A writ of mandamus is a court order compelling a government official or entity to perform a duty they are legally obligated to complete. This legal remedy is used to address failures in official duties or to correct abuses of discretion. Explore the article to understand when and how a writ of mandamus can enforce your rights effectively.
Table of Comparison
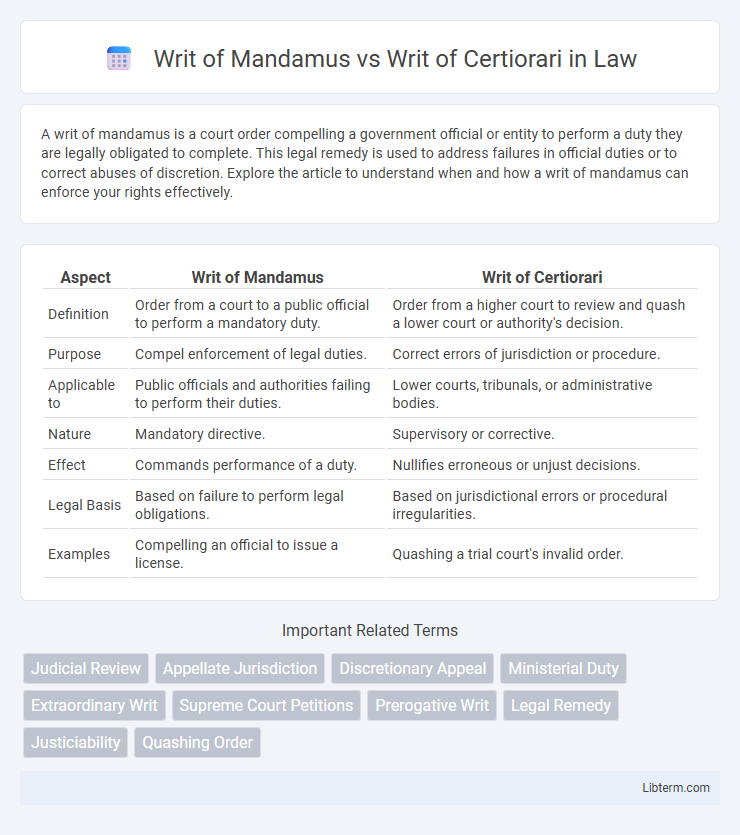
| Aspect | Writ of Mandamus | Writ of Certiorari |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Order from a court to a public official to perform a mandatory duty. | Order from a higher court to review and quash a lower court or authority's decision. |
| Purpose | Compel enforcement of legal duties. | Correct errors of jurisdiction or procedure. |
| Applicable to | Public officials and authorities failing to perform their duties. | Lower courts, tribunals, or administrative bodies. |
| Nature | Mandatory directive. | Supervisory or corrective. |
| Effect | Commands performance of a duty. | Nullifies erroneous or unjust decisions. |
| Legal Basis | Based on failure to perform legal obligations. | Based on jurisdictional errors or procedural irregularities. |
| Examples | Compelling an official to issue a license. | Quashing a trial court's invalid order. |
Introduction to Writ of Mandamus and Writ of Certiorari
A Writ of Mandamus is a court order directing a government official, lower court, or public authority to perform a mandatory duty that is legally obligated, especially when they fail to fulfill their official duties. In contrast, a Writ of Certiorari is issued by a higher court to review the decisions or proceedings of a lower court to ensure legal correctness and jurisdiction. Both writs serve critical roles in administrative and judicial oversight to uphold legality and prevent abuse of power.
Legal Definition of Writ of Mandamus
The writ of mandamus is a judicial order issued by a higher court directing a lower court, government official, or public authority to perform a mandatory duty that they are legally obligated to complete. It serves as a corrective remedy to ensure the enforcement of rights and duties when no other legal recourse is available. Unlike the writ of certiorari, which is used to review and quash decisions of lower courts or tribunals, mandamus compels the fulfillment of official duties.
Legal Definition of Writ of Certiorari
The Writ of Certiorari is a legal order issued by a higher court directing a lower court or tribunal to transfer the records of a case for review, ensuring that the proceedings were fair and lawful. Unlike the Writ of Mandamus, which compels a governmental body or official to perform a mandatory duty, the Writ of Certiorari focuses on supervising and correcting errors of jurisdiction or procedural violations in judicial or quasi-judicial actions. This writ serves as a critical tool for appellate courts to maintain judicial oversight and uphold the rule of law.
Key Differences Between Mandamus and Certiorari
The Writ of Mandamus compels a government official or lower court to perform a mandatory duty, whereas the Writ of Certiorari orders a lower court to deliver its record for review by a higher court. Mandamus is commonly used to enforce public duties, while Certiorari primarily functions as a supervisory tool to correct jurisdictional errors or ensure proper administration of justice. Unlike Mandamus, which demands action, Certiorari focuses on judicial review and error correction.
When is a Writ of Mandamus Applicable?
A Writ of Mandamus is applicable when a lower court, public authority, or government official fails to perform a duty that is mandatorily required by law. This writ commands the performance of a specific act that is necessary and constitutes a legal obligation, especially when no other adequate remedy is available. It is distinct from a Writ of Certiorari, which primarily serves to review and quash decisions made by lower courts or tribunals.
When is a Writ of Certiorari Applicable?
A Writ of Certiorari is applicable when a higher court reviews the decision of a lower court to ensure there were no legal errors affecting the outcome. It is commonly issued to transfer a case from a subordinate court or tribunal to a superior court for examination of proceedings. This writ plays a crucial role in correcting jurisdictional mistakes and maintaining the integrity of judicial processes.
Procedures for Filing Writ of Mandamus
Filing a Writ of Mandamus requires submitting a verified petition to the appropriate court, usually demonstrating a clear legal duty that the respondent, typically a government official, has failed to perform. The petition must include relevant affidavits and evidence establishing the absence of other adequate legal remedies. Courts generally demand strict compliance with procedural rules, including timely filing, to prevent undue delays and ensure proper judicial intervention.
Procedures for Filing Writ of Certiorari
Filing a Writ of Certiorari requires the petitioner to submit a verified petition to the appellate court, specifically highlighting errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion by the lower court. The petition must include the relevant records, affidavits, and certifications, conforming to procedural rules such as time limitations for filing, typically within 60 days from the judgment or order. Strict compliance with these procedural requirements is crucial to ensure the appellate court's acceptance and consideration of the writ.
Landmark Cases Involving Mandamus and Certiorari
Landmark cases involving writs of mandamus include Marbury v. Madison (1803), which established the principle of judicial review by mandating government action through a writ of mandamus. In contrast, the writ of certiorari gained prominence in cases like Brown v. Board of Education (1954), where the U.S. Supreme Court used certiorari to review and overturn lower court decisions on racial segregation. These cases highlight mandamus as a tool to enforce official duties, while certiorari functions primarily as a discretionary review mechanism by higher courts.
Practical Implications: Choosing the Correct Writ
Choosing the correct writ significantly affects case outcomes, as a Writ of Mandamus commands a lower court or public authority to perform a mandatory duty, ensuring immediate enforcement of legal obligations. In contrast, a Writ of Certiorari directs a higher court to review and possibly overturn a lower court's decision, primarily addressing errors of jurisdiction or legal misinterpretation. Proper application of these writs optimizes judicial efficiency and safeguards parties' legal rights by targeting enforcement remedies or appellate corrections accurately.
Writ of Mandamus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com