Opposing counsel plays a crucial role in legal proceedings by representing the interests of the other party and challenging your position with strategic arguments and evidence. Understanding their tactics and anticipating their moves can significantly influence the outcome of your case. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective strategies for handling opposing counsel and strengthening your legal approach.
Table of Comparison
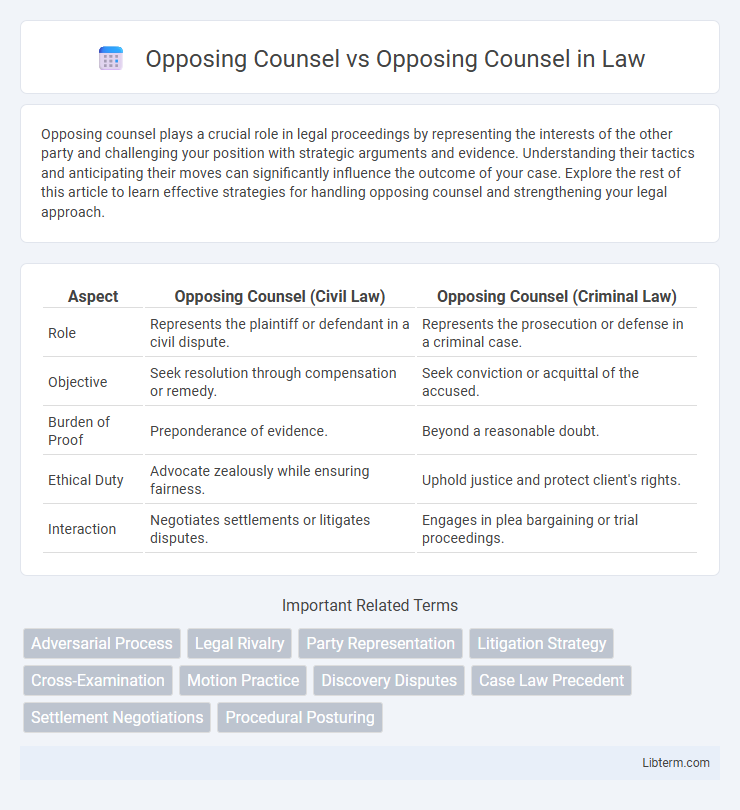
| Aspect | Opposing Counsel (Civil Law) | Opposing Counsel (Criminal Law) |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Represents the plaintiff or defendant in a civil dispute. | Represents the prosecution or defense in a criminal case. |
| Objective | Seek resolution through compensation or remedy. | Seek conviction or acquittal of the accused. |
| Burden of Proof | Preponderance of evidence. | Beyond a reasonable doubt. |
| Ethical Duty | Advocate zealously while ensuring fairness. | Uphold justice and protect client's rights. |
| Interaction | Negotiates settlements or litigates disputes. | Engages in plea bargaining or trial proceedings. |
Understanding the Role of Opposing Counsel
Opposing counsel refers to the attorney representing the adverse party in a legal dispute, tasked with advocating their client's interests and challenging the arguments presented by the opposing side. Understanding the role of opposing counsel involves recognizing their duty to conduct thorough legal research, present evidence, cross-examine witnesses effectively, and negotiate settlements when feasible. Mastery of opposing counsel's strategies and ethical boundaries enhances case preparation and fosters professional courtroom dynamics.
Key Responsibilities of Opposing Counsel
Opposing Counsel plays a critical role in litigation by rigorously challenging the claims and evidence presented by the other side to protect their client's interests. Key responsibilities include conducting comprehensive legal research, drafting pleadings, and presenting arguments in court to counter opposing claims effectively. They also collaborate with clients to develop defense strategies while ensuring compliance with procedural rules and ethical standards throughout the legal process.
Opposing Counsel vs. Co-Counsel: Clarifying the Differences
Opposing counsel represents the adversary party in a legal dispute, advocating against your client's position, while co-counsel collaborates with you as part of the same legal team, sharing responsibilities and strategy. Understanding the distinction between opposing counsel and co-counsel is crucial for effective communication and case management in litigation. Managing relationships with opposing counsel requires negotiation and conflict resolution skills, whereas working with co-counsel emphasizes coordination and unified advocacy.
Navigating Interactions with Opposing Counsel
Navigating interactions with opposing counsel requires strategic communication and a clear understanding of legal boundaries to protect client interests while fostering professional respect. Effective negotiation skills and thorough preparation promote productive dialogue and can lead to favorable settlements without escalating conflicts. Maintaining professionalism and avoiding emotional responses safeguard the attorney's credibility and uphold ethical standards throughout legal proceedings.
Strategies for Effective Communication with Opposing Counsel
Effective communication with opposing counsel requires clarity, professionalism, and strategic negotiation techniques to reach mutually beneficial agreements. Employing active listening and understanding the opposing counsel's priorities can help identify common ground and streamline conflict resolution. Consistently documenting communications and maintaining a respectful tone guard against misunderstandings and foster a collaborative environment.
Common Ethical Considerations in Dealing with Opposing Counsel
Common ethical considerations in dealing with opposing counsel include maintaining professionalism, honesty, and confidentiality throughout all communications. Attorneys must avoid conflicts of interest, refrain from making false statements, and adhere to the rules of professional conduct established by their jurisdiction. Respecting opposing counsel's role ensures a fair legal process and upholds the integrity of the judicial system.
Handling Difficult Opposing Counsel in Litigation
Handling difficult opposing counsel in litigation requires strategic communication, maintaining professionalism, and setting clear boundaries to prevent delays and obstructive tactics. Employing assertive negotiation techniques and documenting all interactions can mitigate conflicts and strengthen your position during discovery and trial phases. Courts often view cooperation favorably, so demonstrating a willingness to resolve disputes amicably can influence judicial perception and case outcomes.
The Impact of Opposing Counsel on Case Outcomes
Opposing counsel plays a critical role in shaping case outcomes by influencing negotiation dynamics and trial strategies. The experience, expertise, and approach of opposing counsel can directly affect settlement terms, evidentiary rulings, and jury perceptions. Understanding the strengths and tactics of opposing counsel allows legal teams to adapt their case presentations and improve the likelihood of favorable results.
Professionalism and Civility Towards Opposing Counsel
Professionalism and civility towards opposing counsel are essential in maintaining ethical standards and fostering constructive legal proceedings. Treating opposing counsel with respect enhances communication, reduces conflicts, and promotes efficient dispute resolution despite adversarial roles. Upholding these values reflects positively on legal practitioners and supports the integrity of the judicial system.
Frequently Asked Questions About Opposing Counsel
Frequently asked questions about opposing counsel often address how to effectively communicate and negotiate with them during legal proceedings. Key concerns include understanding opposing counsel's strategy, assessing their credibility, and managing conflicts to protect client interests. Knowing the proper protocols for interaction can streamline case resolution and reduce litigation risks.
Opposing Counsel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com