Waive refers to voluntarily giving up a right, claim, or privilege, often in legal or contractual contexts. Understanding when and how to waive certain rights can significantly impact your obligations and protections. Explore the article to learn more about waivers and their implications for your specific situation.
Table of Comparison
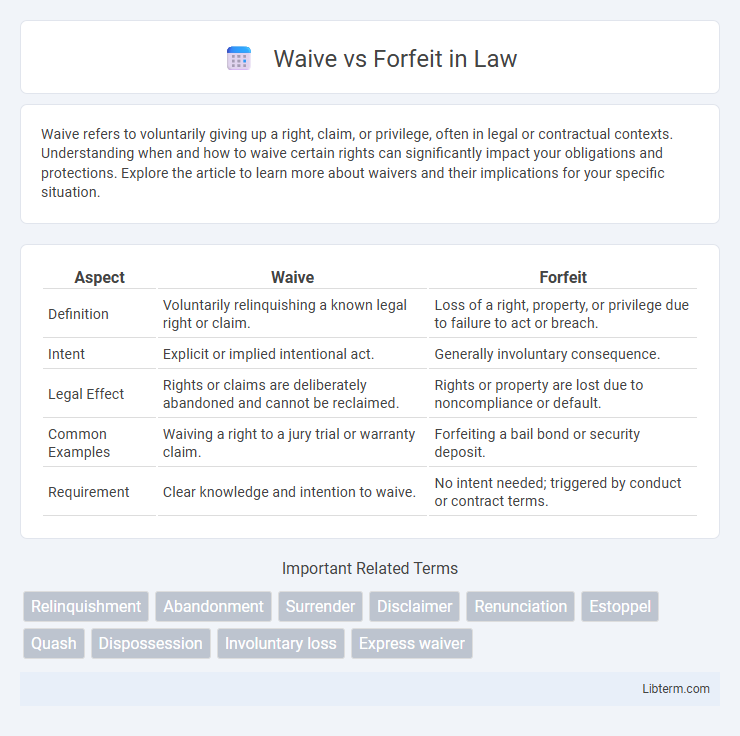
| Aspect | Waive | Forfeit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntarily relinquishing a known legal right or claim. | Loss of a right, property, or privilege due to failure to act or breach. |
| Intent | Explicit or implied intentional act. | Generally involuntary consequence. |
| Legal Effect | Rights or claims are deliberately abandoned and cannot be reclaimed. | Rights or property are lost due to noncompliance or default. |
| Common Examples | Waiving a right to a jury trial or warranty claim. | Forfeiting a bail bond or security deposit. |
| Requirement | Clear knowledge and intention to waive. | No intent needed; triggered by conduct or contract terms. |
Introduction to Waive and Forfeit
Waive refers to the intentional relinquishment of a known right, claim, or privilege, often voluntarily chosen by an individual or party in legal or contractual contexts. Forfeit involves the loss or surrender of a right, property, or privilege as a penalty for a breach, violation, or failure to fulfill specific conditions. Understanding the distinction between waive and forfeit is crucial in areas such as contract law, insurance, and dispute resolution to determine whether a right is given up by choice or lost due to consequence.
Definitions: Waive vs Forfeit
Waive refers to voluntarily giving up a legal right, claim, or privilege, often through explicit action or agreement. Forfeit means losing a right, property, or privilege as a penalty for a breach of rule or failure to meet an obligation. Waiving involves intentional relinquishment, while forfeiture results from default or violation.
Legal Contexts of Waiver and Forfeiture
Waiver in legal contexts refers to the voluntary and intentional relinquishment of a known right, claim, or privilege, often requiring clear evidence of the party's intent to forgo that right. Forfeiture involves the loss of property or rights as a penalty for a breach of contract, violation of law, or failure to fulfill a condition, typically imposed by a court or governing authority. Understanding the distinction between waiver and forfeiture is crucial, as waiver is an active, voluntary act by the party, while forfeiture is a consequence imposed due to noncompliance or wrongdoing.
Key Differences Between Waive and Forfeit
Waive involves voluntarily giving up a right, claim, or privilege without any penalty, often requiring clear and intentional action. Forfeit refers to losing a right or property as a consequence of failing to meet obligations or rules, typically resulting in a penalty or loss imposed by law or contract. The key difference lies in the voluntary nature of waiving rights versus the involuntary loss or penalty represented by forfeiture.
Common Scenarios for Waiving Rights
Common scenarios for waiving rights include signing contracts where individuals voluntarily relinquish claims, such as agreeing to non-disclosure agreements or opting out of class-action lawsuits. Employees may waive rights to certain benefits or claims when accepting severance packages or arbitration clauses in employment contracts. Consumers often waive rights by accepting terms and conditions that limit liability or dispute resolution options in service agreements.
Situations Leading to Forfeiture
Situations leading to forfeiture typically involve the failure to meet contractual obligations, such as missing payment deadlines, breaching terms, or failing to deliver agreed-upon goods or services. Forfeiture often occurs in legal contexts where a party loses certain rights or property due to non-compliance with stipulated conditions. Unlike waivers, which are voluntary relinquishments of rights, forfeiture results from actions or omissions that trigger automatic penalties or loss.
Implications of Waiving Rights
Waiving rights involves voluntarily relinquishing a known legal entitlement, which may prevent future claims related to that right. This action often requires clear, informed consent to ensure enforceability and can impact contract negotiations, dispute resolutions, or statutory protections. Failure to properly document a waiver can lead to legal uncertainties and unintended liability.
Consequences of Forfeiture
Forfeiture results in the automatic loss of a right or property, often without compensation, and can severely impact financial or legal standing. It typically occurs due to breach of contract, non-compliance, or failure to meet specified conditions, leading to irreversible consequences. Unlike waiving, forfeiture eliminates any future claims or recoveries related to the forfeited asset or right.
Waiver and Forfeiture in Contracts
Waiver in contracts refers to the voluntary relinquishment of a known right or claim, allowing parties to intentionally forgo enforcement without penalty. Forfeiture involves the loss of rights, property, or money as a consequence of breaching a contract or failing to meet contractual obligations. Understanding the distinction between waiver and forfeiture is crucial for contract enforcement, as waivers avoid penalties while forfeitures often result in financial or legal loss.
Choosing Between Waive and Forfeit: Best Practices
Choosing between waive and forfeit depends on the intention behind relinquishing a right or claim. Waive implies a voluntary, informed decision to give up a right without penalty, often documented through a formal agreement or statement. Forfeit refers to losing a right or property as a consequence of a rule violation or failure to meet obligations, typically enforced automatically or by legal statute.
Waive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com