Summary judgment is a legal decision made by a court without a full trial when there is no dispute over the material facts of the case. It aims to resolve cases efficiently by determining the outcome based on the evidence presented in motions. Explore the full article to understand how summary judgment might impact your legal strategy.
Table of Comparison
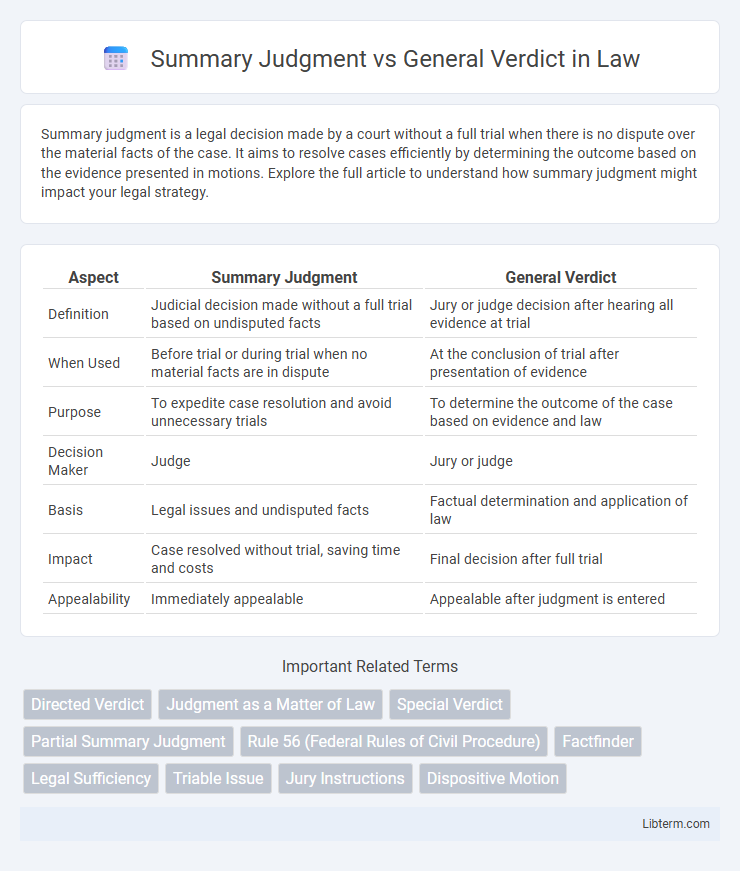
| Aspect | Summary Judgment | General Verdict |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial decision made without a full trial based on undisputed facts | Jury or judge decision after hearing all evidence at trial |
| When Used | Before trial or during trial when no material facts are in dispute | At the conclusion of trial after presentation of evidence |
| Purpose | To expedite case resolution and avoid unnecessary trials | To determine the outcome of the case based on evidence and law |
| Decision Maker | Judge | Jury or judge |
| Basis | Legal issues and undisputed facts | Factual determination and application of law |
| Impact | Case resolved without trial, saving time and costs | Final decision after full trial |
| Appealability | Immediately appealable | Appealable after judgment is entered |
Introduction to Summary Judgment and General Verdict
Summary judgment is a legal ruling by a court without a full trial, granted when there are no material facts in dispute and one party is entitled to judgment as a matter of law. A general verdict, by contrast, is the decision rendered by a jury or judge after evaluating all evidence during a trial, determining the outcome on all claims or issues. Understanding the distinction between summary judgment and general verdict is crucial for effective litigation strategy and case resolution.
Defining Summary Judgment
Summary judgment is a legal ruling made by a court without a full trial, typically granted when there is no genuine dispute of material fact, allowing the case to be decided solely on legal issues. It streamlines litigation by resolving cases or specific claims efficiently, preventing unnecessary trials when evidence overwhelmingly favors one party. This contrasts with a general verdict, which is reached by a jury's decision after examining the full trial evidence.
Defining General Verdict
A general verdict is a jury's conclusive decision on the issues in a case, typically indicating the party that prevails and the amount of damages awarded without specifying findings on individual factual questions. In contrast, summary judgment is a pre-trial motion that resolves a case or specific claims based on legal issues without a full trial, often granted when there is no genuine dispute of material fact. Understanding the general verdict is essential as it reflects the overall judgment rendered by the jury after evaluating all presented evidence during the trial.
Key Differences Between Summary Judgment and General Verdict
Summary judgment is a legal decision made by the court without a full trial, based on the argument that there are no material facts in dispute, allowing the judge to rule as a matter of law. A general verdict is the final decision given by a jury after evaluating evidence and determining the outcome of a case on both facts and law. The key difference lies in summary judgment being judge-decided and pre-trial, while a general verdict is jury-delivered following a complete trial.
Legal Standards for Summary Judgment
Summary judgment requires the movant to show there is no genuine dispute of material fact, meeting the burden under Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 56 by presenting all evidence in a light most favorable to the non-moving party. The legal standard mandates that courts assess whether a reasonable jury could find for the non-moving party based on evidentiary records rather than weighing credibility or conducting a trial. Unlike general verdicts, which reflect jury decisions on contested facts, summary judgment resolves claims pre-trial when factual issues are conclusively clear.
Legal Standards for General Verdict
General verdicts require the jury to render a decision based on the facts presented without specifying the findings on individual issues, reflecting the overall judgment in favor of one party. The legal standard for a general verdict demands that the evidence, when viewed in the light most favorable to the non-moving party, supports a reasonable conclusion that justifies the jury's decision. Courts uphold general verdicts unless no reasonable jury could have reached the conclusion based on the evidentiary record, ensuring deference to the jury's role in fact-finding.
When Is Summary Judgment Appropriate?
Summary judgment is appropriate when there is no genuine dispute of material fact, allowing the court to decide the case as a matter of law without a trial. It is typically granted after discovery when one party shows that the evidence overwhelmingly supports their claim or defense. Courts use summary judgment to streamline litigation, avoid unnecessary trials, and resolve cases efficiently.
When Is a General Verdict Used?
A general verdict is used when a jury determines the facts and renders a final decision on both liability and damages in a civil or criminal case, providing a clear resolution without itemizing specific findings. This verdict applies in trials where the court seeks a straightforward conclusion rather than detailed jury findings, often after all evidence and arguments have been presented. It contrasts with summary judgment, which is a pre-trial ruling by the judge to resolve a case or specific issues without a jury trial.
Impact of Summary Judgment and General Verdict on Litigation
Summary judgment significantly reduces litigation time and costs by resolving key issues early without a full trial, streamlining case management and enabling parties to avoid unnecessary expenses. General verdicts, issued by juries or judges after a full trial, provide a conclusive decision but can extend litigation duration and increase uncertainty due to fact-finding nuances. The strategic use of summary judgment enables parties to focus litigation efforts on genuinely disputed issues, whereas reliance on general verdicts may lead to longer, more complex proceedings and potential appeals.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Summary Judgment and General Verdict
Summary judgment offers a swift resolution by deciding the case based on legal issues without a full trial, often reducing costs and time for clearly established facts. General verdict involves a jury's decision after evaluating evidence, providing a more comprehensive assessment when material facts are disputed. Selecting between summary judgment and general verdict depends on the clarity of facts, the need for a trial, and the strategic goals of the parties involved in litigation.
Summary Judgment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com