Plea bargaining plays a critical role in the criminal justice system by allowing defendants to negotiate reduced charges or sentences in exchange for a guilty plea. This process helps manage court caseloads efficiently and can provide defendants with a clearer understanding of potential outcomes. Discover how plea bargaining can impact your case and the broader justice system by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
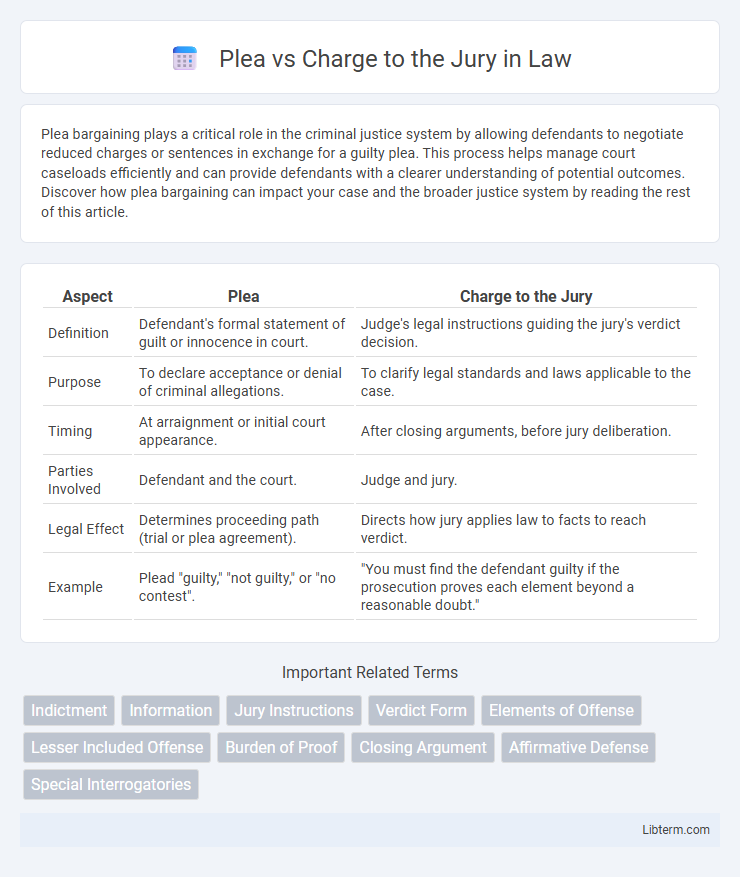
| Aspect | Plea | Charge to the Jury |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Defendant's formal statement of guilt or innocence in court. | Judge's legal instructions guiding the jury's verdict decision. |
| Purpose | To declare acceptance or denial of criminal allegations. | To clarify legal standards and laws applicable to the case. |
| Timing | At arraignment or initial court appearance. | After closing arguments, before jury deliberation. |
| Parties Involved | Defendant and the court. | Judge and jury. |
| Legal Effect | Determines proceeding path (trial or plea agreement). | Directs how jury applies law to facts to reach verdict. |
| Example | Plead "guilty," "not guilty," or "no contest". | "You must find the defendant guilty if the prosecution proves each element beyond a reasonable doubt." |
Understanding Pleas in Criminal Trials
Understanding pleas in criminal trials involves knowing the differences between guilty, not guilty, and no contest pleas, each shaping the trial's course and legal consequences. Pleas can expedite the process, avoiding lengthy trials by resolving charges swiftly, yet they also influence sentencing and potential appeals. Charges presented to the jury are contested when the defendant pleads not guilty, leading to a trial where evidence is examined and verdicts are determined.
Definition of a Charge to the Jury
A Charge to the Jury is a formal instruction given by the judge explaining the legal standards and principles that jurors must apply when deliberating on the facts of the case. This guidance clarifies the elements of the offenses involved and outlines the burden of proof required to reach a verdict. Unlike a plea, which is the defendant's formal response to criminal charges, the Charge to the Jury directs how jurors should consider evidence and the law in their decision-making process.
Key Differences Between Plea and Jury Charge
A plea is a defendant's formal statement in court admitting guilt, innocence, or no contest, whereas a charge to the jury is the judge's instruction on the legal standards that the jury must follow to reach a verdict. Pleas resolve cases without a trial, often resulting in sentencing agreements, while a jury charge guides jury deliberations during a trial in determining guilt or innocence. The key difference lies in pleas being a defendant's confession or denial, while jury charges involve judicial guidance on applying law to evidence.
The Role of Pleas in Criminal Proceedings
Pleas in criminal proceedings significantly influence case outcomes by allowing defendants to admit guilt, which can result in reduced charges or lighter sentences compared to trial verdicts. The plea bargaining process helps courts manage caseloads efficiently, enabling faster resolutions without requiring the jury to deliberate on every case. This mechanism balances judicial resources while protecting defendants' rights through negotiated agreements, often leading to fewer jury trials and streamlined criminal justice administration.
Purpose and Importance of Jury Instructions
Jury instructions serve a critical purpose in clarifying the legal standards that jurors must apply when evaluating pleas versus charges, ensuring accurate interpretation of the defendant's statements and the prosecution's claims. These instructions guide jurors in distinguishing between different types of pleas, such as guilty, not guilty, or no contest, and understanding how these relate to the specific charges presented. Clear and precise jury instructions are essential to uphold fairness, prevent misunderstandings, and promote just verdicts based on the law and evidence.
Legal Implications of Entering a Plea
Entering a plea directly influences the court's proceedings and the defendant's legal rights, determining whether the case proceeds to trial or results in an immediate judgment. Pleas such as guilty, not guilty, or no contest carry distinct legal consequences, including potential sentencing or the preservation of the right to a jury trial. Understanding the implications of each plea is crucial for defendants, as it affects trial strategies, plea bargain opportunities, and subsequent appeals.
How Jury Charges Influence Verdicts
Jury charges significantly shape verdict outcomes by framing the legal standards and guiding jurors on how to apply the law to the facts presented, ensuring clarity in complex cases. Precise and well-structured jury instructions reduce confusion, minimize juror bias, and promote consistent application of legal principles, directly influencing the likelihood of conviction or acquittal. Studies indicate that the specificity and comprehensibility of jury charges correlate with higher rates of accurate and fair verdicts in criminal trials.
Common Types of Pleas Explained
Common types of pleas include guilty, not guilty, and no contest, each affecting the trial process differently. A guilty plea admits to the offense, often resulting in sentencing without a jury trial, while a not guilty plea leads to a jury evaluating the charges. The no contest plea means the defendant does not admit guilt but accepts punishment, influencing how the jury perceives the case and legal outcomes.
Steps in Delivering a Charge to the Jury
The process of delivering a charge to the jury involves several critical steps, including reviewing the applicable laws, outlining the elements of each charge, and instructing the jury on how to apply the law to the facts presented in the trial. Judges must clearly explain the legal standards for guilt, the burden of proof, and any relevant defenses to ensure jurors understand their responsibilities. Precise jury instructions help prevent misunderstandings and are essential for a fair verdict in criminal cases involving pleas or charges.
Impact of Pleas and Jury Charges on Trial Outcomes
Plea decisions significantly influence trial outcomes by potentially reducing charges and sentencing severity, impacting jury deliberations by limiting the scope of contested issues. Jury charges shape trial results through judicial instructions that guide jurors on legal standards and burden of proof, affecting their interpretation of evidence and verdict consistency. The interplay between pleas and jury charges determines trial efficiency, conviction rates, and defendant sentencing, underscoring their critical role in the criminal justice process.
Plea Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com