provide temporary, limited rights to possess property, Fee Simple Absolute ensures full control and transferability without conditions or time limits. This ownership type is fundamental in real estate law, offering the highest degree of security and flexibility for landholders.
Key Differences Between Leasehold and Fee Simple
Leasehold estate grants the tenant a temporary right to use and occupy property for a specified term, while fee simple absolute provides the owner with complete, indefinite ownership and control. Leasehold interests are limited by duration and can include conditions, whereas fee simple ownership is unrestricted and inheritable. Key differences include duration, ownership rights, transferability, and the ability to modify or improve the property without landlord consent.
Duration of Ownership Explained
Leasehold estate grants ownership rights for a fixed duration, typically ranging from months to several years, after which the property reverts to the landlord. Fee simple absolute provides unlimited, perpetual ownership with complete control over the property and the ability to transfer it freely. The duration of ownership in leasehold estates is inherently temporary and bound by contract terms, while fee simple absolute offers permanent, indefinite tenure.
Rights and Responsibilities of Each Estate
Leasehold estates grant tenants the right to possession and use of the property for a specified term, but ownership remains with the landlord, who retains the responsibility for major repairs and property taxes. Fee simple absolute confers full ownership rights, including the ability to sell, lease, or bequeath the property, with the owner bearing all responsibilities for maintenance, taxes, and compliance with local laws. Tenants in leasehold estates have limited rights focused on occupancy, while fee simple owners hold unrestricted rights and duties tied to property management and legal obligations.
Financial Implications and Value
Leasehold estates typically involve lower upfront costs but limited ownership duration, resulting in reduced long-term equity and potential resale value compared to fee simple absolute properties. Fee simple absolute ownership offers full control and perpetual ownership, often leading to higher property appreciation and greater financial security. Investors generally prefer fee simple estates for maximizing asset value and leveraging equity in financial planning.
Common Uses and Real-World Examples
Leasehold estates commonly serve residential and commercial rental agreements, providing tenants with possession rights for a fixed term, such as apartment leases and retail storefront rentals. Fee simple absolute represents the most complete ownership interest, frequently applied in single-family home ownership and commercial property acquisitions, granting owners indefinite control and the ability to sell or bequeath the property. Real-world examples include tenants leasing office spaces under leasehold agreements, while homeowners typically hold fee simple title, allowing full control and transferability of their property.
Legal Considerations and Restrictions
Leasehold estates grant tenants possession and use rights for a specified term but impose restrictions outlined in the lease agreement, limiting alterations and subleasing. Fee simple absolute provides the owner with the most comprehensive property rights, including indefinite ownership and the ability to freely transfer, sell, or bequeath the land, subject only to government regulations and zoning laws. Legal considerations for leasehold focus on contract compliance and expiration, while fee simple ownership entails broader responsibilities such as property taxes and compliance with easements or covenants.
Choosing the Right Ownership Structure
Choosing between leasehold estate and fee simple absolute depends on long-term control and investment goals; fee simple absolute provides full ownership rights with indefinite duration, maximizing property control and value appreciation. Leasehold estates grant possession for a specified term without ownership, suitable for temporary use or lower upfront costs but limiting property control and resale value. Evaluating financial capacity, intended use, and future plans ensures selecting the optimal real estate ownership structure aligned with personal and business objectives.
Leasehold Estate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com